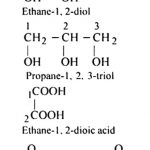
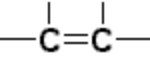Organic compounds which contain two or more functional group are called polyfunctional compounds. The IUPAC names are obtained as follows: (1) Principal functional group : When an organic compound contains two or more different functional groups, one of the functional is selected as the principal functional group while all other groups are treated as … [Read more...] about Rules For IUPAC Nomenclature Of Polyfunctional Compounds
Chemistry
Rules For IUPAC Nomenclature Of Compounds Containing Functional group, Multiple Bond And Substituents
(1) Parent chain : Select the longest possible chain of carbon atoms containing the functional group and the maximum number of multiple bonds as the parent chain without caring whether it also denotes the longest possible carbon chain or not. (2) Lowest locant rule for the functional group: Number the parent chain in such a way that the functional group gets the … [Read more...] about Rules For IUPAC Nomenclature Of Compounds Containing Functional group, Multiple Bond And Substituents
Rules For IUPAC Nomenclature Of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
1. The parent chain must contain the multiple bond regardless of the fact whether it also denotes the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms or not. 2 If both double and triple bonds are present, the numbering of the parent chain should always be done from that end which is nearer to the double bond or triple bond , i.e. the lowest set of locant rule for the multiple … [Read more...] about Rules For IUPAC Nomenclature Of Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
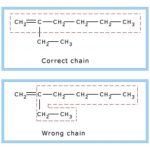
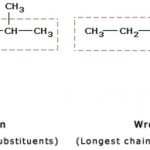
Rules for IUPAC nomenclature of Branched chain alkanes
Longest chain rule: Select the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms. This is called the parent chain while all other carbon atoms which are not included in the parent chain are called branch chain or side chains or substituent.it may be noted that the longest chain may or may not be straight but it must be continuous. 2) Rule for larger number of side chain : If two … [Read more...] about Rules for IUPAC nomenclature of Branched chain alkanes
Functional Or Characteristic Group
Hydrocarbons are the parent organic compounds. All other compounds are considered to have been derived from them by replacing one or more of their hydrogen atoms by some other more reactive atom or group. R—H --------> R—G -H and +G Each organic molecule consist of two parts i.e. R and G. The first part, i.e. R denotes the carbon -hydrogen framework of the … [Read more...] about Functional Or Characteristic Group