Contents
Nernst Equation
The standard electrode potentials are measured in their standard states when the concentration of the electrolyte solutions are fixed as 1M and temperature is 298 K. In actual practice electrochemical cells do not have always fixed concentration of the electrolyte solutions. The electrode potentials depend on the concentration of the electrolyte solutions.
Nernst gave a relationship between electrode potentials and the concentration of electrolyte solutions known as Nernst equation.
For a general electrode reaction,
Mn+(aq) + ne¯ ——-> M(s)
the Nernst equation is
Where E (Mn+|M) = Electrode potential
Eø (Mn+|M) = Standard Electrode potential
R= Gas constant
T =Temperature
F = Faraday of electricity
n= Number of electrons gained during the electrode reaction.
[Mn+ (aq)] = Molar concentration of ions
[M] = Molar concentration of metal
Substituting the values of R (8.314 JK-1 mol-1), T (298 K), and F (96500 coulombs), the Nernst equation at 25°C becomes
The concentration of the solid phase, [M(s)] is taken to be unity.
The above equation may also be written as:
Application Of Nernst Equation
1) Calculation of cell potential using Nernst Equation
Considering a Daniel Cell in which concentration of the solution may not be 1 M.The cell is : Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu
the e..m.f. of the cell is :
Ecell = Ecathode– Eanode
= E (Cu2+| Cu ) – E ( Zn2+ |Zn)
The electrode reactions are :
Zn(s) ——-> Zn2+ (aq) + 2e¯
Cu2+ (aq) + 2e¯ ——> Cu (s)
The electrochemical cell reaction is:
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) ——> Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
The electrode potential for the two electrodes can be calculated by using Nernst equation:
Now Eø (Cu2+| Cu ) – Eø ( Zn2+ |Zn) = Eøcell and the concentration of solids is taken as unity so that [Zn] =1 and [Cu]=1
The valencies of zinc and copper are the same i.e. n=2.
Consider an example in which the valencies of the two metals used in the two half cells are not same.
Cu| Cu2+(aq) || Ag+(aq) |2Ag(s)
The cell reaction is :
Cu(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) ——> Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
The EMF of a cell,
Ecell = Ecathode– Eanode
Two electrons are released by one copper atom but one electron is accepted by Ag+ according to the reaction.
Cu(s) ——-> Cu2+ (aq) +2e¯
2Ag+ (aq) +2e¯ ———>2 Ag(s)
The electrode potential of two electrodes may be written according to Nernst equation as:
Electrode potential for silver electrode ,
Some examples of Nernst Equation for cells
1) Al|Al3+ (aq) || Ni2+ (aq) |Ni
The cell reaction is : 2 Al (s) + 3 Ni2+ (aq) ———-> 3 Ni(s) + 2 Al3+ (aq)
Here n=6
The Nernst equation is :
2) Mg |Mg2+(aq) || Ag+ (aq) |Ag
The cell reaction is : Mg(s) + 2 Ag+(aq) ———> Mg2+ (aq) +2 Ag(s)
Here n=2
The Nernst equation is :
3) Zn|Zn2+ (aq) || HCl |H2 , Pt
The cell reaction is : Zn(s) + 2 H+ (aq) ——-> Zn2+ (aq) + H2 (g)
Here n=2
The Nernst equation is :
2) Calculation of concentration of a solution of Half cell
When in a galvanic cell, all the concentrations except one are known, then the unknown concentration can be calculated by measuring the cell potential and using Nernst equation.
Equilibrium constant from Nernst Equation
The e.m.f. of the cell may be used to calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction.At equilibrium , the electrode potentials of two electrodes become equal so that e.m.f. of the cell is zero.
Zn(s) + Cu2+ (aq) ⇔ Zn2+ (aq) + Cu (s)
The concentration of Zn2+ (aq) and Cu2+ (aq) are equilibrium concentration and the equilibrium constant , Kc is
Electrochemical Cell and Gibbs energy of the Reaction
In electrochemical cells, the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy. The cell potential is related to Gibbs energy change.
In an electrochemical cell, the system does work by transferring electrical energy through an electric circuit.
ΔrG = maximum work
For a reaction, occurring in an electrochemical cell whose electrodes differ in a potential by Ecell , the work done when amount of charge nF is pushed along by the potential of the cell is given by nFEcell so that
Maximum work = nFEcell
where F is the Faraday constant (the charge on one mole of electrons) and n is the number of moles of electrons transferred in them. When voltaic cell operates, work is done on the surroundings, as electrical energy flows through the external circuit. Such work by convention is taken as negative.
Thus,
ΔrGø = wmax = -nFEøcell
We use standard cell potential, Eøcell
Therefore
ΔrGø = -nFEøcell
where ΔrGø is the standard Gibbs energy for the reaction.
If the activity of all the reacting species is unity, then E=Eø and we have
ΔrGø = -nFEøcell
Thus, from the measurement of Eø we can calculate an important thermodynamic property. From the temperature dependence of Eø we can also calculate ΔrHø and ΔrSø
From the standard Gibbs energy, we can also calculate equilibrium constant by the equation:
Significance
The above equation helps us to predict the feasibility of the cell reaction. For a cell reaction to be spontaneous, ΔrG must be negative. This means that E must be positive for a spontaneous cell reaction.
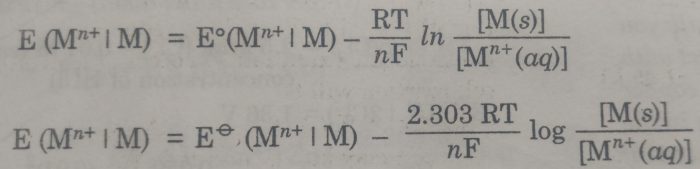
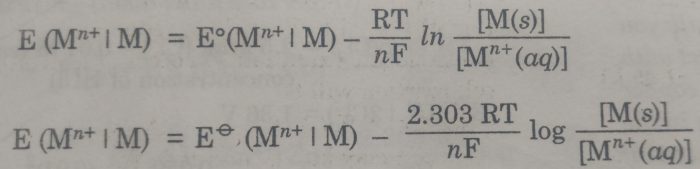
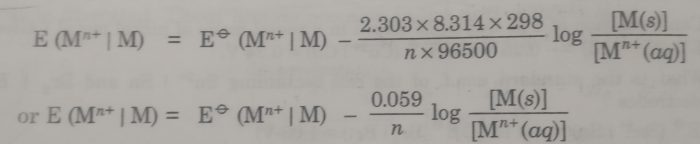
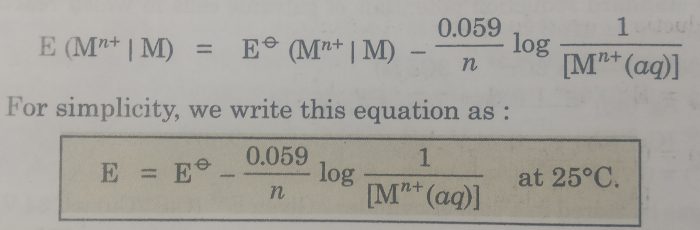

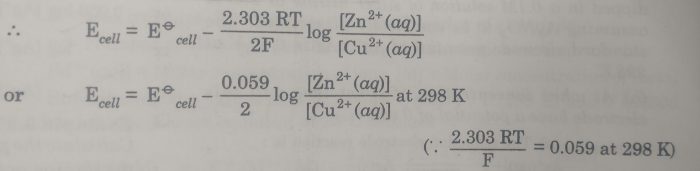

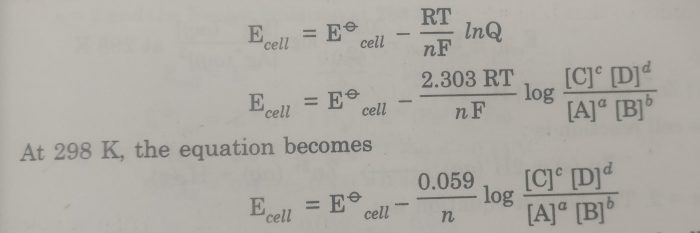
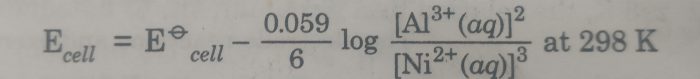
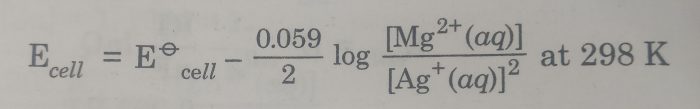
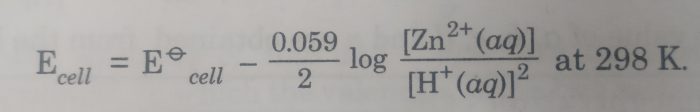
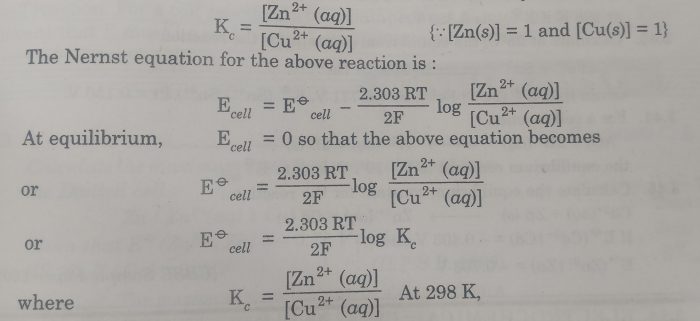
thank u mam
Tqs for this accurate information
It’s too easy to learn a topic completely and to take note of it tq