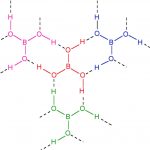
Preparation of Boric Acid 1) From Borax Boric acid is obtained by treating a hot concentrated solution of borax with hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid. The resulting solution on concentration and cooling gives crystals of boric acid. Na2B4O7 + 2 HCl + 5 H2O → 4 H3BO3 + 2 NaCl Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5 H2O → 4 H3BO3 + 2 Na2SO4 2) By hydrolysis of boron compounds Boric acid … [Read more...] about Boric Acid
Chemistry
Anomalous Properties of Boron
Boron, the first member of group 13 elements, shows anomalous behaviour and differ from rest of the members of its family. The main reason for this difference are : 1) exceptionally small atomic and ionic size. 2) high ionization enthalpy. 3)absence of d orbital in its valence shell. Important properties in which boron differ from the rest of the members of its … [Read more...] about Anomalous Properties of Boron
Physical Properties Of Boron Family
The group 13 of the periodic table consists of the elements Boron, aluminium, gallium indium, thallium and the newly discovered elements ununtrium(uut). Occurrence Boron occurs in two forms . Its abundance in the earth's crust is very low. Boron mainly occur as: 1) Orthoboric acid, H3BO3 2)Borax, Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O or Na2B4O7.10H2O 3)kernite, … [Read more...] about Physical Properties Of Boron Family
General Characteristics of p-Block elements
Elements in which the last electron enters any one of the three p orbitals of their respective outermost shells are called p block elements. A p-subshell has three degenerate p-orbitals, each of which can accommodate 2 electrons, therefore, in all, there are six groups of p-block elements i.e. group 13,14,15, 16, 17 and 18 each containing 6 elements. The atoms of elements … [Read more...] about General Characteristics of p-Block elements
Silicon Tetrachloride
Preparation Silicon tetrachloride is prepared by heating either silicon or silicon carbide with chloride. Si (s) + 2 Cl2 (g) ------> SiCl4 (l) SiC(s) + 4 Cl2 (g) -------> SiCl4 (l) + CCl4 (l) Properties 1) It is a volatile liquid , b.p. 330.57 K. 2) Hydrolysis Hydrolysis of SiCl4 gives silicic acid , Si(OH)4 which upon further heating undergoes … [Read more...] about Silicon Tetrachloride