Classical concept of acids and bases
Acid is a substance whose aqueous solution possessed the following characteristic properties
1) conduct electricity
2) reacts with active metals like zinc ,magnesium to give hydrogen
3) turns blue litmus to red
4) has a sour taste
5) whose acidic properties disappear on reaction with a base
Base is a substance whose aqueous solution possessed the following characteristic properties:
1)turns red litmus blue
2) has a bitter taste
3) has a soapy touch
4) whose basic properties are destroyed on reaction with an acid
Arrhenius concept of acids and bases
Arrhenius in 1884 put forward a theory popularly known as Arrhenius theory of ionization
When an electrolyte is dissolved in water ,it dissociates into positively and negatively charged ions.
An acid is defined as a substance which contains hydrogen and which when dissolved into water gives hydrogen ions (H+)
Substances like HCl, HNO3 , H2SO4 containing hydrogen, when dissolved in water dissociates completely into H+ ions and negative ions.
HCl ———-> H+ + Cl‾
H2SO4 ————–> 2H+ + SO42-
HNO3 ———> H+ + NO3‾
Such acids are called strong acids.
Substance like acetic acid ,carbonic acid, phosphoric acid when dissolved in water dissociate into ions to a small extent.
CH3COOH CH3COO‾+ H+
H2CO3 2H+ + CO32‾
H3PO4 3H+ + PO43‾
Such acids are called weak acids.
A base is defined as a substance which contain hydroxyl group, when dissolved in water gives hydroxide ion (OH‾).
Substances like NaOH and KOH containing hydroxyl group when dissolved into water, dissociate completely to give OH‾ ions as:
NaOH ————> Na+ + OH‾
KOH —————> K+ + OH‾
These are called strong bases.
Substances like NH4OH , Ca(OH)2 , Mg(OH)2 , Al(OH)3 dissociates to a small extent as :
NH4OH NH4 + + OH‾
Ca(OH)2 Ca2+ + 2OH¯
These are called weak bases.
Existence of H+ ion and OH‾ ion in aqueous solution
H+ ion is simply a proton which is very small in size. It has a strong electric field. It takes up a lone pair of electrons from water molecule to form called hydronium ion, H3O+.This ion in aqueous solution can combine with more of water molecules to form species like H5O2+ , H7O3+ etc.
OH‾ ion in aqueous solution can be can combine with one or more water molecules to form species like H3O2‾ , H5O3‾ etc.
The dissociation of an acid in water may be expressed as :
HCl + water H+ (aq ) + Cl‾ (aq)
CH3COOH + water H+ (aq ) + CH3COO‾ (aq)
HCl + H2O H3O+ (aq ) + Cl‾ (aq)
The dissociation of base may be expressed as :
NaOH + water Na+ (aq ) + OH‾ (aq)
NH4OH NH4+(aq) + OH‾(aq)
When an acid and base are mixed together, they react to form salt and water. The reaction is called neutralization.
NaOH + HCl ———–> NaCl + H2O
Neutralization is defined as the process in which hydrogen ions given by the acid and hydroxyl Ion given by the base combine to form unionized molecules of water.
Advantage of Arrhenius concept
The Arrhenius concept of acids and bases was able to explain a number of phenomena like neutralization, salt hydrolysis ,strength of acids and bases.
Limitation of Arrhenius concept
1) Nature of H+ and OH‾ ion
According to Arrhenius concept ,acids and bases were defined as substances which gave H+ ions and OH‾ ions in aqueous solution. But these ions cannot exist as such in aqueous solution but exist as hydrated ion.
2) Inability to explain acidic and basic character of certain substances
Arrhenius concept says that an acid must contain hydrogen and a base must contain hydroxyl group. However a number of substances like NH3 , Na2CO3, CaO are known to be basic but do not contain any hydroxyl group. Similarly a number of substances like CO2, SO2 ,SO3 etc are known to be acidic but do not contain any hydrogen.
NH3 (g) + H2O NH4+ (aq) + OH‾ (aq)
CaO+ H2O Ca2+ (aq) + 2OH‾ (aq)
3)Inability to explain the reaction between an acid and base in the absence of water.
NH3 (g) + HCl(g) ——> NH4Cl (s)
CaO(s) + SO3(g) ——–>CaSO4 (s)
Bronsted- lowry concept of acid and bases
Bronsted and lowry in 1923 proposed concept of acids and bases.
Acid is defined as a substance which has the tendency to give a proton and base is defined as a substance which has a tendency to accept a proton.
An acid is a proton donor whereas base is a Proton acceptor.
HCl +H2O H3O+ + Cl‾
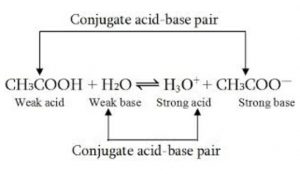
CH3COOH + H2O H3O+ (aq ) + CH3COO‾ (aq)
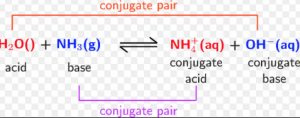
NH3 (g) + H2O NH4+ (aq) + OH‾ (aq)
NH3 + HCl NH4+ + Cl‾
CO32‾ + H2O NH4+ + Cl‾
1) HCl and CH3COOH are acids because they donate a proton to H2O.
2) NH3 and CO32‾ are bases because they accept a proton from water.
3)Not only molecules but even the ions can act as acids or bases.
4)Water is accepting a proton and hence is base.
HCl +H2O H3O+ + Cl‾
CH3COOH + H2O H3O+ (aq ) + CH3COO‾ (aq)
Water is donating a proton and hence is acting as acid.
NH3 (g) + H2O NH4+ (aq) + OH‾ (aq)
CO32‾ + H2O NH4+ + Cl‾
Water acts both as an acid as well as base and hence is called amphoteric.
5) Bronsted – lowry definition of acid and bases are not restricted to aqueous solution. HCl is acid because it gives a protons and NH3 is a base because it accepts the proton.
6) The presence of hydroxyl group is not essential for a substance to act as a base. The only requirement is that it should have tendency to accept a proton.
7) A substance acts as an acid i.e. gives a proton only when another substance to accept the proton i.e. a base is present.
8) The reverse reaction are also acid – base reaction.
In reaction HCl +H2O H3O+ + Cl‾ ,the reverse process H3O+ can give a proton and hence is an acid while Cl‾ can accept the proton and hence is a base.
There are two acid base pair in reaction. These are HCl-Cl‾ and H3O+ -H2O .These acid base pair are called conjugate acid – base pair.
Advantages of Bronsted-lowry concept
1) Bronsted-lowry concept is not limited to molecules but includes even the ionic species to act as acids or bases.
2) It can explain the basic character of the substances like Na2CO3 , NH3 etc on the basis that they are proton acceptor.
3) It can explain the acid base reaction in the non aqueous medium or even in the absence of solvent.
Disadvantage of Bronsted-lowry concept
1) It cannot explain the reaction between acidic oxides like CO2 , SO2 , SO3 and the basic oxides like CaO, BaO, MgO which takes place even in the absence of solvent.
2) Substances like BF3 , AlCl3 etc do not have any hydrogen and hence cannot give a proton but are known to behave as Lewis acid.
Lewis concept of acids and bases
G.N. Lewis in the same year i.e. 1923 ,proposed:
An acid is defined as substance which is capable of accepting a pair of electrons and base is defined as a substance which is capable of donating an unshared pair of electrons.
An acid is an electron pair acceptor while a base is an electron pair donor.
The reaction between an acid and base amount to the formation of a co-ordinate Bond or dative bond between them:
For Ex:
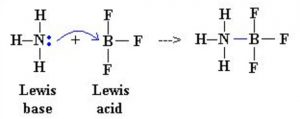
1) Reaction between BF3 and NH3
Since NH3 can donate a lone pair of electron while BF3 can accept a pair of electron , NH3 is a base and BF3 is an acid.
Types of Lewis bases
Lewis bases can be of two types:
1) Neutral molecules like NH3 , R-NH2 , R-OH, H-O-H etc. in which one of the atoms has got at least one lone pair of electrons.
2) All negative ions like F‾ , Cl‾ , Br‾, OH‾, CN‾
Types of Lewis acids
Lewis acids can be of 4 types:
1) Molecules having a central atom with incomplete octet.
For Ex: BF3 , AlCl3 , FeCl3
2) Simple cations e.g. Ag+ , Cu2+ , Fe3+
These ions can accept pairs of electrons and hence are Lewis acids.
3) Molecules having central atoms with empty d orbitals
The central atoms in these molecules can expand their outer octet by taking up electrons in the empty d orbitals.
For ex: SnCl4 , SiF4 , PCl5
4) Molecules containing a multiple bond between two atoms of different electronegativities.
For Ex: CO2 contain double bonds between carbon and oxygen. Since oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, therefore carbon acquires a slight positive charge and thus can accept a pair of electrons. Hence CO2 acts as Lewis acid.
Advantage of Lewis concept
1) It could explain even those acids and base reactions which could not be explained by others concepts.
Drawback of Lewis concept
1) Lewis concept is so general that it considers every reaction forming a co-ordinate bond to be acid base reaction. This however, may not be always true.
2) The requirement in Lewis concept is the formation of a co-ordinate bond between the acid and base. However acids like HCl and H2SO4 do not form any co-ordinate Bond and therefore should not be acids according to this concept.
3) Acid – base reactions are usually fast but formation of co-ordinate compound is slow. Hence it does not fit in the acid base concept.
4) The catalytic activity of an acid is due to H+ ion.Since the presence of hydrogen is not an essential requirement for a Lewis acid, many Lewis acids will not have this property.
5) Lewis concept cannot explain the strength of acids and bases.
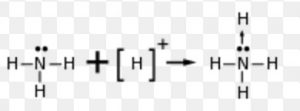
Thanks so much for this auspicious note.written in simple so easy to understand .
GOOD CONCEPT FOR ACID N BASE
Good
Thanks to do our help
Good notes very easy to study about acid base concept
best notes for study and helpful for understanding so thank you mam
Its very useful to me thank ua
To good for preparation on exam tym
THANKU MAM
A brilliantly written compact note is really helpful.