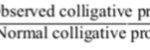Abnormal Molecular Masses The accurate values of molar masses can be obtained only if the following two conditions are met. (i) The solutions should be dilute The solutions used for measuring colligative properties must not be too concentrated. In the concentrated solutions, the particles begin to interact with each other as well as with the solvent. As a result, the vapour … [Read more...] about Abnormal Molar Masses
Solutions
Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure
Osmosis Consider an aqueous solution of sugar placed in an inverted thistle funnel having a semipermeable membrane (SPM) such as animal bladder or parchment paper, attached to its bottom. The thistle funnel is lowered into a beaker containing water. The membrane is such that it allows only the molecules of the solvent and not of the solute to pass through it. Thus, there … [Read more...] about Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure
Colligative Properties
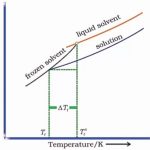
Colligative Properties The properties of the solutions which depend only on the number of solute particles but not on the nature of the solute are called Colligative properties. The four important colligative properties are: (i) Relative lowering in vapour pressure (ii) Elevation in boiling point (iii) Depression in freezing point (iv) Osmotic pressure. Relative … [Read more...] about Colligative Properties
Ideal and Non-Ideal Solution
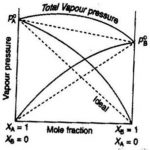
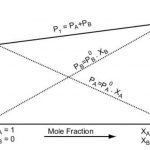
Ideal and Non-Ideal Solution The binary liquid-liquid solution may be classified into two types : (1) Ideal solutions (2) Non-ideal solutions 1) Ideal Solutions An ideal solution may be defined as the solution which obeys Raoult's law over the entire range of concentration. a) Such solutions are formed by mixing two components which are identical in molecular size, … [Read more...] about Ideal and Non-Ideal Solution
Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions
Vapour Pressure of Liquid When a liquid is allowed to evaporate in a closed vessel, part of the liquid evaporates and fills the available space with the vapours. Since the vapours leave the container, these get collected in the vapour state above the surface of the liquid. Due to vaporisation, liquid changes into vapours and level of liquid decreases. As the evaporation … [Read more...] about Vapour Pressure of Liquid Solutions