Contents
Modes of Occurrence of Elements
The elements generally occur in the free state (called native state) or in the combined state. This is mainly because of different chemical reactivities of elements.
1) Native State
The elements which have very low reactivity and are not attacked by oxygen or air, moisture, carbon dioxide or other non-metals occur in the free state, called native state.
For example: carbon, sulphur, nitrogen, noble gases, metals like gold, silver, platinum, etc. occur in nature in the native state.
Therefore, these elements are also called native elements.
2) Combined State
The elements which are reactive and have a tendency to combine with oxygen or air, moisture, carbon dioxide and non-metals like carbon, nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, arsenic, halogen, etc. occur in the combined state.
These elements occur in the crust of the earth in the form of their compounds. In the combined state the non-metals are usually found in the reduced form and the metals in the oxidised form.
Among the metals, only a few metals, such as silver, gold, platinum, etc. occur in native state. Non-metals such as carbon and sulphur also occur in native state as well as in combined state.
Abundance of Elements
Most metals occur in the combined states. The most common forms of metals in the combined state are oxides, carbonates, sulphides, silicates, halides, sulphates, arsenides, phosphate, etc.
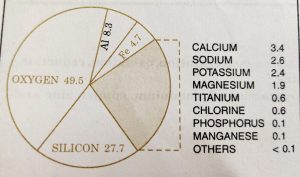
Among metals, aluminium is the most abundant. It is the third most abundant element in earth’s crust (8.31% by wt). It occurs widely as a constituent of rocks and soils. It is a major component of many igneous minerals including mica and clay.
Iron is the second most abundant metal in earth’s crust. It forms a variety of compounds which have various important uses. This makes iron a very important element. Iron is also one of the essential elements in biological systems.
Mineral and Ores
Most of the metals have a tendency to react with moisture, oxygen, sulphur, halogens, etc. and therefore, occur in the crust of the earth in the form of their compounds such as oxides, sulphides, halides, silicates, carbonates, nitrates, phosphates, etc.
The naturally occurring chemical substances in which metals occur in the earth’s crust are called minerals. The mineral, from which the metal can be economically and conveniently extracted, is called an ore.
The type of mineral from which the metal can be extracted is decided on the basis of
profitability.
For example: Metals are not generally extracted from silicate minerals because of the difficulties during extraction.
2) Aluminium occurs in the earth’s crust in the form of two minerals, bauxite (Al2O3.2H20)
and clay (Al2O3.2SiO2.2H20). Aluminium can be conveniently and economically extracted from bauxite, while it has not been possible to extract aluminium from clay by some easy and cheap method.
3) The main minerals of copper are copper glance (Cu2S), cuprite (Cu2O), copper pyrites (CuFeS2), malachite [CuCO3 Cu(OH)2], etc. but copper can be conveniently extracted from copper pyrites. Therefore, the ore of copper is copper pyrites.
| Metal | Name | Composition |
| Aluminium | Bauxite | AlOx(OH)3-2x |
| Feldspar | KAlSiO8 | |
| Cryolite | Na3AlF6 | |
| Kaolinite | Al2(OH)4Si2O5 | |
| Iron | Haematite | Fe2O3 |
| Magnetite | Fe3O4 | |
| Siderite | FeCO3 | |
| Iron Pyrites | FeS2 | |
| Limonite | Fe2O3.3H2O | |
| Copper | Copper glance | Cu2S |
| Copper pyrite | CuFeS2 | |
| Malachite | CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 | |
| Cuprite | Cu2O | |
| Azurite | 2 CuCO3. Cu(OH)2 | |
| Zinc | Zinc blende | ZnS |
| Calamine | Zn2SiO4 | |
| Zincite | ZnO.Fe2O3 | |
| Willemite | ZnO.Fe2O3 | |
| Manganese | Pyrolusite | MnO2 |
| Braunite | Mn2O3 | |
| Calcium | Limestone | CaCO3 |
| Gypsum | CaSO4.2H2O | |
| Magnesium | Magnesite | MgCO3 |
| Dolomite | CaCO3.MgCO3 | |
| Lead | Galena | PbS |
| Cerrusite | PbCO3 | |
| Mercury | Cinnabar | HgS |
Please upload the p block elements
It is very useful for me