Reactive Intermediates Most of the organic reactions occur through the involvement of certain chemical species. These are generally short lived and highly reactive and hence cannot be isolated. These short lived highly reactive chemical species through which the majority of the organic reactions occur are called reactive intermediates. Example: Carbocation, carboanion, free … [Read more...] about Carbocations
Class 11
Hyperconjugation Effect
The inductive effect of the alkyl group on a saturated carbon chain follows the order: (CH3)3C > (CH3)2CH- > CH3CH2-> CH3- When an alkyl group is attached to an unsaturated system such as double bond or a benzene ring, the order of inductive effect is actually reversed.This effect is called hyperconjugation effect or Baker-Nathan effect. Resonance effect … [Read more...] about Hyperconjugation Effect
Resonance or mesomerism
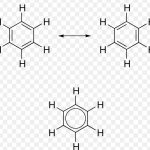
The phenomenon of resonance is said to occur whenever for a molecule we can write two or more Lewis structure which differ in the position of electrons but not in the relative position of atoms. The various Lewis structure, none of which is capable of describing all the known properties of the compound are called canonical or resonance structures. The actual structure of … [Read more...] about Resonance or mesomerism
Inductive and Electromeric Effect
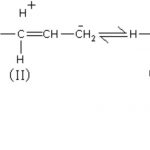
Fission of a covalent bond Homolytic fission If a covalent bonds breaks in such a way that each atom takes away one electron of the shared pair, it is called homolytic or symmetrical fission. Homolytic fission is usually indicated by a fish arrow which denotes a one electron displacement. For Ex: The neutral chemical species which contain an odd or unpaired … [Read more...] about Inductive and Electromeric Effect
Electrophiles and Nucleophiles
In an organic reaction, the organic compound called the substrate reacts with a suitable attacking species called the reagent to form products. The formation of products may occur either directly from the reactants through a transition state or through the formation of one or more intermediates. Sometimes by products are also formed from intermediates. Organic … [Read more...] about Electrophiles and Nucleophiles