As an atom is so small a particle that it cannot be seen or isolated ,therefore it is impossible to determine the actual mass of a single atom by weighing it.
The problem was finally solved by Avogadro’s hypothesis. If equal volumes of two different gases are taken under similar conditions of temperature and pressure and then weighted, the ratio of their masses will be equal to the ratio of their single molecules. Thus, though the actual masses of the atoms could not be determined but their relative masses could be determined. If the atomic mass of the hydrogen is taken is 1 ,the relative atomic mass of oxygen is 16 .
Initially, the atomic masses of all the elements were obtained by comparing with the mass of hydrogen taken as 1 but by doing so, the atomic masses of most of the elements came out to be fractional.
Therefore carbon is taken reference for the determination of atomic masses.
Atomic mass of an element is the number of times an atom of that element is heavier than an atom of carbon taken as 12.
One atomic mass unit is equal to one twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon 12 isotope.
The atomic mass of an element is the average relative mass of its atoms as compared with an atom of carbon 12 taken as 12.
Fractional abundance of an isotope is the fraction of the total number of atoms that is comprised of that particular isotope.
Gram Atomic mass
The atomic mass of an element expressed in grams is called gram atomic mass.
For Ex: Atomic mass of oxygen is 16 amu.
Gram atomic mass of oxygen = 16 g.
Molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the number of times the molecule of the substance is heavier than one twelfth the mass of an atom of carbon -12.
or
Molecular mass of water =2 × atomic mass of H+1 × atomic mass of O
=2 × 1 + 16 × 1
= 18 u
Gram molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance expressed in grams is called gram molecular mass.
For Example : Molecular mass of oxygen = 32u
Gram molecular mass of oxygen=32 g
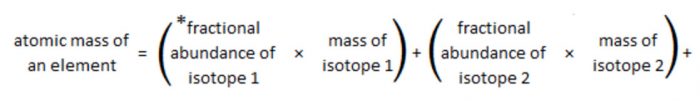
Thank You so much Ma’am…This article was really helpful. Sending loads of wishes and gratitude from Bhopal.
Tq for these solutions
It helped me alot
Lot of thanks
Thanks ma’am for this helpful topic
Thank you mam
Thank You So much Mam
For this website for us…….