Wolfgang Pauli a German physicist in 1925 put forward a principle known after his name as Pauli exclusion principle.
No two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum number.
In an atom, any two electrons may have the same values for any of the three quantum numbers but the 4th must be different.
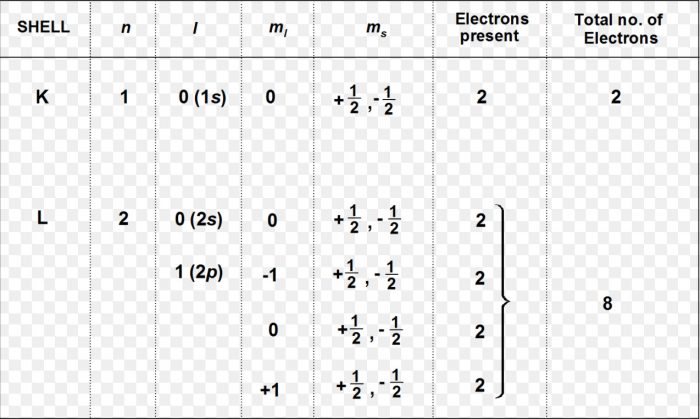
Any particular orbital is described by three quantum numbers i.e. n, l and m.
For Ex: 3s orbital has n=3, l=0 and m=0.
Since for each value of m, there are two values of the spin quantum number i.e. + ½ and – ½ therefore 3s orbital can have two electrons, one with quantum number n=3 , l=0, m=0 and s= + ½ and other with quantum number, n=3 , l=0, m=0 and s= – ½ .
An orbital can have a maximum two electrons and these have opposite Spins.
Number of sub shells in nth shell = n.
Number of orbitals in a sub shell = 2l + 1
Maximum number of electrons in a sub shell=2(2l +1)
Number of orbitals in nth shells = n2
Maximum number of electrons in nth shell = 2n2
Leave a Reply