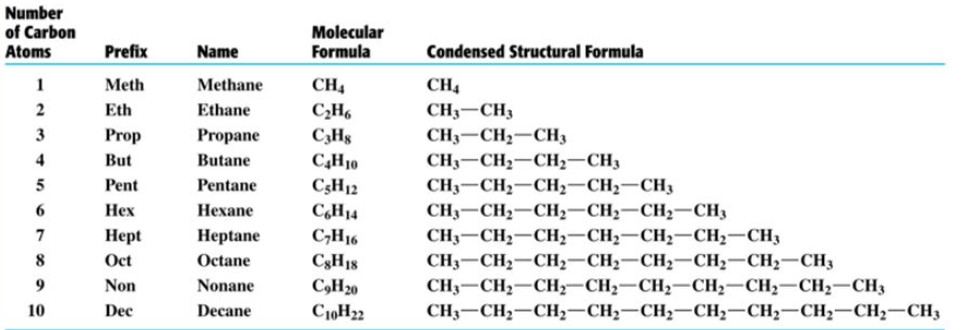
Compounds of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
These are further divided into two classes: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon.
1) Saturated hydrocarbons- alkanes
Hydrocarbons in which all the carbon atoms are linked to one another by only single bonds are called saturated hydrocarbons.
These ma be either acyclic or cyclic hydrocarbons.
Saturated acyclic hydrocarbons are called alkanes. They are also called paraffins since they are relatively inert towards most of the chemical reagents.
General Formula: CnH2n+2
Primary suffix: ane
The IUPAC names of alkanes are obtained by adding suffix ane to he word root indicating the number of carbon atoms.
Types of alkanes
Depending upon the structure of the carbon chain, alkanes are of following two types :
Straight chain alkanes : These alkanes contains straight chains of carbon atoms in their molecules. Alkanes in which no carbon atom is linked to more than two other carbon atoms are called Staight chain alkanes.
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH3 Butane
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 Hexane
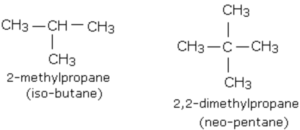
Branched chain alkanes
Alkanes in which at least one carbon atom is linked to three or four other carbon atoms are called branched chain alkanes.
The prefix iso is used when the second carbon of the branched chain alkanes carries 1 methyl group while the prefix neo is used when second carbon of the branched chain alkanes carries 2 methyl group.
Types of carbon and hydrogen atoms in alkanes
The carbon atom in an alkane molecules may be classified into four types as primary(1°) ,secondary (2°) , tertiary (3°) and quaternary (4°).
A carbon atom attached to one other carbon atom is called a primary carbon atom and is designated as 1°.
A carbon atom attached to two other carbon atom is called a secondary carbon atom and is designated as 2°
A carbon atom attached to three other carbon atoms is called a tertiary carbon atom and is designated as 3°.
A carbon atom attached to 4 other carbon atoms is called a quarternary carbon atom and is designated as 4°.
The hydrogen atoms attached to 1° ,2° ,3° carbon atoms are called Primary ,secondary and tertiary hydrogen atoms.
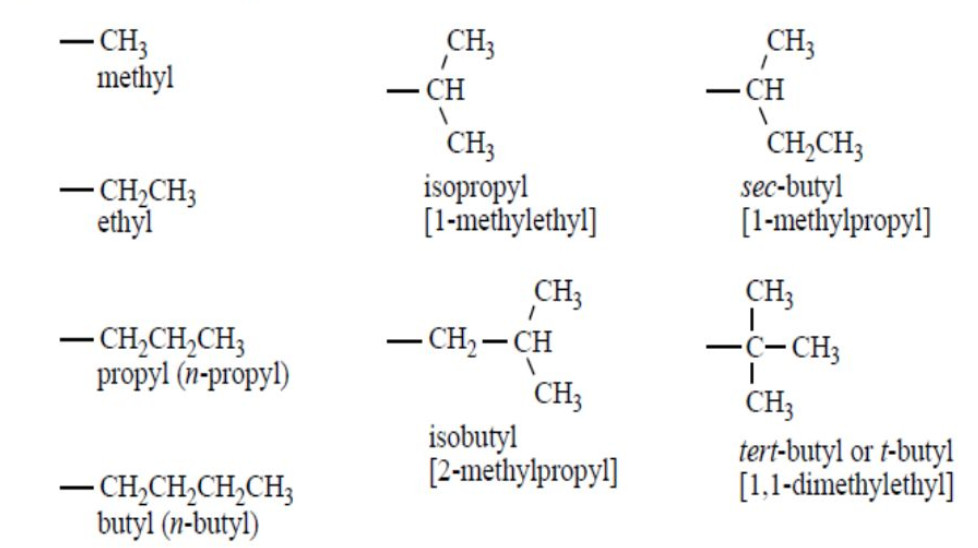
Alkyl groups
The removal of one hydrogen atom from the molecule of an alkane gives an alkyl group.
General formula: CnH2n+1
Their names are derived by replacing the terminal ane of corresponding alkane by the suffix yl.
Alkane -ane +yl =Alkyl
2)Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Open chain hydrocarbons which contain carbon-carbon double or triple bonds in their molecules are called unsaturated hydrocarbons.
These are of two types :alkenes and alkynes.
Alkenes : Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing a carbon carbon double bond are called alkene.
They are also called all olefins since the lower members of this class react with chlorine to form oily products.
General Formula: CnH2n
Primary suffix : ene
Common name : Alkane -ane + ylene
IUPAC name: Alkane -ane +ene = Alkene
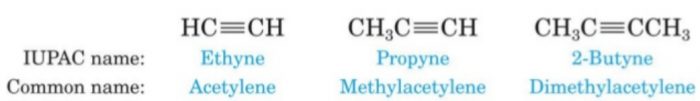
Alkynes
Unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons containing a carbon carbon triple bonds are called alkynes.
They are called acetylenes after the name of the first member of this family.
General formula: CnH2n-2
Primary suffix: yne
3)Haloalkanes
Halogen derivatives of alkanes are called haloalkanes.
They are further classified as mono, di, tri and tetra haloalkanes accordingly as they contain 1, 2, 3,4 halogen atoms respectively in their molecules.
1) Monohaloalkanes : The monohalogen derivatives of alkanes are called alkyl halides.
General formula : CnH2n+1 X where X=F,Cl, Br,I
Functional group : X (halogen)
Secondary prefix : Halo
Common names : Add the word halide (fluoride, chloride ,bromide, iodide) to the name of the alkyl group i.e. Alkyl + halide = Alkyl halide
IUPAC names :Add the secondary prefix halo to the name of corresponding alkane i.e. Halo + alkane=Haloalkanes
The position of both the halogen atoms are indicated.
2) Dihaloalkanes
Alkanes containing 2 halogen atoms per molecule are called dihaloalkanes.
General Formula: CnH2nX2 where n=1,2,3 etc
Common name: Dihalogen derivatives of alkanes have been divided into three categories:
1) Alkylidene dihalogen : Dihalogen derivatives of alkanes in which the two halogen atoms are attached to same carbon atom are called alkylidene dihalides or alkylidene halides.
Since the position on the same carbon atom are called geminal position, therefore, alkylidene dihalides are also called geminal dihalides or simply gem-dihalides.
2) Alkylene dihalides : Dihalogen derivatives of alkanes in which the 2 halogen atoms are attached to adjacent carbon atoms of the chain are called alkylene dihalides or alkylene halides.
Since position on the adjacent carbon atom are called vicinal position, therefore, alkylene dihalides are also called vicinal dihalides or simply vi-dihalides.
3) Polymethylene dihalides : Dihalogen derivatives of alkanes in which the 2 halogen derivatives are present on the terminal carbon atoms i.e. α , ω-position of the carbon chain are called polymethylene dihalides.
All types of dihalides are called dihaloalkanes, the position of the halogen atoms being indicated by lowest possible arabic numerals.
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC |
| CH2Cl2 | Methylene chloide | Dichloromethane |
| CH3-CHBr2 | Ethylidene dibromide | 1,1-Dibromoethane |
| BrCH2-CH2Br | Ethylene dibromide | 1,2-Dibromoethane |
| CH3-CHCl-CH2Cl | Proplidene dichloride | 1,1-Dichloropropane |
| CH3-CCl2-CH3 | Isoproplidene dichloride | 2,2-Dichloropropane |
| ClCH2-CH2-CH2-Cl | Trimethylene dichloride | 1,3-Dichloropropane |
3) Tri and tetrahaloalkanes
The general formula of trihaloalkanes is CnH2n-1X3 while that of tetrahaloalkanes is CnH2n-2X4 where n=1,2,3,4….
The position of the halogen atoms on the carbon chain be indicated by Arabic numerals.
4) Alcohols or alkanols
Alcohols are classified as monohydric ,dihydric, trihydric and polyhydric according as their molecule contains 1,2,3 and many hydroxyl groups.
Presence of two or more hydroxyl groups on the same carbon atom makes the molecule unstable, therefore, in di, tri and polyhydric alcohol , each hydroxyl group is present on a different carbon atom.
1) Monohydric alcohols
General formula: CnH2n+1 OH (where n=1,2,3…) or R-OH
Functional group : OH (hydroxyl)
Secondary suffix : ol
Common names: Add the word alcohol to the name of alkyl group i.e.
Alkyl + alcohol = Alkyl alcohol
IUPAC names: Replace the terminal e from the name of corresponding alkane by the suffix ol.
Alkane -e +ol = Alkanol
| Formula | Common Name | IUPAC name |
| CH3OH | Methyl alcohol | Methanol |
| CH3CH2OH | Ethyl alcohol | Ethanol |
| CH3CH2CH2OH | n-Propyl alcohol | Propan-1-ol |
| CH3CHOHCH3 | Isopropyl alcohol | Propan-2-ol |
2) Dihydric alcohols
General formula: CnH2n+1(OH)2
Because of their sweet taste ,dihydric alcohols are called glycols.
Depending upon the relative position of the two hydroxyl groups, they are further classified as α, β, γ …ω glycols.
α-glycols are named by adding the word glycol to the common name of the alkene from which they have been prepared by direct hydroxylation.
β, γ ,ω glycols are named as the corresponding polymethylene glycols.
IUPAC name: Add the suffix diol to the name of the alkane containing the same number of carbon atoms as the diol.
Alkane + diol =Alkanediol
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| OHCH2-CH2OH | Ethylene glycol | Ethane-1,2-diol |
| CH3-CHOH-CH2OH | Propylene glycol | Propane-1,2-diol |
| OHCH2-CH2-CH2OH | Trimethylene glycol | Propane-1,3-diol |
3) Trihydric alcohol
General Formula: CnH2n-1 (OH)3
IUPAC name: Add the suffix triol to the name of the alkane containing the same number of carbon atoms as the triol.
Alkane + triol =Alkanetriol
The position of the hydroxyl group is indicated by arabic numerals.
5) Ethers
General Formula: R-O-R’ where R and R’ are same or different alkyl group.
If R=R’ ,ethers are called simple ethers and if R≠R’ then ethers are called mixed ethers.
Common names: In mixed ethers, add the word ether to the name of the alkyl groups arranged in alphabetical order.
In simple ethers , the numerical prefix di is added to the name of the alkyl group followed by the word ether.
IUPAC name: In the IUPAC system, ethers are called alkoxyalkanes.
The smaller alkyl group forms a part of the alkoxy group while the bigger alkyl group forms a part of the alkane.
The name of the ethers are then derived by adding the suffix alkoxy to the name of the alkane i.e. Alkoxy + alkane = Alkoxyalkane
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| CH3-O-CH3 | Dimethyl ether | Methoxymetahne |
| CH3-O-CH2CH3 | Ethyl methyl ether | Methoxyethane |
| CH3CH2-O-CH2CH3 | Diethyl ether | Ethoxyethane |
6) Alkanoic acids
General Formula: CnH2n+1 COOH or R-COOH
Functional group: -COOH
Secondary suffix : oic acid
IUPAC names: Replace terminal e from the name of the corresponding alkane by the suffix oic acid
i.e. Alkane – e + oic acid = Alkanoic acid
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-COOH | Formic acid | Methanoic acid |
| CH3-COOH | Acetic acid | Ethanoic acid |
| CH3CH2-COOH | Propionic acid | Propanoic acid |
| CH3CH2CH2CH2 -COOH | Butyric acid | Butanoic acid |
7) Aldehydes or Alkanals
General formula : CnH2n+1 CHO or R-CHO
Functional group: -CHO
Secondary suffix: al
Common name: Replace ic acid from the common name of the corresponding acid which they give upon oxidation by the word aldehyde.
IUPAC : Replace the terminal e from the name of the corresponding alkane by the suffix ,al.
Alkane -e+al = Alkanal
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-CHO | Formaldehyde | Methanal |
| CH3-CHO | Acetaldehyde | Ethanal |
| CH3CH2-CHO | Propionaldehyde | Propanal |
| CH3CH2CH2CH2-CHO | Butryaldehyde | Butanal |
8) Ketone or Alkanones
General Formula: CnH2n+1 CO CnH2n+1 where n=1,2,3…. or R-CO-R’ where R and R’ may be same or different alkyl group.
If R = R’ , ketones are called simple ketones.
If R≠ R’ , ketones are called mixed ketones.
Functional group : -CO
Secondary suffix: one
Common name: In case of mixed ketones , name the alkyl group in alphabetical order and then add the word ketone.
In simple ketones, the numerical prefix di is used before the name of the alkyl group.
IUPAC : Replace the terminal e from the name of the corresponding alkane by the suffix , one.
Alkane -e +one = Alkanone
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| CH3-CO-CH3 | Dimethyl ketone or acetone | Propanone |
| CH3-CO-CH2CH3 | Ethyl methyl ketone | Butan-2-one |
| CH3-CO-CH2CH2CH3 | Methyl propyl ketone | Pentan-2-one |
| CH3CH2-CO-CH2CH3 | Diethyl ketone | Pentan-3-one |
9) Acid chlorides or acyl chlorides or Alkanoyl chlorides
General formula: RCOCl where R=H or any alkyl group
Functional group: -COCl
Secondary suffix: oyl chloride
Common name: Replace ic acid from the common name of the corresponding acid by yl chloride
IUPAC name: Alkane -e + oyl chloride = Alkanoyl chloride
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-COCl | Formyl chloride | Methanoyl chloride |
| CH3-COCl | Acetyl chloride | Ethanoyl chloride |
| CH3CH2-COCl | Propionyl chloride | Propanoyl chloride |
| CH3CH2CH2-COCl | Butyryl chloride | Butanoyl chloride |
10) Acid anhydride
General formula: R-CO-O-CO-R’ or (RCO)2O where R and R’ may be same or different alkyl group.
Functional group: -CO-O-CO-
Secondary suffix: anhydride
Common name: Replace the word acid from the common or IUPAC name of the corresponding acid by word anhydride.
Symmetrical anhydride of substituted carboxylic acids are named by adding the prefix bis to the name to indicate that two identical acyl group are present.
Unsymmetrical anhydride are named by writing the names of the two acids alphabetically before the word anhydride.
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| (CH3CO)2O | Acetic anhydride | Ethanoic anhydride |
| (CH3CH2CO)2O | Propionic anhydride | Propanoic anhydride |
| (ClCH2CO)2O | Bis(Chloroacetic anhydride) | Bis(Chloroethanoic anhydride) |
| HCO-O-COCH3 | Acetic formic anhydride | Ethanoic methanoic anhydride |
11) Esters
General formula: R-COOR’
Functional group: -COOR“
Secondary suffix: oate
Common name or IUPAC name: Write the name of the alkyl group before the common or IUPAC name of the parent acid with its terminal ic acid replaced by oate.
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-COOCH3 | Methyl formate | methyl methanoate |
| H-COOC2H5 | Ethyl formate | Ethyl methanoate |
| CH3-COOCH3 | Methyl acetate | Methyl ethanoate |
| CH3-COOC2H5 | Ethyl acetate | Ethyl ethanoate |
12) Acid amide or Alkanamides
General formula: R-CONH2
Functional group: -CONH2
Secondary suffix: amide
Common name : Replace ic acid from the common name of the corresponding acid by the secondary suffix amide.
IUPAC name: Replace the terminal e from the name of the corresponding alkane by the suffix amide i.e. Alkane -e + amide = Alkanamide
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-CONH2 | Formamide | Methanamide |
| CH3-CONH2 | Acetamide | Ethanamide |
| CH3-CH2-CONH2 | Propanamide | Propanamide |
13) Primary amines
General formula: R-NH2
Functional group: -NH2
Secondary suffix: amine
Common name : 1) Add the word amine to the name of the alkyl group , i.e.
Amino + amine = Alkylamine
2) Attach the prefix amino to the name of the corresponding alkane , i.e.
Amino + alkane = Aminoalkane
IUPAC name : Replace the terminal e from the name of the corresponding alkane by the secondary suffix amine i.e. Alkane -e + amine = Al
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| H-CONH2 | Formamide | Methanamide |
| CH3-CONH2 | Acetamide | Ethanamide |
| CH3-CH2-CONH2 | Propanamide | Propanamide |
14) Secondary amines
General formula: R-NH-R’ where R and R’ may be same or different alkyl group.
Functional group: -NH (imino)
Secondary prefix: N-alkyl
Secondary suffix: amine
Common name : 1) Name the alkyl group in alphabetical order and then add the word amine.In case the two alkyl groups are same, the numerical prefix di is used before the name of the alkyl group.
2) Add the prefix N-alkyl before the name of the aminoalkane ; the smaller alkyl group forma a part of the N-alkyl group while the larger alkyl group forms a part of the alkane.
IUPAC name: Add the prefix N-alkyl to the name of the alkanamine corresponding to the larger alkyl group , i.e. N-alkyl + alkanamine = N-Alkylalkanamine
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC |
| CH3NHCH3 | Dimethyl or N-Methylaminomethane | N-Methylmethanamine |
| CH3CH2CH2NHCH3 | Ethylmethylamine or N-Methylaminoethane | N-Methylethanamine |
| (CH3CH2)3N | Diethylamine or N-Ethylaminoetahne | N-Ethylethanamine |
15) Tertiary amines
General formula: R-N(R’R“) where R , R’ , R“ may be same or different alkyl group or two of them may be same while the third may be different.
Functional group: -N-
Secondary prefix: N-alkyl , N-alkyl
Secondary suffix: amine
Common name : 1) Name the alkyl group in alphabetical order and then add the suffix amine.In case the two or all the three alkyl groups are same, the numerical prefix di and tri are used before the name of the alkyl group.
2) Add the prefix N-alkyl and N-alkyl to the name of the aminoalkane corresponding to the largest alkyl group.
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC name |
| (CH3)3N | Trimethylamine or N,N-Dimethylaminomethane | N,N-Dimethylmethanamine |
| CH3CH2N(CH3)2 | Ethyldimethylamine or N,N-Dimethylaminoethane | N,N -Dimethylethanamine |
| (CH3CH2)2NCH3 | ||
| (CH3CH2)3N | Triethylamine or N,N-Diethylaminoethane | N,N-Diethylethanamine |
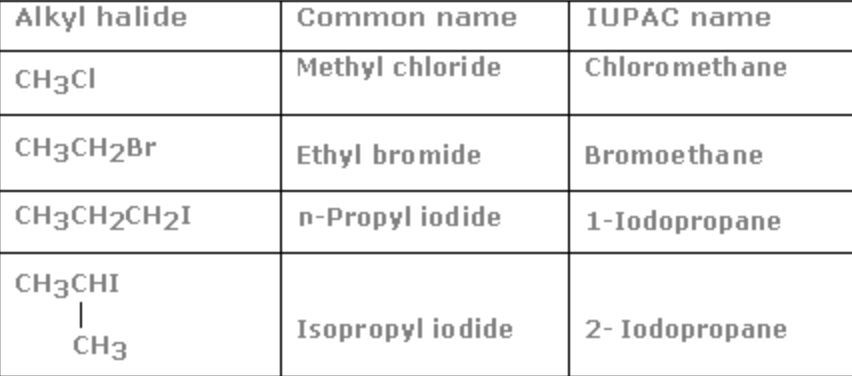
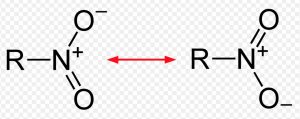
16) Nitroalkane
General formula: R-NO2
Functional group :
Secondary prefix: nitro
Common name: There are no common names for nitroalkanes
IUPAC name: Add the secondary prefix nitro to the name of the alkane
Nitro+ alkane = Nitroalkane
| Formula | Common name |
| CH3-O-N=O | Methyl nitrite |
| CH3CH2-O-N=O | Ethyl nitrite |
| CH3CH2CH2NO2 | n-Propyl nitrite |
| CH3CH(NO2)CH3 | Isopropyl nitrite |
17) Alkyl nitrites
General formula: R-O-N=O
Functional group : -O-N=O
Secondary suffix: nitrite
Common names: Add the secondary suffix nitrite to the name of the alkyl group i.e.
Alkyl + nitrite = Alkyl nitrite
IUPAC name: There are no IUPAC names for alkyl nitrites.
| Formula | Common name |
| CH3-O-N=O | Methyl nitrite |
| CH3CH2-O-N=O | Ethyl nitrite |
| CH3CH2CH2NO2 | n-Propyl nitrite |
| CH3CH(NO2)CH3 | Isopropyl nitrite |
18) Alkyl cyanide
General formula: R-C≡N
Functional group: -C≡N
Secondary suffix: nitrile
Common name: 1) Add the suffix cyanide to the name of the alkyl group ,i.e.
Alkyl + cyanide = Alkyl cyanide
2) Replace ic acid from the common name of the corresponding acid by the suffix onitrile.
Acetic acid -ic acid + onitrile = Acetonitrile
IUPAC name: Add the suffix nitrile to the name of the alkane containing the same number of carbon atoms as the alkyl cyanide i.e. Alkane + nitrile = Alkanenitrile
| Formula | Common name | IUPAC Name |
| CH3-CN | Methyl cyanide or Acetonitrile | Ethanenitrile |
| CH3CH2-CN | Ethyl cyanide or Propionitrile | Propanenitrile |
| CH3CH2CH2-CN | Propyl cyanide or Butyronitrile | Butanenitrile |
19) Isocyanide
General formula: RNC
Functional group:
Secondary suffix: Isocyanide or isonitrile
Common name: Add the suffix isocynanide or carbylamine to the name of the alkyl group.
IUPAC name: There are no IUPAC for isocynaide or isonitrile.
| Formula | Common name |
| CH3NC | Methyl isocyanide or Methyl carbylamine or Methyl isonitrile |
| CH3CH2NC | Ethyl isocynaide or Ethyl carbylamine or Ethyl isonitrile |

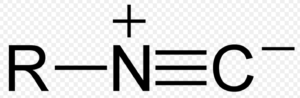
All nitrite compound of organic in nomenclature please sir
best
Madam this content is very useful and also plzz upload b.sc chemistry content also, because in b.sc we are not having any proper notes this type of content will be very helpful in m.sc entrance exams