The simplest organic compound containing only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
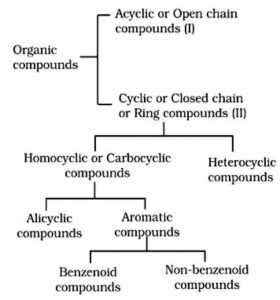
Organic compounds have been divided into two categories depending upon the nature of their carbon skeleton. These are:
(1) Acyclic or open chain compounds
(2) Cyclic or closed chain compounds
Acyclic or open chain compounds
These compounds contain open chains of carbon atoms in their molecules.The carbon chains may be either straight or branched chains.
(1) Straight chain compounds
n-butane CH3—CH2—CH2—CH3
But-2-ene
But-2-yne
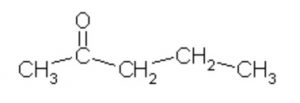
Pentanone
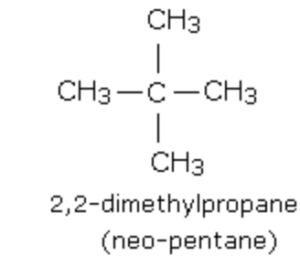
(2) Branched chain compounds
Open chain compounds are also called aliphatic compounds since the earlier compounds of this class were obtained either from animals or vegetable fats.
Cyclic or closed chain or ring compounds
These compounds contain one or more closed chains or rings of atoms in their molecules.
Depending upon the constitution of the ring, these are further divided into following two categories:
(1) Homocyclic or carbocyclic compounds: These compounds contain rings which are made up of only one kind of atoms i.e. carbon atoms.These are further divided into the following two sub-classes.
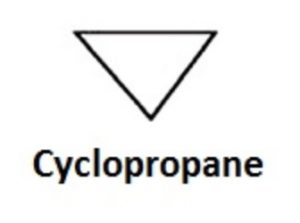
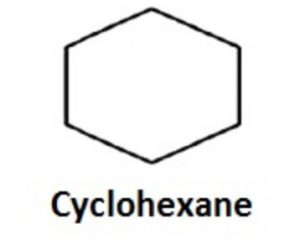
(a) Alicyclic compounds
Carbocyclic compounds which resemble aliphatic compounds in most of their properties are called aliphatic compounds.
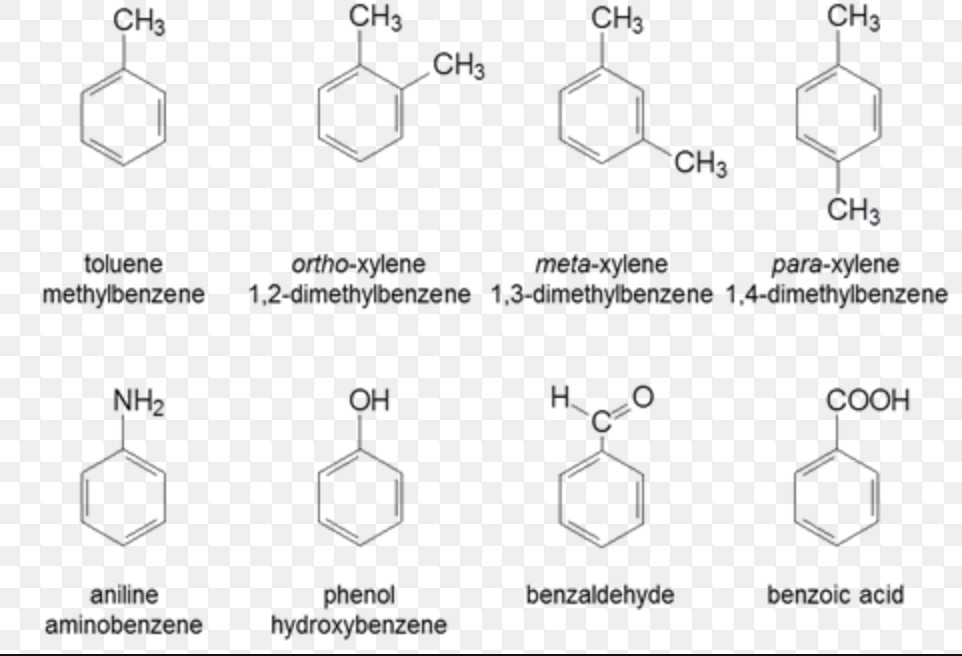
(b) Aromatic compounds
These are special type of cyclic unsaturated compounds.The name aromatic for this class of cyclic unsaturated compounds has been derived from the Greek word aroma meaning fragrant smell since most of the compounds discovered has pleasant smell.
They are of two types:
(1) Benzenoid aromatic compounds: Organic compounds containing one or more fused or isolated benzene rings and their functionalized derivatives are called benzenoid aromatic compounds.
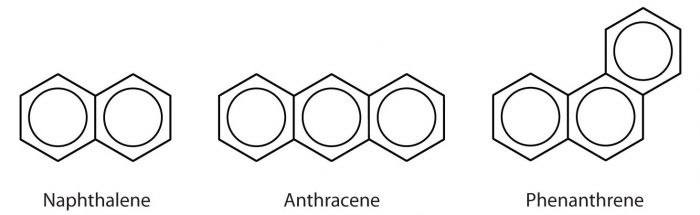
Depending upon the number of benzene rings fused together, benzenoid compounds may be monocyclic, bicyclic, tricyclic aromatic compounds.
(1) Monocyclic aromatic compounds
(2) Bicyclic or tricyclic aromatic compounds
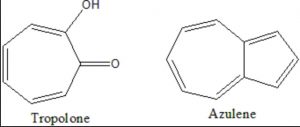
(2) Non-benzenoid aromatic compounds
Aromatic compounds which do not contain a benzene ring but instead contain other highly unsaturated rings are called non-benzenoid aromatic compounds.
Examples:
Heterocyclic compounds
Cyclic compounds containing one or more heteroatoms in their rings are called heterocyclic compounds.
The heteroatoms found in these compounds are oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur, boron, silicon etc.
They are further classified into the following two categories:
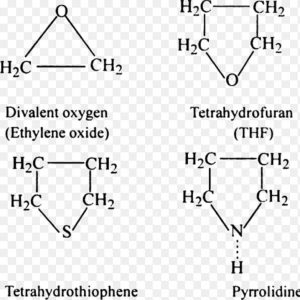
(1) Alicyclic heterocyclic compounds: Aliphatic cyclic compounds containing one or more heteroatoms in their rings are called alicyclic heterocyclic compounds.
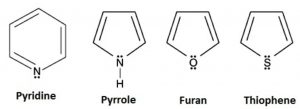
(2) Aromatic heterocyclic compounds
Aromatic cyclic compounds containing one or more heteroatoms in their molecules are called aromatic heterocyclic compounds.
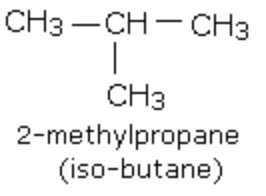
I like this content because it has really benefited me.
Thank you very much
I am interested in organic chemistry and i very like this classification and contents.
Thanks.
Thank you very much
Thank you for this notes because it was helpful for me in my project
This is the best note for classification of organic chemistry
well thought classification