Hydrocarbons are the parent organic compounds. All other compounds are considered to have been derived from them by replacing one or more of their hydrogen atoms by some other more reactive atom or group.
R—H ——–> R—G
-H and +G
Each organic molecule consist of two parts i.e. R and G.
The first part, i.e. R denotes the carbon -hydrogen framework of the molecule while the second part i.e. G is called the functional group.
A functional group may be defined as as atom or a group of atoms present in a molecule which largely determines its chemical properties.
The remaining part of a molecule mainly affects the physical properties such as melting point, boiling point , density, solubility, refractive index etc.
The chemical properties of any organic compound are the properties of its functional group.
All the organic compounds containing the same functional group show similar chemical reactions.
| Class of organic compounds | Name of the functional group | Structure of the functional group |
| Alkenes | Double bond | |
| Alkynes | Triple bond | |
| Halogen derivative | Halogen | —X (F, Cl, Br, I) |
| Alcohols | Hydroxy | —OH |
| Thioalcohol | Thiols | —SH |
| Ethers | Divalent oxygen | —O— |
| Thioethers | Divalent sulphur | —S— |
| Aldehydes | Aldehydic | |
| Ketones | Thiol | |
| Thioketones | Thione | |
| Carboxylic acid | Carboxyl | 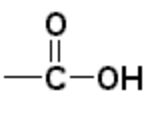 |
| Acid chlorides | Chlorocarbonyl | 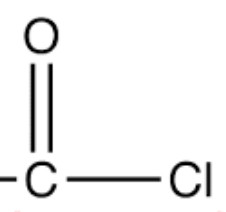 |
| Acid anhydride | Anhydride | 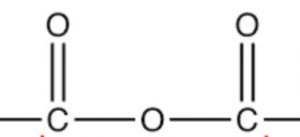 |
| Esters | Alkoxycarbonyl | 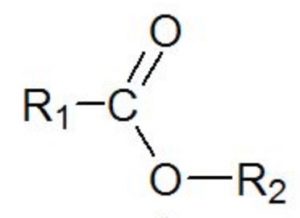 |
| Acid amide | Amide | 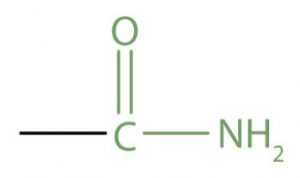 |
| Sulphonic acid | Sulphonic acid | 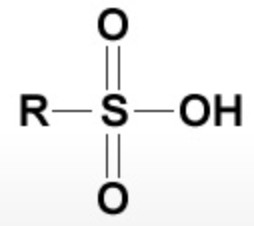 |
| Primary amines | Amino | 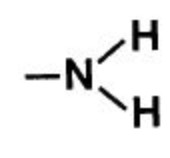 |
| Secondary amines | Imino | 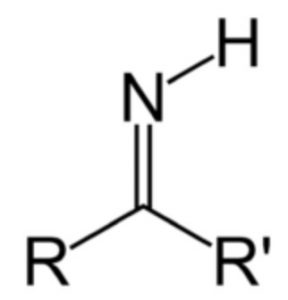 |
| Tertiary amines | Tertiary -N- atom | 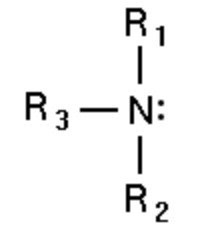 |
| Alkyl cyanide | Cyano or nitrile | |
| Alkyl isocyanide | Isonitrile | 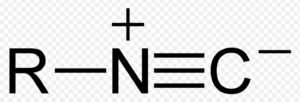 |
| Nitroalkanes | Nitro | 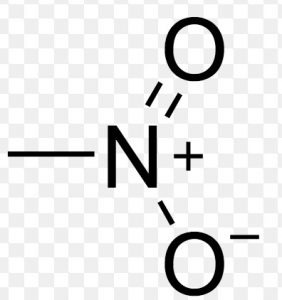 |
| Alkyl nitrites | Nitrite | 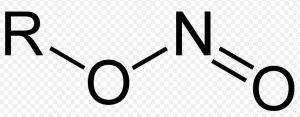 |
Leave a Reply