NCERT Answers for Class 6 Maths
Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Exercise 14.1
Page 276
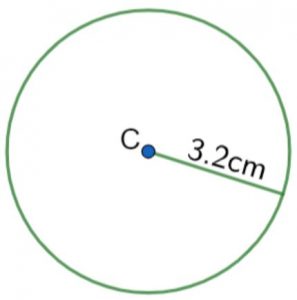
Ex 14.1 Class 6 Maths Question 1. Draw a circle of radius 3.2 cm.
Answer
Step 1: Focus a center point as O.
Step 2: Raise the compass to 3.2 cm radius.
Step 3: Center O with the compass needle.
Step 4: Hold compass to takes one full round with pencil. The resulting figure is the appropriate 3.2 cm circle.
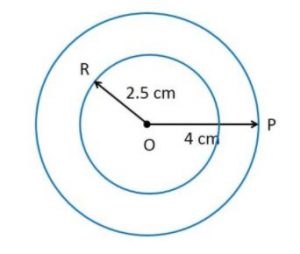
Ex 14.1 Class 6 Maths Question 2. With the same centre O, draw two circles of radii 4 cm and 2.5 cm.
Answer
Step 1: Take O centre and open up to 4 cm.
Step 2: Draw a circle with the needle at O.
Step 3: Take the same O centre and raise the compass up to 2.5 cm.
The figure indicates two circles with the same middle.
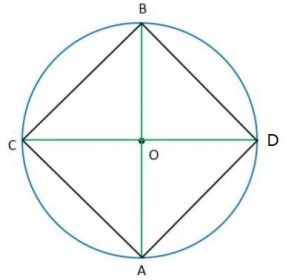
Ex 14.1 Class 6 Maths Question 3. Draw a circle and any two of its diameters. If you join the ends of these diameters, what is the figure obtained? What figure is obtained if the diameters are perpendicular to each other? How do you check your answer?
Answer
Step 1:
Draw a circle with centre O with suitable radius.
Step 2:
AB and CD may be any two diameters.
Step 3:
On joining the end points of the diameters, we get a quadrilateral ACBD.
Step 4:
We note that OA = OB = OC = OD [Same radius]
and AC = DB, AD = BC
∠A = ∠C = ∠B = ∠D = 90°
Thus ACBD is a rectangle.
Again if the diameters are perpendicular to each other then on measuring,
we get AC = DB = AD = BC
Thus, ACBD is a square.
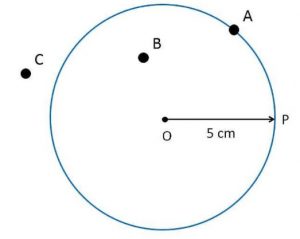
Ex 14.1 Class 6 Maths Question 4. Draw any circle and mark points A, B and C such that
(a) A is on the circle. (b) B is in the interior of the circle.
(c) C is in the exterior of the circle.
Answer
Draw a circle with centre O and a suitable radius.
Here
(a) A is on the circle.
(b) B is in the interior of the circle.
(c) C is in the exterior of the circle.
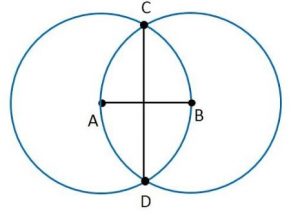
Ex 14.1 Class 6 Maths Question 5. Let A, B be the centres of two circles of equal radii; draw them so that each one of them passes through the centre of the other. Let them intersect at C and D. Examine whether AB and CD are at right angles.
Answer
Draw two circles of equal radii taking A and B as their centre such that one of them passes through the centre of the other. They intersect at C and D. Join AB and CD. Yes, AB and CD intersect at right angle as ∠COB is 90°
Leave a Reply