Electromagnetic wave theory
This theory was put forward by James clark Maxwell in 1864.
The main points of this theory are:
1)The energy is emitted from any source continuously in the form of radiations and is called the radiant energy.
2)The radiations consist of electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to each other and both perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the radiation.
3)The radiations possesses wave character and travel with the velocity of light.
The radiations are called electromagnetic radiations or electromagnetic waves.
4)These waves do not require any material medium for propagation.
Characteristics of a wave
1)Wavelength
Wavelength of a wave is defined as the distance between any two consecutive crest or trough.
It is represented by λ (Lambda) and is expressed in A° or m or cm or nm or pm.
1 A° = 10-8 cm = 10-10 m
1nm = 10-9 m, 1pm= 10-12 m
2)Frequency
Frequency of a wave is defined as the number of waves passing through a point in 1 seconds.
It is represented by ν (nu) and is expressed in hertz(Hz) or cycles/second or sec-1
3)Velocity
Velocity of a wave is defined as the linear distance travelled by the wave in 1 seconds.
It is represented by c and is expressed in cm/sec or m/sec.
4)Amplitude
Amplitude of a wave is the height of the crest or the depth of the trough.
It is represented by a and is expressed in the units of length.
5)Wavenumber
Wavenumber is defined as the number of waves present in 1 cm length.
It will be equal to the reciprocal of the wavelength.
It is represented by
Relation between velocity ,wavelength and frequency of a wave
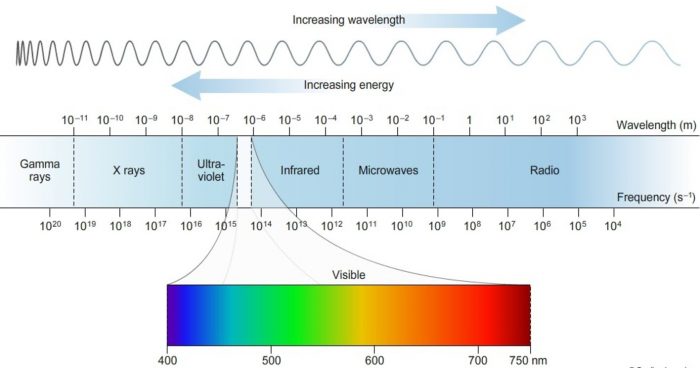
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The different types of electromagnetic radiations differ only in their wavelength and hence frequency.
Their Wave length increases in the following order:
When these electromagnetic radiations are arranged in order of their increasing wavelength or decreasing frequencies, the complete spectrum obtained is called electromagnetic spectrum.
Limitations of electromagnetic wave theory
It could not explain the :
1)The phenomena of black body radiation
2)The photoelectric effect
3)The variation of heat capacity of solid as a function of temperature.
4)The line spectra of atoms with special reference to hydrogen.
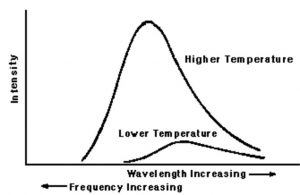
Black body radiation
If any substance with high melting point is heated, it first becomes red, then yellow and finally begins to glow with white and then blue light.
If the substance being heated is a black body (which is a perfect absorber and perfect radiator of energy ie. which can emit and absorb all frequencies) the radiations emitted is called black body radiation
The energy of any electromagnetic radiation is proportional to its intensity, ie. square of amplitude and is independent of its frequency or wavelength.
The change of colours shows that on heating ,the frequency of the radiations emitted is increasing.
At a given temperature, intensity of radiation emitted increases with decrease of wavelength, reaches a maximum value at a particular wavelength and then start decreasing with further decrease of wavelength.
Photoelectric effect
When radiations with certain minimum frequency ( νo) strike the surface of a metal, the electrons are ejected from the surface of the metal. This phenomenon is called Photoelectric effect
The electrons emitted are called photoelectrons.
1) The electrons are ejected only if the radiation striking the surface of the metal has at least a minimum frequency(νo) . If the frequency is less than νo , no electrons are ejected(hνo). This value is called threshold frequency.
The minimum energy required to eject the electrons is called work function( Wo)
2) The velocity of the electron ejected depends upon the frequency of the incident radiation and is independent of its intensity.
3) The number of photoelectrons ejected is proportional to the intensity of incident radiation.
Planck’s Quantum Theory
Max Planck in 1900, put forward a theory known after his name as Planck’s Quantum theory
The main points of this theory are :
1)The radiant energy is emitted or absorbed not continuously but discontinuously in the form of small discrete packets of energy. Each such packet of energy is called quantum. In case of light ,the quantum of energy is called Photon.
2)The energy of each quantum is directly proportional to the frequency of the radiation ie.
E=hν
Where h is the proportionality constant, called Planck’s Constant.
Its value is 6.626 × 10 -27 erg sec or 6.626 × 10 -34 joule sec.
3)The total amount of energy emitted or absorbed by a body will be some whole number quanta.
Hence E= nhν
Explanation of black body radiation
When some solid substance is heated, the atoms of the substance are set into oscillations and emit radiations of frequency, ν. Now ,as heating is continued, more and more energy is being absorbed by the atoms and they emit radiations of higher and higher frequency. As red light has minimum frequency and yellow light has higher frequency, therefore the body on heating becomes first red, then yellow and so on.
Explanation of Photoelectric Effect
1)When light of some particular frequency falls on the surface of metal, the photon gives its entire energy to the electron of the metal atom. The electron will be detached from the metal atom only if the energy of the photon is sufficient to overcome the force of attraction of the electron by the nucleus. That is why photoelectrons are ejected only when the incident light has a certain minimum frequency (threshold frequency ν0)
2If the frequency of the incident light is more than the threshold frequency ,the excess energy is imparted to the electron as kinetic energy.
Greater is the frequency of the incident light, greater is the kinetic energy of emitted electron.
3)When the intensity of light is increased, more electrons are ejected but the energies of these electrons are not altered.
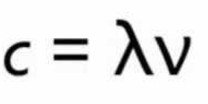
written in easy language and easy to understand
Easy too understand
It is easy for student, TNX
this is the best sites for chemistry notes at the google.
because explanation is too easy for understanding to the students.
I request you to please also make notes for physics
language is too easy. Every topic is easy to understand but the problem is I am not able to copy it on my computer. I wanted a print of your matter so that I could study it anywhere easily
Best Notes I Found
Awesome
Very easily understandable and also informative hats off to this website this is the first time I am using this and I had liked it.this information is not there in any of the website except this tq for this information
It’s very helpful because it is written on the basis of NCERT and is written in a very easy language. Thanks for this….
thank you it was very helpul 🙂
it is the best notes for studying board
it was reallt helpfull
these notes has helped me a lot in understanding the so called hard concepts of photoelectric effect…..
THANKS A LOT!! : )
Thanks for these notes
best website for study mam
Thanks for these notes
Very helpful notes
THIS IS ONE OF THE BEST WEBSITES PRESENT ON GOOGLE FOR CLASS NOTES
VERY HELPFUL
TAKE A BOW DEVELOPERS
waaaawwwwwww!!!!!
I’m like “why didn’t I notice this website earlier and was referring some other websites which gave me unwanted notes out of the topic”
But I’m reallllyyyyy loving this site where I could get better notes in easy english which is easy to understand and the information given is up to the mark
thank you soooo much mam !!!!!
Best notes of chemistry
Best notes madam
Greatful beyond words
Simple and to the point explanation .