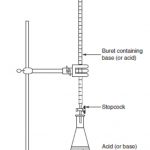
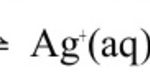Titration is the measurement of the volume of a solution of one reactant that is required to react completely with a measured amount of another reactant. As both the reactants are taken in the form of solution and the titration is the measurement of volume of one solution that must be added to another solution till the reaction is complete, this method of quantitative … [Read more...] about Acid- Base Titration using Indicator
Ionic Equilibrium
Calculation of pH of a Buffer Mixture
For Acidic Buffer mixture( Henderson- Hasselbalch equation) For Basic Buffer mixture pOH = pKb + log [salt] / [Base] pH + pOH =14 pOH = 14 - pH pKa + pKb = 14 pKb=14 - pKa 14 - pH = 14 - pKa + log [salt) / [base] pH = pKa - log [salt] / [base] pH = pKa + log [base] / [salt] where Ka is the ionization constant of the conjugate acid of the … [Read more...] about Calculation of pH of a Buffer Mixture
Buffer solution and Buffer Action
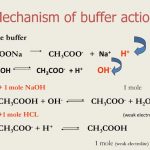
Buffer Solution A buffer solution is defined as a solution which resist any change in its pH value even when small amount of acid or base are added to it. Types of the buffer solution 1) Solution of single substance The solution of the salt of weak acid and weak base eg : ammonium acetate ( CH3COOH) act as a buffer. 2) Solution of Mixture: These are of 2 … [Read more...] about Buffer solution and Buffer Action
Common Ion Effect
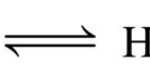
If to an ionic equilibrium, AB A+ + B‾ , a salt containing a common ion is added, the equilibrium shifts in the backward direction. This is called common Ion effect. Acetic acid being a weak acid, ionizes to a small extent as: CH3COOH CH3COO‾ + H+ To this solution , suppose the salt of this weak acid with a strong base is added. It ionizes almost completely in … [Read more...] about Common Ion Effect
Solubility Equilibrium and Solubility Product
If a sparingly soluble salt like AgCl is stirred with water ,only a small amount of it goes into solution while most of the salt remain undissolved. But little amount of salt dissolves, it gets completely dissociated into ions. when a sparingly soluble salt is added to water ,there exist a dynamic equilibrium between the undissolved solid salt and the ions which is … [Read more...] about Solubility Equilibrium and Solubility Product