Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds contain one or more isolated or fused benzene rings. An aromatic compound consist of two parts :
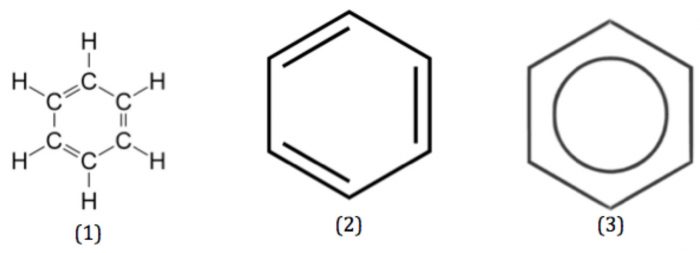
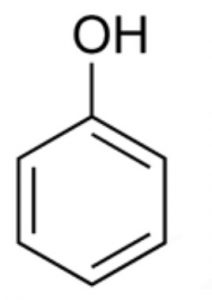
(1) Nucleus: The most ideal aromatic compound is benzene. It is represented by a regular hexagon of six carbon atoms with three alternate single and double bonds. This is called the nucleus. The ring may be represented by any of the following three ways:
A circle inside the cyclohexane ring represents six completely delocalised π-electrons or three conjugated double bonds.
(2) Side Chain : The alkyl group or any other aliphatic group containing at least one carbon atom which is attached to the benzene ring is called the side chain.
Each family of aromatic compounds consist of the following two types of compounds with quite different chemical properties.
(1) Nuclear substituted : Those in which the functional group is directly attached to the benzene ring.
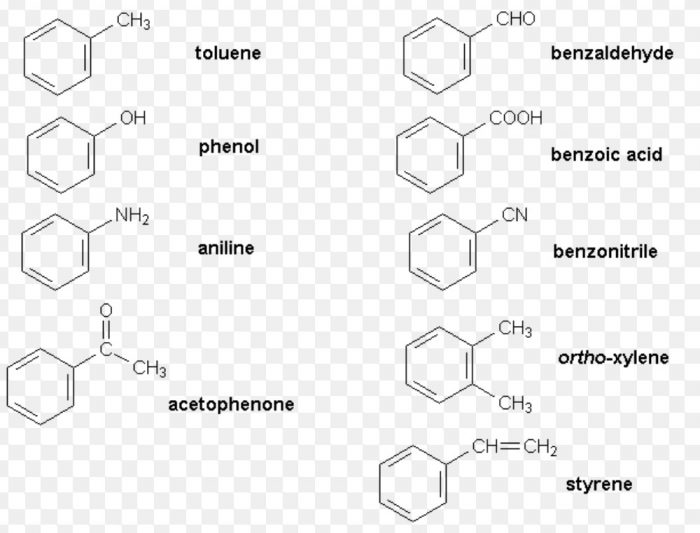
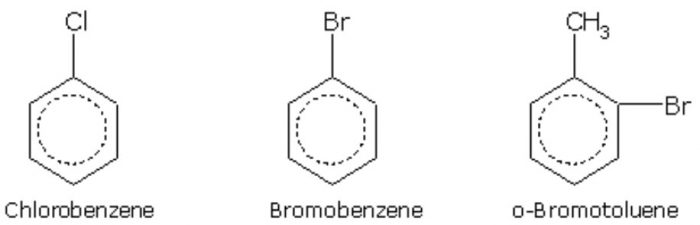
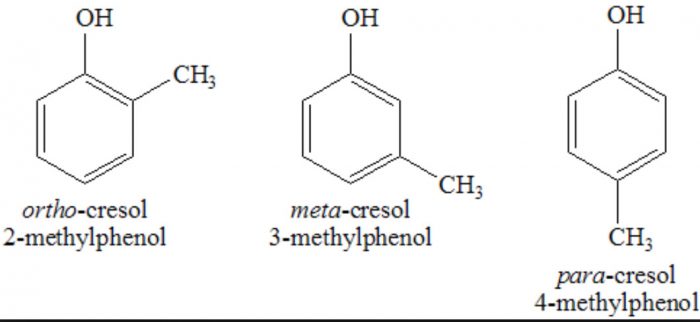
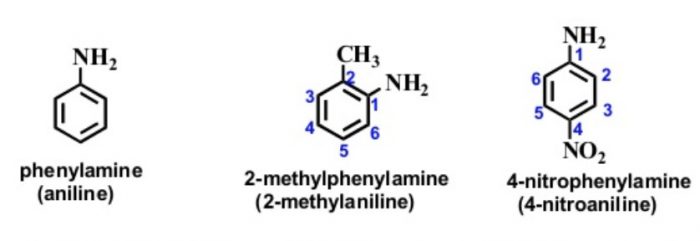
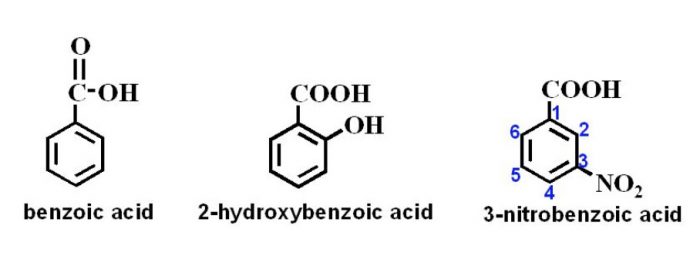
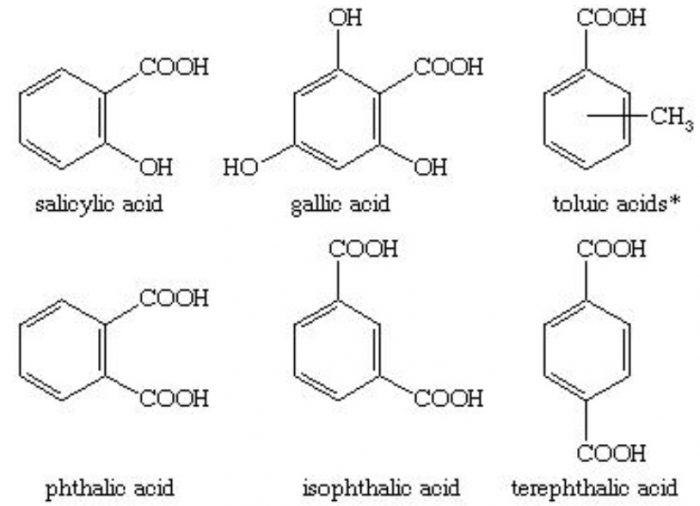
In the IUPAC system, they are named as derivatives of benzene. The position of the substituent in disubstituted benzene are indicated either by prefixes or by arabic numerals such as ortho (o) for 1, 2 ; meta (m) for 1,3 and para (p) for 1,4.
(2) Side chain substituted: Those in which the functional group is present in the side chain of the benzene ring. Both in the common and IUPAC systems, these are usually named as phenyl derivatives of the corresponding aliphatic compounds.
The positions of the substituents on the side chain including the benzene ring are indicated by Greek letters α, β,ϒ.. in the common system and by the arabic numerals i.e. 1,2, 3 etc. in the IUPAC system.
Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons which contain both aliphatic and aromatic units are called arenes.
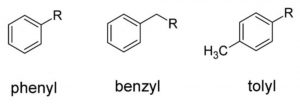
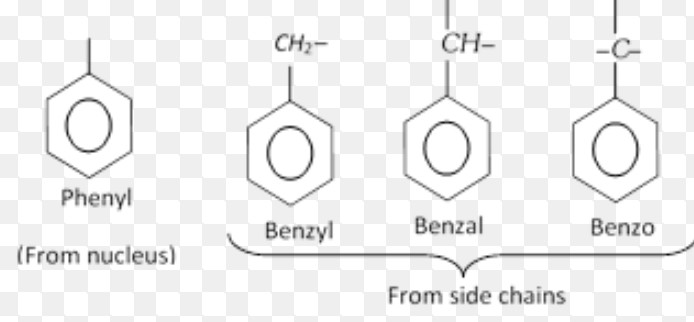
Aryl groups
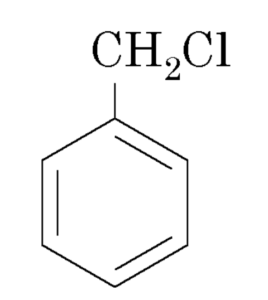
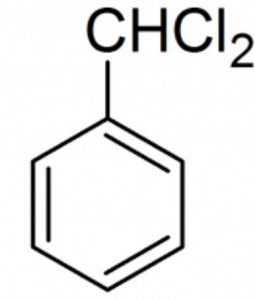
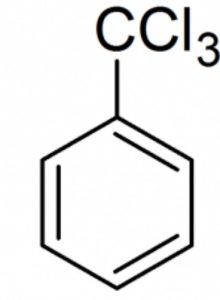
Halogen derivatives
Benzyl chloride
Benzal dichloride
Benzotrichloride
Hydroxy derivatives
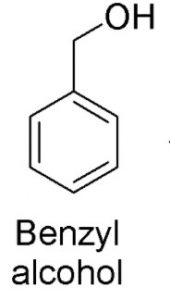
Hydroxy derivatives : The nuclear hydroxy derivatives are called phenols while the side chain substituted hydroxy derivatives are called aromatic alcohols.
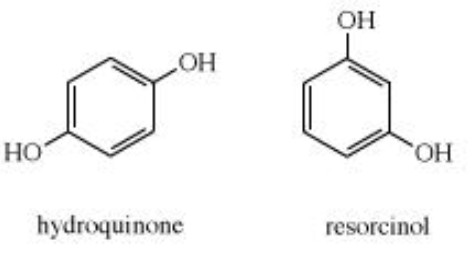
Phenols
Aromatic alcohols
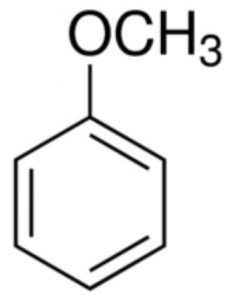
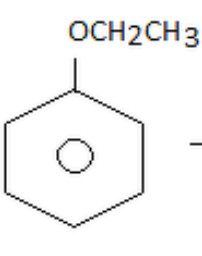
Aromatic ethers
Anisole
Ethoxybenzene
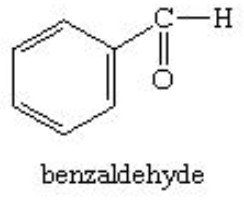
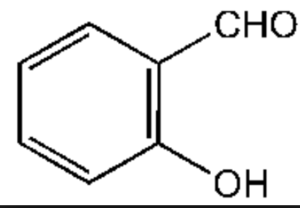
Aldehydes
Salicylaldehyde
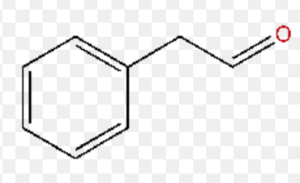
2-Phenylethanal
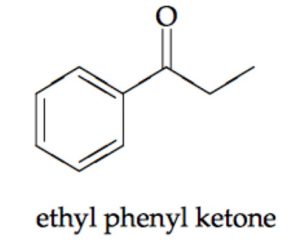
Ketones
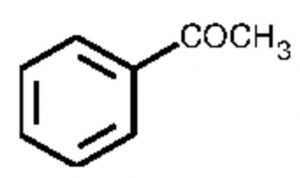
Acetophenone or Methyl phenyl ketone
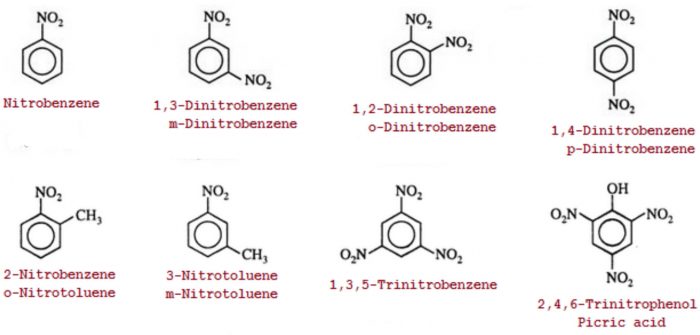
Nitro compounds
Amines
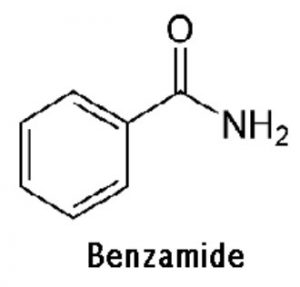
Carboxylic acids
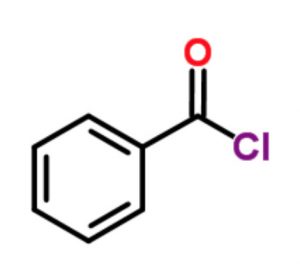
Acid derivatives
Benzoyl chloride
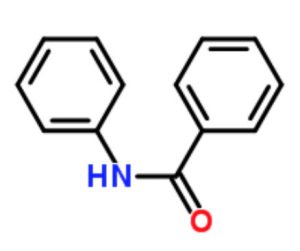
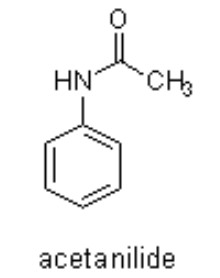
Benzanilide
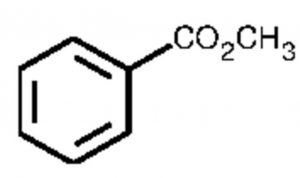
Methyl benzoate
Sulphonic acids
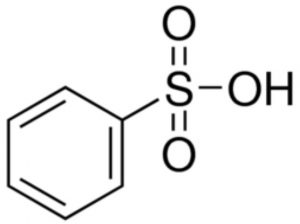
Benzenesulphonic acid
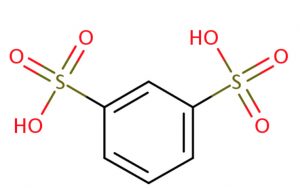
m-Benzenedisulphonic acid
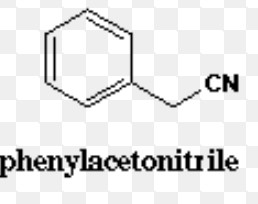
Cyanides
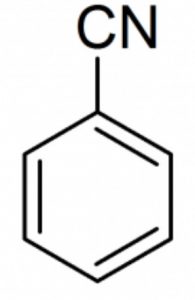
Benzonitrile
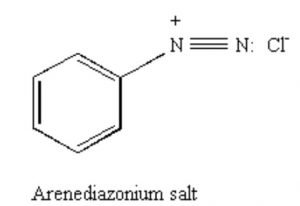
Arenediazonium salts
Benzenediazonium chloride
This is a good website for aromatic compounds naming and their structures. i appreciate positively/