Characteristics of Actinides The fourteen elements which follow actinium from thorium (Z = 90) to lawrencium (Z = 103) in the periodic table are called actinides. They involve the filling of 5f orbitals. 1) Electronic Configurations The actinides involve the filling of 5f-subshell. Actinium has the electronic configuration 6d17s2. From thorium ( Z= 90) onwards, 5f … [Read more...] about Characteristics of Actinides
Class 12
Lanthanoid Contraction
Lanthanoid Contraction In the lanthanoid series, with increasing atomic number, the atomic and ionic radii decrease from one element to another but the decrease is very small. Far example : On moving from Ce to Lu, the atomic radii decrease from 183 pm to 173 pm and the decrease is only 10 pm. The ionic radii decrease from 103 pm to 85 pm on moving from Ce3+ to Lu3+ … [Read more...] about Lanthanoid Contraction
Chemical Reactivity, Solubility and Basic Character of Lanthanoids
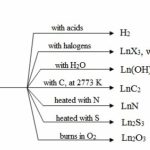
Chemical Reactivity All the lanthanoids are highly electropositive metals and have almost similar chemical reactivity. This is due to the fact that the lanthanoids differ only in the number of 4f-electrons. Since these electrons are very effectively shielded from interaction with other elements by the overlying 5s, 5p and 6s-electrons, they show very little differences in … [Read more...] about Chemical Reactivity, Solubility and Basic Character of Lanthanoids
Potassium Permanganate
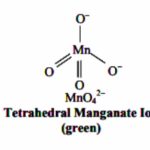
Potassium Permanganate, KMnO4 It is prepared from mineral pyrolusite (MnO2) by following steps : 1) Conversion of Pyrolusite ore to Potassium Manganate The pyrolusite is fused with caustic soda or potassium carbonate in the presence of air or oxidising agent such as potassium nitrate or potassium chlorate to give a green mass due to the formation of potassium manganate. 2 … [Read more...] about Potassium Permanganate
Characteristics of Lanthanoids
f-block elements The elements in which the last electron enters the f-orbital of the atoms are called f-block elements. In these elements, the last electron is added to the third to the outermost (called antepenultimate) energy level i.e. (n-2)f. Their general electronic configuration is (n-2)f1-14 (n-1)d0-1ns2 These elements are also called inner transition … [Read more...] about Characteristics of Lanthanoids