Pure water is poor conductor of electricity.
Water is a weak electrolyte i.e. it is ionized to a very small extent as:
H2O ![]() H+ + OH‾
H+ + OH‾
H2O + H2O ![]() H3O+ + OH‾
H3O+ + OH‾
This ionization is called self ionization of water.
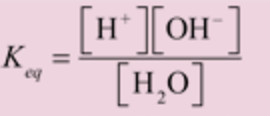
where Keq is the dissociation constant of water.

Kw is the ionic product of water.
Ionic product of water may be defined as the product of the molar concentration of H+ ions and OH‾ ions.
As H+ ions in water exist as H3O+ ions, therefore, ionic product may also be defined as the product of molar concentration of H3O+ ions and OH‾ ions, i.e.
OR
Ionic product of water is constant only at constant temperature.
Kw at 298 K
Kw = 1.00 × 10-14
Dissociation or ionization of constant of water is different from ionic product of water.
Keq = Kw / 55.55
Kw = Keq × 55.55
Keq = 10-14 /55.55 = 1.8 × 10-16
In pure water
Effect of temperature on Kw
The ionic product of water increases with increase of temperature.
With increase of temperature ,the degree of ionization of water increases. More of water molecule dissociate into H+ ions and OH‾ ions.The concentration of H+ and OH‾ ions increases and hence the ionic product also increases.
H3O+ ion and OH‾ ion concentration in aqueous solution of acid and bases
If some acid is added to pure water, then ( H3O+ ) > 10-7M
= Kw /
If some base is added to pure water, then = 10-7 M
= Kw /
The increase or decrease of the H3O+ ion concentration in an aqueous solution of an acid or a base may be explained qualitatively on the basis of Le Chatelier’s principle.
2H2O ![]() H3O+ + OH‾
H3O+ + OH‾
If some acid is added to pure water, H3O+ ion concentration increases , therefore the equilibrium shifts in the backward direction.Thus OH‾ ion concentration decreases.
If a base added, OH‾ concentration increases.Again the equilibrium shifts in the backward direction and hence the H3O+ ion concentration decreases.
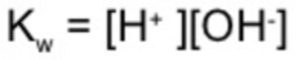
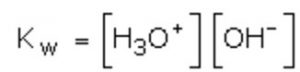
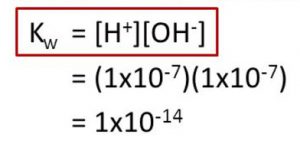
I am very much impressed by the way ionic product is explained. Now I am satisfied and have cleared my doubts.
Thanks
Nice
thank you