NCERT Answers for Class 6 Maths
Chapter 14 Practical Geometry Exercise 14.5
Page 286
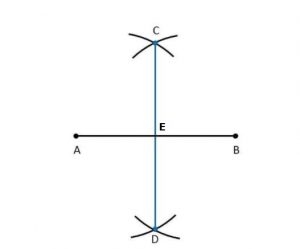
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 1. Draw AB of length 7.3 cm and find its axis of symmetry.
Answer
Step 1: Draw AB = 7.3 cm
Step 2: Taking A and B as centre and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which intersect each other at C and D.
Step 3: Join C and D to intersect AB at E. Thus, CD is the perpendicular bisector or axis of symmetry of AB.
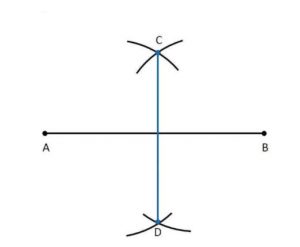
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 2. Draw a line segment of length 9.5 cm and construct its perpendicular bisector.
Answer
Step 1: Draw a line segment AB =9.5 cm
Step 2: With centres A and B and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which meet each other at C and D.
Step 3: Join C and D to meet AB.
Thus, CD is the perpendicular bisector of AB.
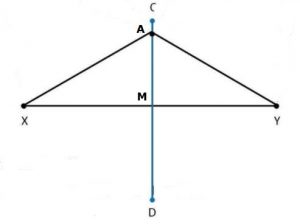
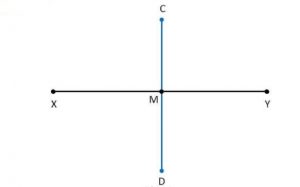
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 3. Draw the perpendicular bisector of XY whose length is 10.3 cm. (a) Take any point P on the bisector drawn. Examine whether PX = PY.
Answer
Step 1: Draw a line segment XY = 10.3 cm.
Step 2: With centre X and Y and radius more than half of XY, draw two arcs which meet each other at C and D.
Step 3: Join C and D which meets XY.
Step 4: Take a point A on CD.
(a) On measuring, AX = AY = 5.6 cm.
(b) On measuring, MX = MY = ½ XY = 5.15 cm.
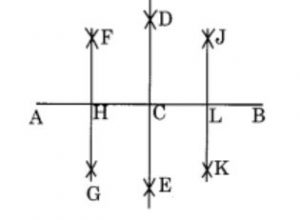
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 4. Draw a line segment of length 12.8 cm. Using compasses, divide it into four equal parts. Verify by actual measurement.
Answer
Step 1: Draw a line segment AB = 12.8 cm
Step 2: With centre A and B and radius more than half of AB, draw two arcs which meet each other at D and E.
Step 3: Join D and E which meets AB at C which is the midpoint of AB .
Step 4: With centre A and C and radius more than half of AC, draw two arcs which meet each other at F and G.
Step 5: Join F and G which meets AC at H which is the midpoint of AC .
Step 6: With centre C and B and radius more than half of CB, draw two arcs which meet each other at J and K.
Step 7: Join J and K which meets CB at L which is the midpoint of CB .
Thus, on measuring, we find AH = HC = CL = LB = 3.2 cm.
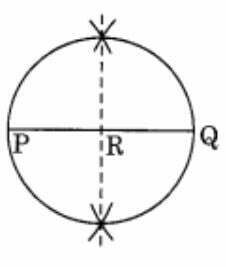
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 5. With PQ of length 6.1 cm as diameter, draw a circle.
Answer
Step1: Draw PQ = 6.1 cm
Step 2: Draw a perpendicular bisector of PQ which meets PQ at R i.e. R is the midpoint of PQ .
Step 3: With centre R and radius equal to RP , draw a circle passing through P and Q.
Thus, the circle with diameter PQ = 6.1 cm is the required circle.
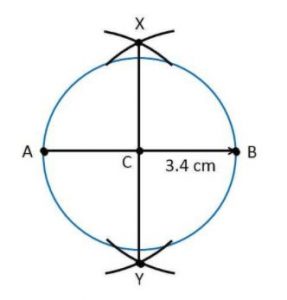
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 6. Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm. Draw any chord AB . Construct the perpendicular bisector of AB and examine if it passes through C.
Answer
Step I: Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm.
Step II: Draw any chord AB .
Step III : Draw the perpendicular bisector of AB which passes through the centre C.
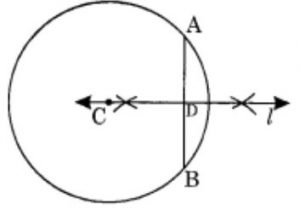
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 7. Repeat Question 6, if AB happens to be a diameter.
Answer
Step 1: Draw a circle with centre C and radius 3.4 cm.
Step 2: Draw a diameter AB of the circle.
Step 3: Draw a perpendicular bisector of AB which passes through the centre C and on measuring, we find that C is the midpoint of AB .
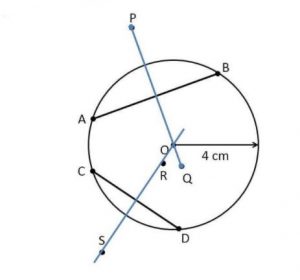
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 8. Draw a circle of radius 4 cm. Draw any two of its chords. Construct the perpendicular bisectors of these chords. Where do they meet?
Answer
Step 1: Draw a circle with centre 0 and radius 4 cm.
Step 2: Draw any two chords AB and CD of the circle.
Step 3 : Draw the perpendicular bisectors of AB and CD i.e. P and S.
Step 4 : On producing the two perpendicular bisectors meet each other at the centre O of the circle.
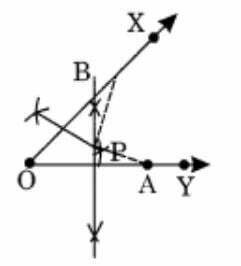
Ex 14.5 Class 6 Maths Question 9. Draw any angle with vertex O. Take a point A on one of its arms and B on another such that OA = OB. Draw the perpendicular bisectors of OA and OB . Let them meet at P. Is PA = PB ?
Answer
Step 1: Draw an angle XOY with O as its vertex.
Step 2: Take any point A on OY and B on OX, such that OA + OB.
Step 3: Draw the perpendicular bisectors of OA and OB which meet each other at a point P.
Step 4: Measure the lengths of PA and PB . Yes, PA = PB .
Leave a Reply