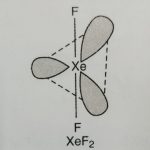
Compounds of Xenon (a) Xenon fluorides The three common fluorides are XeF2, XeF4, and XeF6 (1) Xenon difluoride, XeF2 It is prepared by heating a mixture of xenon and fluorine in the molecular ratio of 2:1 at 673 K in a sealed nickel vessel at 1 bar pressure. On cooling quickly a colourless solid XeF2 is formed. Xe + F2 → XeF2 ( Ni Vessel, 1 bar) (2:1 … [Read more...] about Compounds of Xenon and uses of Noble Gases
The p-Block Elements
Characteristics and Physical Properties of Group 18 Elements
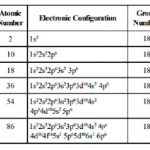
Group 18 The group 18 consists of elements helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe) and radon (Rn). These gases at ordinary temperature do not have chemical reactivity and therefore, these were called inert gases. Because of the low abundance of these gases on earth, they have also been called rare gases. Occurrence of Noble Gases Due to the inert … [Read more...] about Characteristics and Physical Properties of Group 18 Elements
Oxoacids of Halogens and Interhalogen Compounds
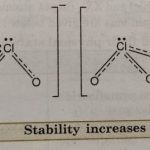
Oxoacids of Halogens Among the halogens, fluorine has very little tendency to form oxoacids due to its high electronegativity and small size. However, it forms one oxoacid HOF known as fluoric (I) acid or hypofluorous acid. The rest of the halogens form four series of oxoacids, HOX, HXO2, HXO3, and HXO4. Most of these cannot be isolated in pure state. They are stable only in … [Read more...] about Oxoacids of Halogens and Interhalogen Compounds
Hydrogen Chloride
Hydrogen Chloride Preparation Laboratory Preparation of Hydrogen Chloride Hydrogen chloride is prepared by heating sodium chloride with concentrated sulphuric acid. NaCl + H2SO4 -----> NAHSO4 + HCl NaCl + NaHSO4 ------> Na2SO4 + HCl HCl gas is dried by passing through concentrated sulphuric acid. On Industrial scale hydrochloric acid is manufactured by heating a … [Read more...] about Hydrogen Chloride
Chlorine
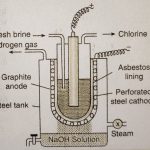
Chlorine Occurrence Chlorine is very reactive and does not occur in nature in free state. It occurs mostly as chlorides of sodium and other alkali and alkaline earth metals. The most abundant compound of chlorine is sodium chloride (rock salt) and occurs in extensive evaporite deposits, saline lakes and brines and in the ocean. Other sources of chlorine are sylvine (KCl), … [Read more...] about Chlorine