Non-polar covalent bonds
If two similar atoms come close to each other and form a bond by sharing their electrons, the shared electrons are equally attracted by the two atoms as the electronegativity of the atoms is same.
Hence no poles are developed. This leads to the formation of completely non-polar bonds.
If two hydrogen atoms form a bond, the electron pair will lie exactly in the middle between the two atoms.
The electron cloud is completely symmetrical and there is no charge separation at all.
For Ex: Cl2 , O2 , N2 , F2
Polar covalent bonds
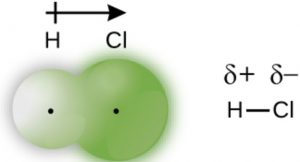
When two dissimilar atoms ,having different electro negativities combined together to form a covalent bond, the shared pair of electrons does not lie at equal distance from the nuclei of both the bonded atom but shift towards the atom having greater electronegativity.
The more electronegative atom attracts the electrons more strongly, the distribution of electrons get distorted i.e. the electron cloud is displaced more towards the more electronegative atom.
One end of the molecule, having more electronegative atom becomes slightly negatively charged while the other end acquire slightly positive charge.
Positive and negative poles are developed and this type of bond is called polar covalent bond.
For Ex: HCl molecule
Chlorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. So the force of attraction, on the shared pair ,exerted by chlorine is more than that by the hydrogen. Chlorine becomes slightly negatively charged and hydrogen become slightly positively charged.
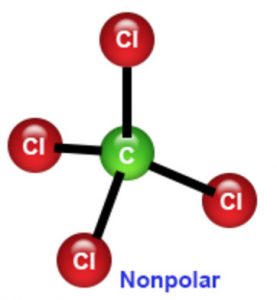
In symmetrical molecules like CO2 , CCl4 , although there are a number of polar bonds present, yet a molecule on the whole or non-polar. This is because the polar bonds cancel the effect of each other.
Partial ionic character of covalent bonds
If two atoms linked together have different electro negativities ,the bond formed is polar.
The bond is said to possess partial ionic character.
The extent of partial ionic character is determined by the difference in electronegativity of the combining atoms. More is the difference in electronegativity, greater will be the ionic character.
1) If electronegativity difference between two atoms is 1.9, the bond is said to have 50% ionic character and 50% covalent character.
2)If the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is more than 1.9 ,the partial ionic character of the bond is more than 50% and the bond is taken as ionic.
3) If the electronegativity difference between two atoms is less than 1.9 ,the bond is predominantly covalent.

Thank mam to help me in the topic