Contents
Free Radical
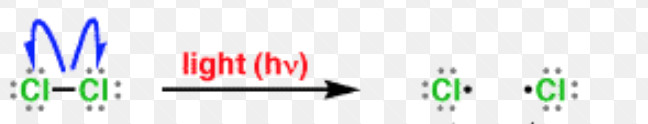
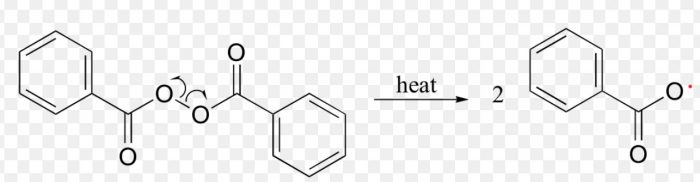
A free radical may be defined as an atom or a group having an odd or unpaired electron. These are generally produced by the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond.
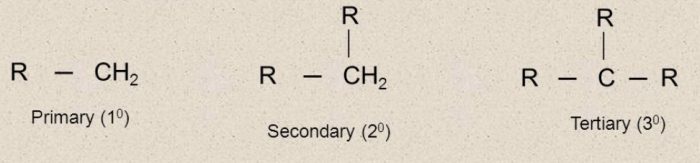
Classification of Free Radicals
Free radicals are also classified as primary (1°) , secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) according as the carbon carrying the unpaired electron is primary, secondary and tertiary.
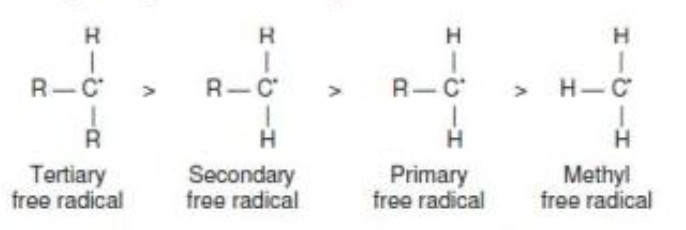
Stability of Free Radicals
The order of stability of free radicals is the same as that of carbocations i.e. 3° >2° >1°
This order of stability can be explained on the basis of hyperconjugation.
Greater the number of alkyl groups attached to the carbon atom carrying the odd electrons, greater is the delocalization of the odd electrons and hence more stable is the alkyl free radical.
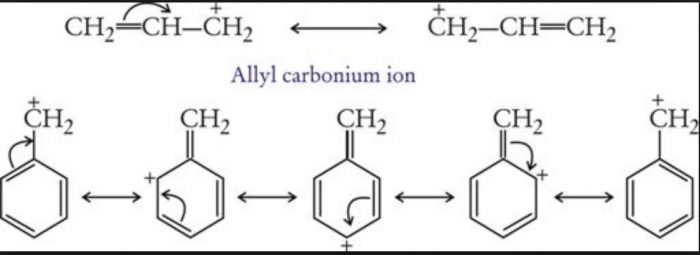
Allyl and benzyl free radicals are stabilized by resonance.
Greater the number of phenyl groups more stable is the free radical.
Free radicals are also very short-lived highly reactive chemical species because of the strong tendency of the carbon atom carrying the odd electron to acquire one more electron to complete its octet.
Orbital structure of Free Radicals
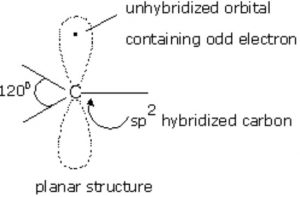
Alkyl free radicals are planar chemical species.In free radicals, the unhybridized p-orbital contains the odd electron.
Like carbanions , free radicals can also assume pyramidal shape since the energy difference between planar and pyramidal shape is not much.
Really basic & useful text for class XI syllabus. Many thanks Madam.
Thanks mam it is very helpful