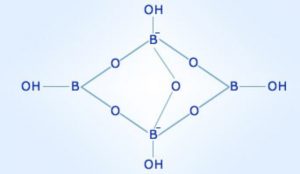
Borax contains the tetranuclear unit i.e. [B4O5(OH)4]2– . The correct formula is Na2[B4O5(OH)4].8H2O.
Preparation of Borax
1) From Tincal
Naturally occurring borax is called tincal or suhaga. Tincal obtained from dried up lakes contains 50% borax. It is boiled with water and filtered to remove insoluble impurities of clay ,sand. The filtrate is concentrated when crystals of borax separate out.
2) From Colemanite
The mineral colemanite is finely powdered and is boiled with sodium carbonate solution.
Ca2B6O11 + 2 Na2CO3 ——–> Na2B4O7 + 2 NaBO2 + 2 CaCO3 ↓
The precipitate of calcium carbonate thus formed is removed by filtration. The filtrate is concentrated and cooled when crystals of borax separate out. Sodium metaborate present in the mother liquor can be converted into borax by passing a current of carbon dioxide through it.
3) From Boric Acid
Borax can also be prepared in small amounts by neutralising boric acid with sodium carbonate.
On cooling crystal of borax i.e. Na2B4O7.10H2O separate out.
Properties of Borax
1) It is a white crystalline solid, less soluble in cold water but more soluble in hot water.
2) The aqueous solution of borax is alkaline due to hydrolysis. Borax is therefore, used as a water softener and cleaning agent.
Na2B4O7 + 2 H2O ———-> 2 NaOH + H2B4O7
H2B4O7 + 5 H2O ———-> 4 H3BO3
Action of heat- borax Bead Test
Borax loses its water of crystallisation and swells up to form a puffy mass. On further heating , it melts into a clear liquid which solidifies to a transparent glass like bead which consists of sodium metaborate (NaBO2) and boric anhydride(B2O3)
Na2B4O7.10H2O ————–> Na2B4O7 + 10 H2O
Na2B4O7 ————-> 2 NaBO2 + B2O3
The glassy bead is commonly known as borax bead and is employed in qualitative analysis for the detection of certain coloured basic radicals such as Ni2+ , Co2+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Mn2+ . Whenever a coloured salt containing these cations is heated with borax bead on a platinum wire , the salt decomposes to form the corresponding metal oxide which then combines with B2O3 present in the glassy bead to form coloured metaborates. This test is called borax bead test.
CoSO4 ———> CoO + SO3
CoO + B2O3 ——> Co(BO2)2
NiO + B2O3 ———-> Ni(BO2)2
Cr2O3 + B2O3 ———-> 2 Cr(BO2)3
MnO + B2O3 ———-> Mn(BO2)2
CuO + B2O3 ———-> Cu(BO2)2
Action of Sodium Hydroxide
On adding a calculated quantity of sodium hydroxide to borax , sodium metaborate is formed.
Na2B4O7 + 2 NaOH ———–> Na2BO2 + H2O
Action of Sulphuric Acid
On adding a calculated quantity of concentrated sulphuric acid to a hot concentrated solution of borax, boric acid is produced.
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 ———> Na2SO4 + H2B4O7
H2B4O7 + 5 H2O ——-> 4 H3BO3
Action of Ethyl Alcohol and Sulphuric Acid
On heating borax with ethyl alcohol and concentrated sulphuric acid , vapours of triethylborates are produced. When ignited these vapours burn with a green edged flame.
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 +5 H2O ———-> Na2SO4 + 4 H2BO3
H3BO3 + 3 C2H5OH ——-> B(OC2H5)3 + 3 H2O
Uses of Borax
Borax is used in:
1) in the manufacture of enamels and glazes for earthen ware. The glazed surface is resistant to heat ,stains and scratches.
2) as a flux in soldering
3) in the preparation of medicinal soaps due to its antiseptic properties.
4) in the manufacture of heat resistant Borosilicate glass.
5) to make peroxoborate- an important cleansing and bleaching agent present in washing powder.
6) as a stiffening agent for candle wicks.
7) to produce a good finish in laboratory.
8) in the laboratory for borax bead test.
9) in softening of water.
Very nice answer and thank very much for give me answer