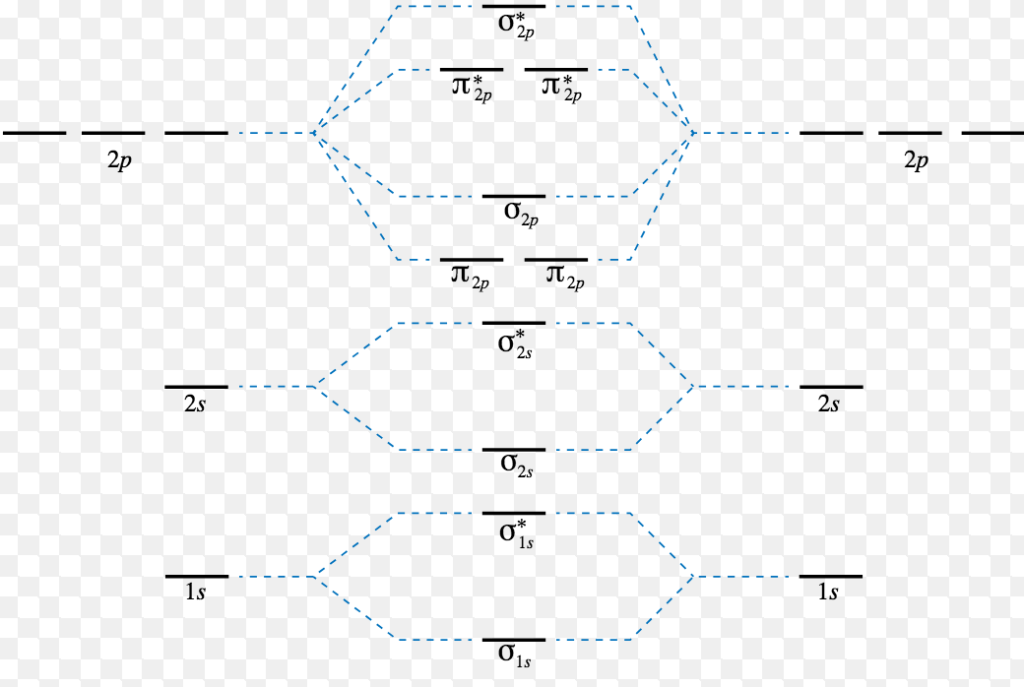
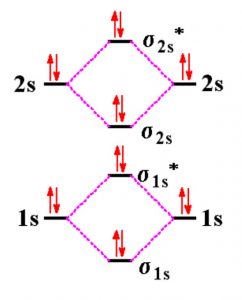
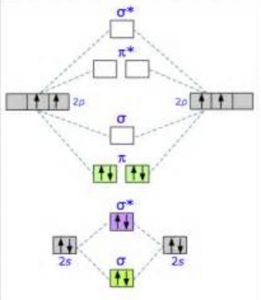
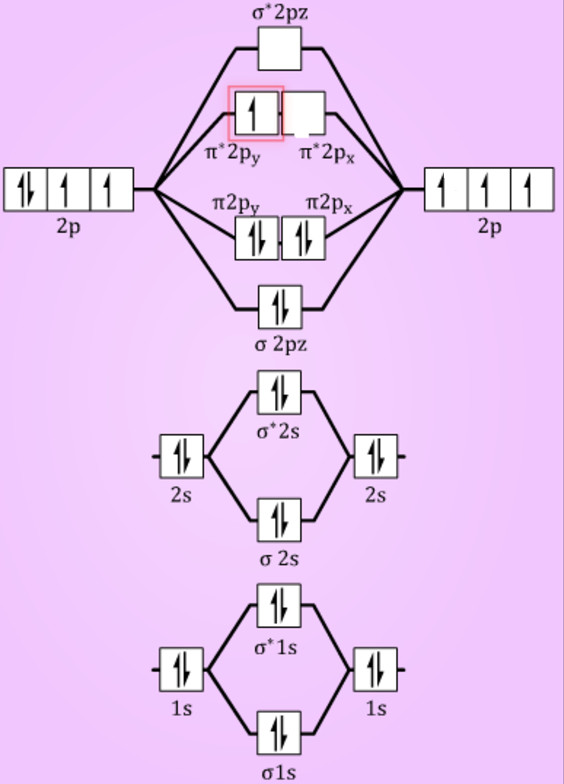
Energy level diagram for Molecular orbitals
The first ten molecular orbitals may be arranged in order of energy as follow:
σ(1s) <σ∗(1s) < σ(2s) <σ∗(2s) < π(2px) = π(2py) < σ(2pz) < π∗(2px) =π∗(2py) <π∗( 2pz)
Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour
1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons
Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by Nb and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.
1) If Nb > Na ,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than antibonding orbital, resulting in a net force of attraction.
2) If Nb < Na , the molecule is unstable because the antibonding influence is greater than the bonding influence, resulting in net force of repulsion.
3) If Nb = Na ,the molecule is again unstable because influence of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital is greater than the bond influence of electron in the bonding molecular orbitals.
2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order
Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals.
Bond Order = ½ ( Nb – Na)
The molecule is stable if Nb > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if Nb < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero.
3) Relative stability of molecule in terms of bond order
For diatomic molecules ,the stability is directly proportional to the bond order.
A molecule with the bond order of 3 is more stable than a molecule with bond order of 2 and so on.
4) Nature of bond in terms of bond order :
Bond order 1 ,2 and 3 mean single ,double and triple bond.
5) Bond length in terms of bond order:
Bond length is found to be inversely proportional to the bond order. Greater the bond order, shorter is the bond length.
6) Diamagnetic and paramagnetic nature of the molecules
If all the electrons in the molecule are paired, it is diamagnetic in nature.
If the molecules has some unpaired electrons ,it is paramagnetic in nature.
Greater the number of unpaired electrons present in the molecular or ion, greater is its paramagnetic nature.
Electronic configuration of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
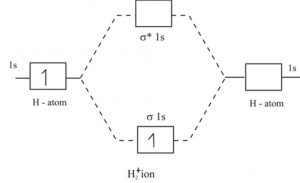
1) H2+
The electronic configuration of H2+ is ( σ(1s) ) 1
1) Nb =1 , Na = 0
Bond Order = 1
2) Positive bond order means it is stable.
3) One unpaired electron is present. Hence it is paramagnetic.
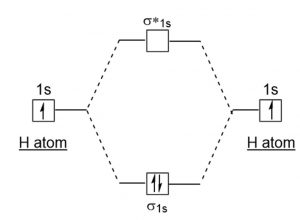
2) H2
The electronic configuration of H2 is ( σ(1s) )2
Nb = 2 , Na =0
Bond order = 1
Positive value of bond order indicates that H2 molecule is stable.
Bond order value of 1 means that two hydrogen atoms are connected by a single bond.
Greater value of bond order for H2 molecule than H2+ ion shows that two H2 molecule is more stable than H2+.
Bond length of H2 is smaller than that of H2+ ion.
As no unpaired electron is present, the H2 molecule should be diamagnetic.
3) H2–
The electronic configuration of H2– is ( σ(1s) )2 (σ∗(1s)) 1
1) Bond order= ½
2) Smaller positive value of bond order indicates that it is somewhat stable.
3) Since it has one unpaired ,it is paramagnetic.
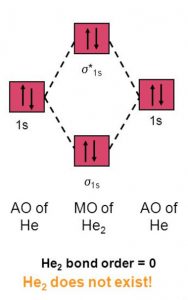
4) He2
Electronic configuration of helium is (σ(1s))2 (σ∗(1s))2
Nb= 2, Na =2
Bond Order =0
No bond is formed between two helium therefore He2 does not exist.
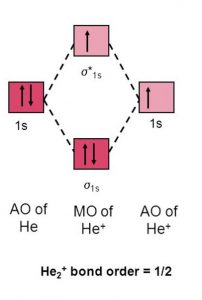
5) He2+
The electronic configuration of He2+ is (σ(1s))2 (σ∗(1s))1
Nb= 2, Na =1
Bond Order= ½
It is paramagnetic in nature.
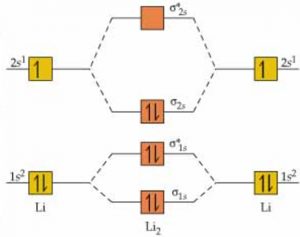
6) Li2
The electronic configuration of Li2 is (σ(1s))2 (σ∗(1s))2 (σ(2s))2
As inner closed closed shells do not participate in bonding therefore the configuration is written as:
KK (σ(2s))2
As the K closed shells do not take part in bonding, they are called non-bonding orbitals.
1)Nb=2, Na= 4
Bond Order= 1
2)Li2 is a stable molecule.
3)It has no unpaired electron ,it should be diamagnetic.
7) Be2
The electronic configuration of Be2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2
Nb= 2, Na =2
Bond order= 0
Be2 does not exist
8) B2
The electronic configuration of B2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 π(2px)1 π(2py)1
Nb= 4 Na =2
Bond order = 1
The molecule is paramagnetic
9) C2
The electronic configuration of C2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2
Nb= 6, Na =2
Bond order= 2
The molecule is diamagnetic
The double bond in C2 consist of both Pi bonds because the four electrons are present in the two pi molecular orbitals.
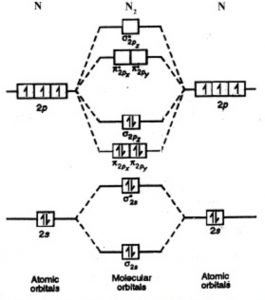
10) N2
The atomic number of nitrogen is 7
The electronic configuration of N2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2
Nb= 8, Na= 2
Bond Order= 3
Bond order value of 3 means that N2 contains a triple bond.
High value of bond order implies that it should have highest bond dissociation energy.
Presence of no unpaired electron indicates it to be diamagnetic.
11) N2+ ion
The electronic configuration is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz)1
Nb= 7, Na =2
Bond order = 2.5
It has one unpaired electron , therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
12) N2−
The electronic configuration is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))1
Nb= 8 , Na =3
Bond Order= 2.5
It has one unpaired electron , therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
13) N22-
The electronic configuration is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))1 (π∗(2py))1
Nb= 8, Na =4
Bond order = 2
It has two unpaired electron , therefore it is paramagnetic in nature.
As bond dissociation energies are directly proportional to the bond order, therefore, the dissociation energies of these molecular species are in the order:
N2 > N2+ = N2− > N22-
As bond length is inversely proportional to bond order, therefore, bond length will be in the order:
N22- > N2– = N2+ > N2
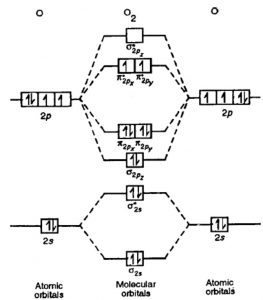
14) O2
The electronic configuration of O2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))1 (π∗(2py))1
Nb=8 , Na=4
Bond order= 2
The bond order of 2 justifies the presence of double bond in O2 molecule.
The presence of 2 unpaired electrons makes the molecule paramagnetic.
15) O2+
The electronic configuration of O2+ is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (π∗(2py))1
Nb= 8, Na= 3
Bond order=2.5
The presence of unpaired electron makes the molecule paramagnetic.
16) O2– ion
The electronic configuration of O2– is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))2 (π∗(2py))1
Nb= 8, Na= 5
Bond order=1.5
The presence of unpaired electron makes the molecule paramagnetic.
17) O22- ion
The electronic configuration of O2– is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))2 (π∗(2py))2
Nb= 8, Na= 6
Bond order=1
The presence of no unpaired electron makes the molecule diamagnetic.
As bond dissociation energies are directly proportional to the bond order, therefore, the dissociation energies of these molecular species are in the order:
O2+ > O2> O2– > O2 2-
As bond length is inversely proportional to bond order, therefore, bond length will be in the order:
O2 2- > O2– > O2 > O2 +
18) Fluorine molecule (F2)
The electronic configuration of O2 is KK (σ(2s))2 (σ∗(2s))2 (π(2px))2 (π(2py))2 (σ(2pz))2 (π∗(2px))2 (π∗(2py))2
Nb= 8, Na= 6
Bond order=1
The presence of no unpaired electron makes the molecule diamagnetic.
Thanks.it was really helpful
I want to a note for this. Chapter.plz send me tha note.
Diagram for O2+ is wrong because 2p atomic orbital of 2nd O atom will have only 3 e-.
Good examples
Thanks for the correction and letting us know, we have made the changes, keep reading this website.
It was really helpful
I like it…..
I didn’t understand this before 1 week
Nice notes
We need notes lyk this,which is specific n appropriate for students with nice pictures
fine every student can understand easily
Nice explanation
Good job
hi nice explanation
Good explanation ✌️
Nice really helpful
It is really helpful
Nice explanation
Thank you.. Well done
I am very successful by reading this clear explanation .
THANK YOU
really helpful…….
It is well detailed and I found it extremely helpful.