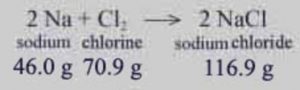
Law of Conservation of Mass
This Law was studied by French chemist Antoine lavoisier in 1789
This law states that
In all physical and chemical changes, the total mass of the reactants is equal to that of the products.
Or
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed.
This law is also called as the law of indestructibility of matter.
The mass and energy are interconvertible but the total sum of the mass and energy during any physical or chemical change the names constant.
Law of constant composition or definite proportions
This law was discovered by a French chemist J.L. Proust in 1799.
It states that
A chemical compound is always found to be made up of the same elements combined together in the same fixed proportion by mass.
For example : A pure water obtained from whatever source or any country will always be made up of only hydrogen and oxygen elements combined together in the same fixed ratio of 1 : 8 by mass.
A sample of carbon dioxide may be prepared in the laboratory (a) heating limestone (b) by burning coal in air (c) by the action of dilute hydrochloric acid on marble (d) by heating sodium carbonate.
It is found that carbondioxide is made up of same element ie. carbon and oxygen combine together in the same fixed ratio of 3:8 by mass.
Limitation
1) It Is not applicable if an element exist in different isotopes which may be involved in the formation of compound.
2) The elements may combine in the same ratio but the compounds formed may be different.
Law of multiple proportion
When two elements combine to form two or more chemical compounds ,then the masses of one of the elements which combined with a fixed mass of the other, bear a simple ratio to one another.
For Ex: Compounds of carbon and oxygen : Carbon combines with oxygen to form two compounds namely carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
In carbon dioxide, 12 parts by mass of carbon combine with 32 parts by mass of oxygen while in carbon monoxide, 12 parts by mass of carbon combine with 16 parts by mass of oxygen.
The masses of oxygen which combined with a fixed mass of carbon in carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide are 16 and 32. These masses of oxygen bear a simple ratio of 16:32 or 1:2 to each others.
For Ex: Compound of Sulphur and oxygen : The element sulphur also form two oxides Sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide.
In sulphur dioxide ,32 parts by mass of Sulphur combine with 32 parts by mass of oxygen but in sulphur trioxide 32 parts by mass of Sulphur combined with 48 parts by mass of oxygen. The masses of oxygen which combined with the fixed mass of sulphur in the two oxides are 32 and 48. These bear a simple ratio of 32 : 48 or 2 : 3 to each other.
Law of reciprocal proportion
This law was put forward by Richter in 1792.
It states that
The ratio of masses of 2 elements A and B which combines separately with a fixed mass of the third element C is either the same or some multiple of the ratio of the masses in which A and B combine directly with each other.
For example: The elements carbon and oxygen combine separately with the third element hydrogen to form methane and water and they combine directly with each other to form carbon dioxide.
In methane 12 parts by mass of carbon combine with 4 parts by mass of hydrogen. In water, 2 parts by mass of hydrogen combine with 16 parts by mass of oxygen. The masses of carbon and oxygen which combine with fixed mass of hydrogen are 12 and 32 i.e.. they are in the ratio 12 : 32 or 3 : 8.
In carbon dioxide 12 parts by mass of carbon combine directly with 32 parts by mass of oxygen ie they combined directly in the ratio of 12 : 32 or 3 : 8 which is the same as the first ratio.
Gay Lussac’s law of gaseous volume
When gases react together they always do so in volumes which bear a simple ratio to one another and to the volume of the products, if these are also gases, provided all measurements of volumes are done under similar conditions of temperature and pressure.
For Example : 1) Combination between hydrogen and chlorine: 1 volume of hydrogen and 1 volume of chlorine always combine to form two volumes of hydrochloric acid gas. The ratio between the volumes of the reactants and the product in this reaction is simple ie. 1 : 1 : 2.
2) Combination between nitrogen and hydrogen :One volume of Nitrogen always combines with 3 volume of hydrogen to form two volumes of ammonia. This reaction also indicate a simple ratio of 1: 3: 2 between the volume of the reactants and products.
Nice
thanks a lot, this has been so helpful to me
Thank you
Please make notes in form pdf
Thank you so much mam ,✌☺
Thanks….
It really helping…
Wonderful explained
good explanation
Thank you very much mam. This helped me a lot. Can I get a pdf of this?
Mam it is helpful to me
Thank mam ☝️
thanks helped me a lot
Thanks, learnt a lot
This is really helpful for my studies
Thank you so much
Thank you so much
Oh thank you so much your explanation is so clear. Make more notes on other topics please
This is very helpful for everyone
Thank you so much ma’am ❣️
Keep going ma’am.
You will shine on day