All the organic reactions can be classified into the following eight types:
- Substitution reactions
- Addition reactions
- Elimination reaction
- Rearrangement reactions
- Condensation reaction
- Isomerisation reaction
- Pericyclic reactions
- Polymerization reactions
Contents
Substitution Reaction
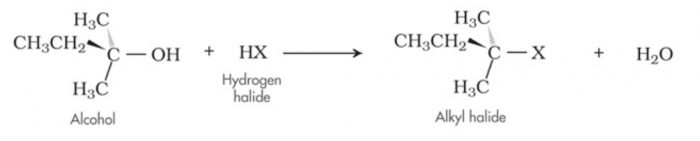
A substitution reaction is that which involves the direct replacement of an atom or a group of atoms in an organic molecule by another atom or group of atoms without any change in the remaining part of the molecule.
Th product obtained as a result of substitution is called substitution product and the new atom or group of atoms which enters the molecule is called a substituent.
Depending upon the nature of the attacking species the substitution reaction are of the following three types:
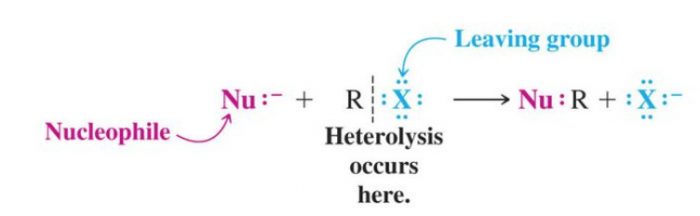
(1) Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction
Substitution reactions which are brought about by nucleophiles are called nucleophilic substitution reaction.
A stronger nucleophile usually displaces a weaker nucleophile.
HO‾ + R-X ———>R-OH +X‾
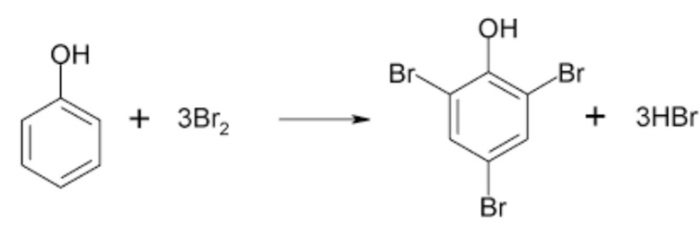
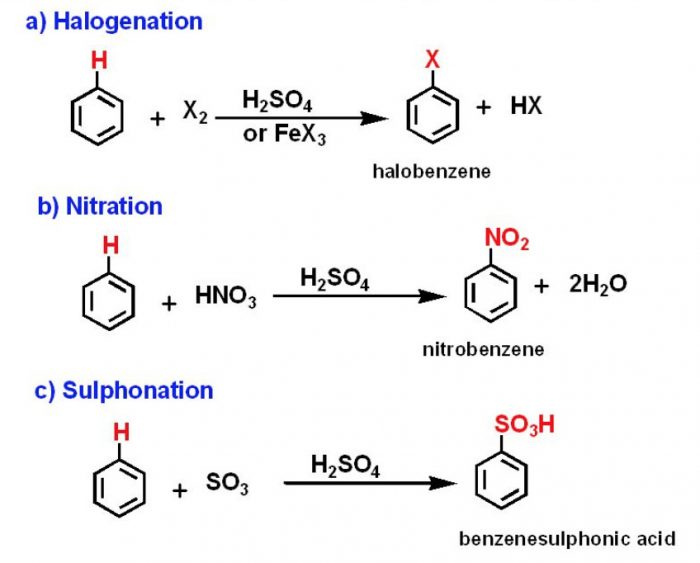
(2) Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
Substitution reactions which are brought about by electrophiles are called electrophilic substitution reaction.
These reactions are typical of arenes and other aromatic compounds.
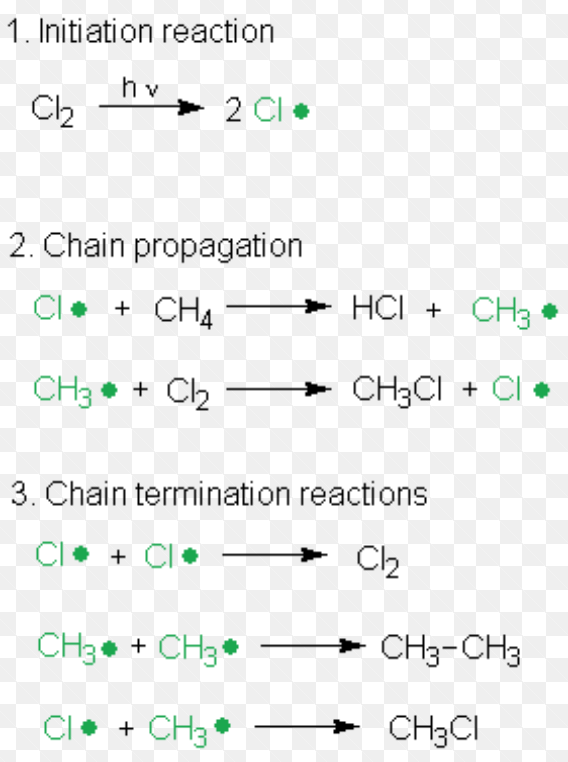
(3) Free radical Substitution Reaction
Substitution reaction brought about by free radicals are called free radical substitution reaction.
Addition Reactions
Reactions which involve combination between two reacting molecules to give a single molecule of the product are called addition reactions.Such reactions are typical of compounds containing multiple bonds.
Depending upon the nature of the attacking species , addition reactions are of the following three types:
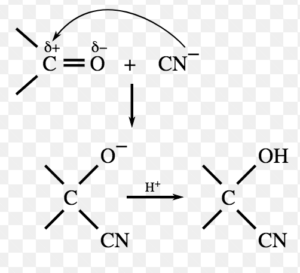
(1) Nucleophilic Addition Reaction
Addition reactions brought about by nucleophiles are called nucleophilic addition reaction.These reactions are typical of aldehydes and ketones.
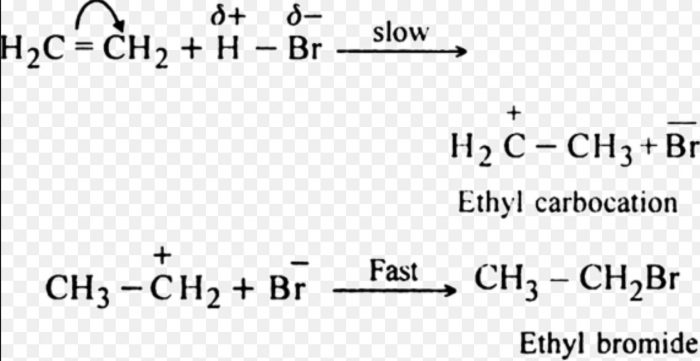
(2) Electrophilic addition Reactions
Addition reactions brought about by electrophiles are called electrophilic addition reaction.These reactions are typical of alkenes and alkynes.
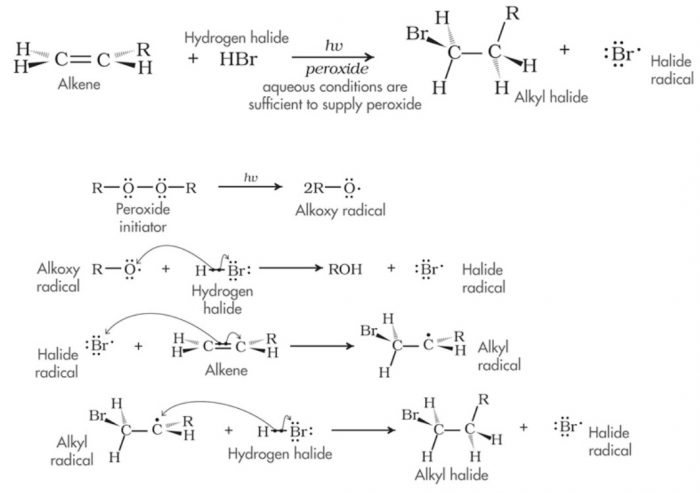
(3) Free radical addition reaction
Addition reactions brought about by free radicals is called free radical addition reaction.
Elimination Reaction
An elimination reaction is one that involves the loss of two atom or groups of atoms from the same or adjacent atoms of a substance leading to the formation of a multiple bond.Depending upon the relative positions of the atoms or groups eliminated, these reactions are classified as alpha(α), beta(β), gamma(γ) elimination reaction.
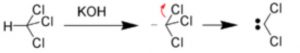
(1) α-Elimination reactions
The loss of two atoms or groups occur from the same atom of the substrate molecule.
For Ex: Base-catalysed dehydrogenation of chloroform to form dichlorocarbene.
(2) β-Elimination reaction
In these reactions , the loss of two or ore atoms or groups occur from the adjacent atoms of the substrate molecule.
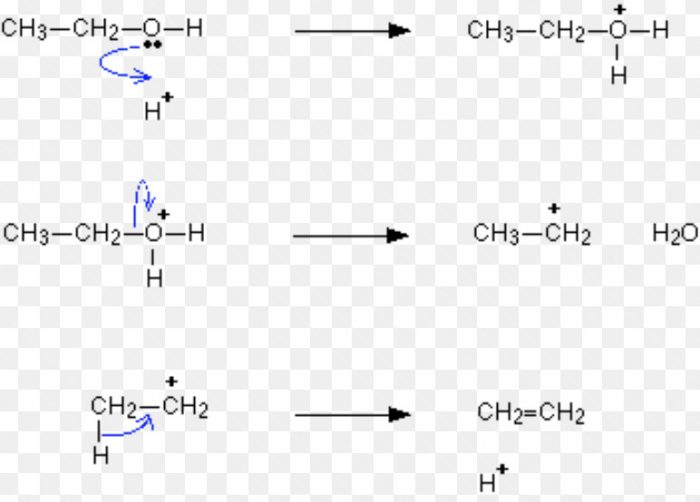
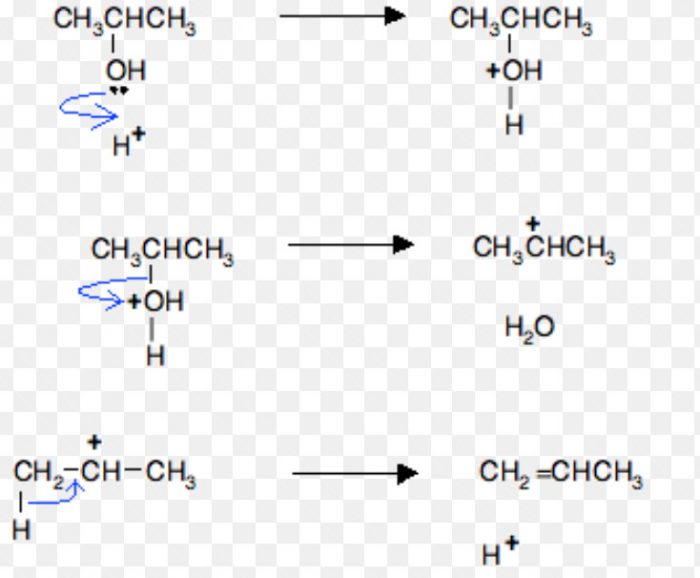
For Ex: Acid-catalysed dehydration of alcohols and base catalysed dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides.
Acid-catalysed dehydration of alcohols
Base catalysed dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides
(3) γ-Elimination
In these reactions, loss of two atoms or group occurs from α and γ position of the molecule leading to the formation of three-membered rings.
This reaction is called Freund reaction and is extensively used for the synthesis of three membered rings.
Condensation Reaction
In these reactions, two or more molecules of the same or different reactants combine to form a product with or without the elimination of simple molecule such as H2O, HCl, NH3, ROH.
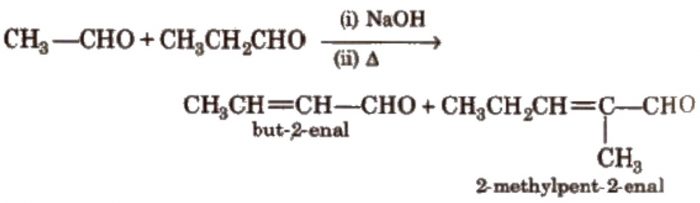
Two molecules of acetaldehyde condense in presence of dilute alkali to from 3-hydroxybutanal.
Since β-hydroxyaldehyde or ketones are called as aldols therefore this reaction is called aldol condensation.
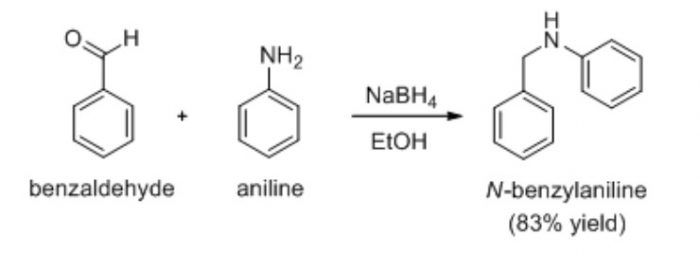
Condensation reaction which occurs with the elimination of a molecule of water is the reaction between benzaldehyde and aniline to from benzylideneaniline.
Rearrangement Reactions
Reactions involving the migration of an atom or a group from one atom to another within the same molecule are called rearrangement reactions.
(1) Dehydration of 2,2-dimethylpropan-1-ol with conc H2SO4 occurs through 1,2-migration of the methyl group to give rearranged product.
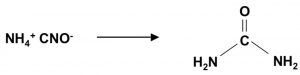
Wohler synthesis of urea from ammonium cyanate is also example of rearrangement reaction.
NH4Cl + NaCNO ———> NH4CNO + NaCl
NH4CNO ———–>NH3 + OH-C≡N
Proton transfer ans tautomerism occur:
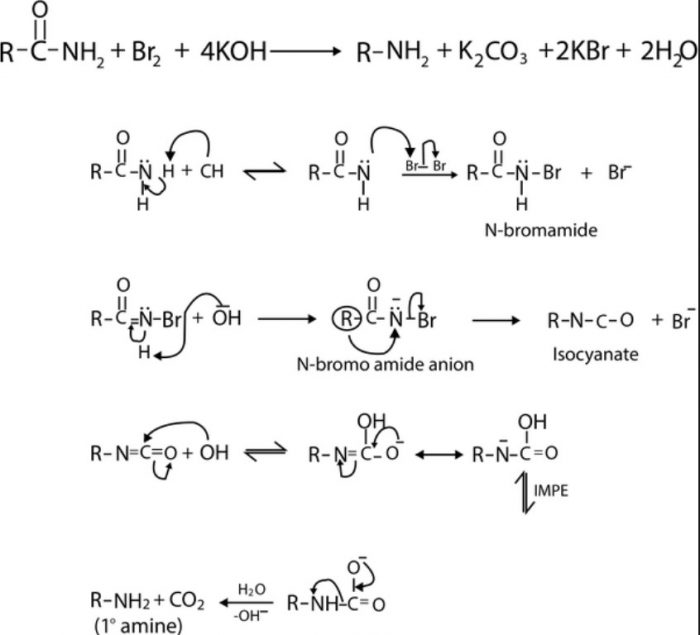
Hofmann bromamide reaction involving the conversion of 1° amides to 1° amines on treatment with Br2 in presence of KOH.
Isomerisation Reactions
Reactions which involve interconversion of one isomer into another keeping the molecular formulae as well as the carbon skeletons of the reactants and the products intact are called isomerization reactions.
For Ex: Interconversion of trans-but-2-ene to cis-but-2-ene and vice versa.
Pericyclic Reactions
These reactions occur in a single step via a cyclic transition state. In these reactions, bond making and bond breaking occurs simultaneously. These reactions do not require any catalyst and are initaited either by heat or light.
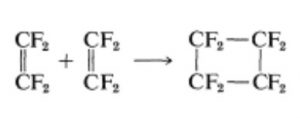
Addition of one ethene molecule(2π-electron system) to another ethene molecule (2π-electron system) is called as 2π+2π or ( 2+2 ) cycloaddition reaction.
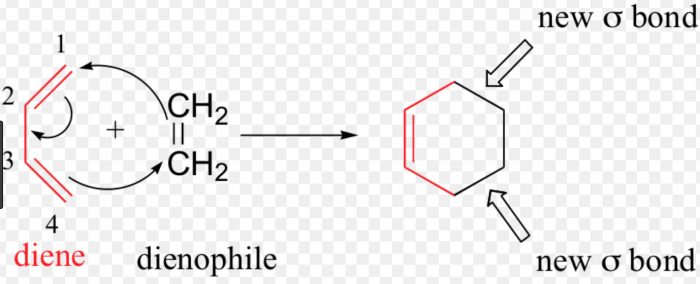
The addition of a diene to a dienophile to form a six-membered ring is called (4+2) cycloaddition reaction or Diel-Alder reaction.

Thank you so much madam for providing notes it is very useful for my assignment
Thank u soooooooooooooooo much, it’s so good
Thanq so much mdm .it’s very useful and simply understanding notes.
Thank you so much mam it really helpful for me
This is very good it help me in very much