A large number of silicate minerals exist in nature. Some of the important minerals are : feldspar i.e. Albite
NaAlSi3O8, zeolites e.g. chabazite Ca2[(AlO2)4 (SiO2)8.H2O, micas [KAl2(Si3AlO10(OH)2] and asbestos [Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4].
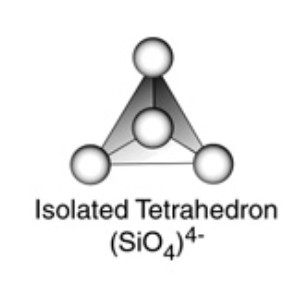
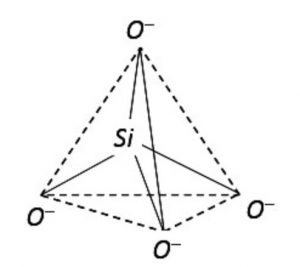
The basic structural unit in silicate is the SiO44- terahedra.
The two important man-made silicates are glass and cement.
Silicates are the compounds in which the anion present are either discrete SiO44- tetrahedra or a number of such units joined together through corners.
Types Of silicates
Silicates are classified into the following different types depending upon the number of corners of SiO44- tetrahedron shared with other tetrahedra through oxygen atoms. The negative charge on silicate structure is neutralized by positively charged metal ion.
1) Orthosilicates : These are simple silicates containing discrete SiO44- tetrahedra i.e. there is no sharing of corners with the other.
For examples : Zircon (ZrSiO4) , Forestrite (Mg2SiO4) , wellimite (Zn2SiO4) , Phenacite (Be2SiO4).
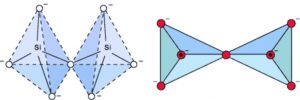
2) Pyrosilicates : When two SiO44- tetrahedra share one corner, Si2O7 6- anion is formed. Silicates containing this anion are called pyrosilicates. The structures possessed by them are also called island structures.
For example : Thortveitite Sc2(Si2O7) , Hemimorphite Zn3(Si2O7)Zn(OH)2·H2O
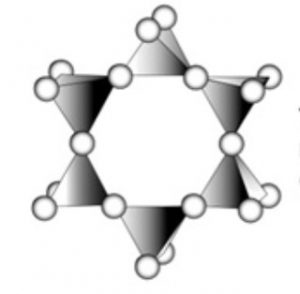
3) Cyclic or ring silicates : If two oxygen atoms per tetrahedra are shred to form closed rings such that the structure with the general formula (SiO32-)n or (SiO3)n2n- are obtained, the silicate containing these anions are called cyclic silicates.
For example: Si3O96- , Si6O1812- , Wollastonite (Ca3Si3O9) , Beryl (Be3Al2Si6O18)
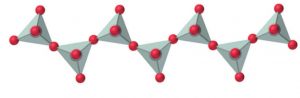
4) Chain silicates : If two oxygen atoms per tetrahedron are shred such that a linear single strand chain of the general formula (SiO32-)n or (SiO3)n2- is formed, then the silicates containing these anions are called chain silicates.
For example: Spodumene ( LiAl(SiO3)2) , Diopside (CaMg(SiO3)2)
If two chains are cross linked, the resulting double-stranded silicates having the formula [(Si4O11)n6-] are called amphiboles.
For ex: Tremolite ( Ca2Mg5(Si4O11)(OH)2) , asbestos (CaMg3O(Si4O11)
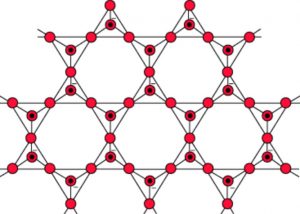
5) Sheet silicates: The sharing of three corners results in an infinite two dimensional sheet structure of the formula (Si2O5)n2n- or (Si2O52-)n
Silicates containing these anions are called sheet silicates.
6) Three dimensional silicates: If all the four corners are shared with other tetrahedra, three-dimensional structure network is obtained.
For example: quartz, tridymite and cristobalite
Zeolites
If some of the Silicon atoms in a three-dimensional network silicates are replaced by Al3+ ions, the overall structure thus obtained carries a negative charge and is called and aluminosilicates. Therefore to balance the negative charge ,some cations such as Na+ , K+ and Ca2+ are incorporated into structure.
Such three dimensional aluminosilicates are called feldspar (KalSi3O8) and zeolites(NaAlSi2O6·H2O).
Zeolites are widely used as a catalyst in petrochemical industries for cracking of hydrocarbons and isomerisation.
For example: ZSM-5 is used to convert alcohols directly into gasoline. Hydrated zeolites called permutit are used as ion exchangers in softening of hard water.
Thank you sooo much.
It was very helpfull……each type is explained so well.