Preparation
1) It is prepared by burning carbon, fossil fuels and other organic compounds in excess of air or oxygen.
C (s) + O2 (g) ——-> CO2 (g)
C5H12 (g) + 8 O2 (g) ——–> 5 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (g)
2) In the laboratory , it is prepared by the action of dilute acids on carbonates.
CaCO3 + 2 HCl ——-> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
3) Commercially , CO2 is produced as a by-product during manufacture of ammonia.The hydrogen needed for the purpose is obtained by passing steam over heated CO or CH4.
CO (g) + H2O(g) ———> CO2(g) + H2 (g)
CH4 (g) + 2 H2O(g) ——–> CO2 (g) + 4 H2 (g)
It is formed during manufacture of lime or ethyl alcohol by fermentation of glucose or fructose.
CaCO3 ——-> CaO + CO2
C6H12O6 ———->2 C2H5OH + 2 CO2
Structure
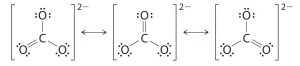
In CO2 molecule , C is sp hybridized, it forms 2 σ bonds with 2 oxygen atoms and two pπ- pπ multiple bonds.As a result , CO2 is a linear , monomeric covalent compound.
Both carbon-oxygen bond lengths in CO2 should be equal and should have a typical bond length of 122 pm. However, experimentally, it has been found that carbon-oxygen bond length in CO2 is only 115pm.
Due to resonance, carbon oxygen bond length acquires some triple bond character and hence the bond length decreases from 122 pm to 115 pm.
Properties
1) It is colourless and odourless gas about 1.5 times heavier than air.
2) CO2 is not poisonous. It does not support life in animals and human beings. However , it can cause suffocation and eventually death due to lack of oxygen.
3) Non- combustible nature: CO2 is neither combustible nor a supporter of combustion.
2 Mg + CO2 —-> 2 MgO + C
4) Solubility: It is slightly soluble in water.Its solubility in water, increases with increase in pressure.Soda water and other aerated soft drinks are , in fact , solutions of carbon dioxide in water under pressure.
5) Acidic nature
When CO2 dissolves in water , only some of the molecules react with water to form carbonic acid while most of the dissolved CO2 remains loosely hydrated.Carbonic acid is a weak dibasic acid.It forms two series of salts i.e. the hydrogen carbonates and carbonates derived from the anions HCO3‾ and CO32‾
CO2 is the anhydride of carbonic acid.
CO2 (g) + H2O (l) ⇔ H2CO3 (aq)
H2CO3 (aq) ⇔ H+ (aq) +HCO3‾ (aq)
HCO3‾ (aq) ⇔ H+ (aq) + CO32‾
A solution of CO2 in water is actually an equilibrium mixture of CO2 , H2CO3 , HCO3‾ and CO32‾
These equilibria are very important in H2CO3 / HCO3‾ buffer system which helps to maintain the pH of the human blood between 7.26-7.42.
6) Reaction with lime water
When CO2 is passed through lime water , it turns lime water milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 —–> CaCO3 + H2O
If CO2 is passed for a longer period, the turbidity disappears due to the formation of soluble calcium bicarbonate.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 —-> Ca(HCO3)2
Ca(OH)2 + 2 CO2 —–> Ca(HCO3)2
7) Photosynthesis
Carbon dioxide, is absorbed by plants.In presence of chlorophyll and sunlight, the absorbed CO2 combines with water to form glucose and starch which are used as food by the plants.This process is called photosynthesis.
6 CO2 + 12 H2O —-> C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
Plants prepare food for themselves as well as for animals and human being.But the increase in combustion of fossil fuels and decomposition of limestone for cement manufacture during the pas two decades has considerably increased the CO2 content in the atmosphere.
7) Action of ammonia
When CO2 is reacted with liquid ammonia 453-473 K under a pressure of 220 atm, it first forms ammonium carbonate which subsequently rearrange to give urea.
2 NH3 + CO2 ———> [NH2COONH4] —–> NH2CONH2 + H2O
Uses
1) In the preparation of aerated water.
2) As a fire extinguisher because it is a non-supporter of combustion.
3) In the manufacture of washing soda by Solvay ammonia process.
4) Solid carbon dioxide is used as a refrigerant.
5) For artificial respiration as a mixture of 95% O2 and 5% CO2 under the name carbogen.
6) For purification of sugar in sugar industry.
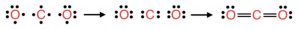
Leave a Reply