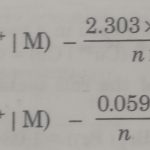Corrosion When metals are exposed to atmospheric conditions, they react with air or water in the environment to form undesirable compounds (usually oxides). This process is called corrosion. The least active metals such as gold, platinum and palladium are attacked by environment. For example: Silver tarnishes, copper develops a green coating, lead or stainless steel lose … [Read more...] about Corrosion
Electro Chemistry
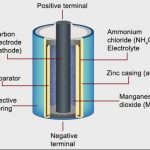
Batteries
Electrochemical cell vs Electrolytic cell Electrochemical cell Electrolytic cell It is a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. It is a device which converts electrical energy into chemical energy. The redox reaction is spontaneous and is responsible for the production of electrical energy. The redox reaction is non-spontaneous and … [Read more...] about Batteries
Products of Electrolysis
Products of Electrolysis During electrolysis, the reactions occurring at the electrodes are oxidation and reduction reactions. The products of electrolysis depend on the nature of material being electrolysed and the types of electrodes being used. If the electrode is inert such as gold or platinum, it does not take part in the chemical reaction and acts only as a source or … [Read more...] about Products of Electrolysis
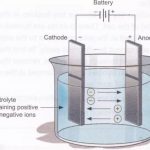
Electrolytic Cells
Electrolytic cells Electrolysis is a process in which chemical changes take place by the passage of electric current. The cells used to carry out electrolysis are electrolytic cells Process of electrolysis 1) The process of electrolysis is carried out by taking the solution of an electrolyte in a suitable vessel. The vessel is called electrolytic tank. 2) It is made … [Read more...] about Electrolytic Cells
Nernst Equation
Nernst Equation The standard electrode potentials are measured in their standard states when the concentration of the electrolyte solutions are fixed as 1M and temperature is 298 K. In actual practice electrochemical cells do not have always fixed concentration of the electrolyte solutions. The electrode potentials depend on the concentration of the electrolyte solutions. … [Read more...] about Nernst Equation