A large number of silicate minerals exist in nature. Some of the important minerals are : feldspar i.e. Albite NaAlSi3O8, zeolites e.g. chabazite Ca2[(AlO2)4 (SiO2)8.H2O, micas [KAl2(Si3AlO10(OH)2] and asbestos [Mg3(Si2O5)(OH)4]. The basic structural unit in silicate is the SiO44- terahedra. The two important man-made silicates are glass and cement. Silicates are … [Read more...] about Silicates
p-Block Elements
Silicones
Silicones are synthetic organosilicon polymers containing repeated R2SiO units held by Si-O-Si linkages. These compounds have general formula (R2SiO)n where R=methyl or aryl group. Preparation When methyl chloride reacts with silicon in the presence of copper as a catalyst at 570 K , various types of methyl substituted chlorosilanes of formula CH3SiCl3 , … [Read more...] about Silicones
Allotropes Of Carbon
The phenomenon of existence of an element in two or more forms which have different physical properties but identical chemical properties is called allotropy and the different forms are called allotropes. Carbon exists in 2 allotropic forms: 1) Crystalline 2) Amorphous Crystalline form of carbon: 4 allotropes of carbon having well defined crystal structure … [Read more...] about Allotropes Of Carbon
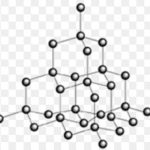
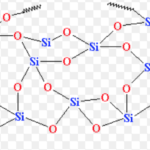
Silicon Dioxide, Silica
Silicon dioxide is known as Silica , SiO2. 95 % of the earth crust is made up of silica and silicates. It occurs in several crystallographic forms , namely , quartz , cristobalite and tridymite. These crystalline forms are interconvertible at suitable temperature. Structure Silicon dioxide is covalent , three- dimensional network solid in which each silicon atom is … [Read more...] about Silicon Dioxide, Silica
Carbon dioxide
Preparation 1) It is prepared by burning carbon, fossil fuels and other organic compounds in excess of air or oxygen. C (s) + O2 (g) -------> CO2 (g) C5H12 (g) + 8 O2 (g) --------> 5 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g) 2) In the laboratory , it is prepared by the action of dilute acids on carbonates. CaCO3 + 2 HCl -------> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O 3) Commercially , CO2 is … [Read more...] about Carbon dioxide