Salt hydrolysis is defined as the process in which a salt reacts with water to give back the acid and the base.
Salt +water ———-> Acid + Base
BA + H2O ———> HA + BOH
All salts are strong electrolytes and thus ionize completely in the aqueous solution.
(1) If the acid produced is strong and the base produced is weak.
B+ + A‾ + H2O ——-> H+ + A‾ + BOH
or
B+ + H2O ——-> H+ + BOH
In this case the cation reacts with water to give an acidic solution. This is called cationic hydrolysis.
(2) If the acid produced is weak and the base produced is strong.
B+ + A‾ + H2O ——-> HA + B+ + OH‾
or
A‾ + H2O ——-> HA + OH‾
In this case the anion reacts with water to give basic solution. This is called acidic hydrolysis.
Salt hydrolysis may be defined as the reaction of the cation or the anion of the salt with water to produce acidic or basic solution.
Depending upon the relative strength of the acid and the base produced, the resulting solution is acidic, basic or neutral.
(1) Salts of strong acid and strong base
NaCl, NaNO3, Na2SO4, KCl, KNO3 , K2SO4
NaCl + H2O ——-> NaOH + HCl
Na+ + Cl‾ + H2O ——-> Na+ + OH‾ + H+ + Cl‾
H2O ——->OH‾ + H+
It involves only ionization of water and no hydrolysis.So the solution is neutral.
The salts of strong acids and strong bases do not undergo hydrolysis and the resulting solution is neutral.
(2) Salts of weak acid and strong bases
CH3COONa, Na2CO3, K2CO3, Na3PO4
CH3COONa + H2O CH3COOH + NaOH
CH3COO‾ + Na+ + H2O CH3COOH + Na+ + OH‾
CH3COO‾ + H2O ——-> CH3COOH + OH‾
As it produces OH‾ ions, the solution of such a salt is alkaline in nature.
(3) Salts of strong acid and weak base
NH4Cl , CuSO4, NH4NO3 , AlCl3, CaCl2
NH4Cl + H2O NH4OH + HCl
NH4+ + Cl‾ + H2O NH4OH + H+ + Cl‾
NH4+ + H2O ——-> NH4OH + H+
As it produces H+ ions, the solution of such a salt is acidic in nature.
(4) Salts of weak acid and weak base
CH3COONH4 , AlPO4 , (NH4)2CO3
CH3COONH4 + H2O CH3COOH + NH4OH
It involves both anionic and cationic hydrolysis
Hydrolysis constant
Equation for the hydrolysis of a salt (BA) may be written as:
Degree of Hydrolysis
The degree of hydrolysis of a salt is defined as the function of the total salt which is hydrolyse i.e.
h = No. of moles of the salt hydrolysed / Total no. of moles the salt taken
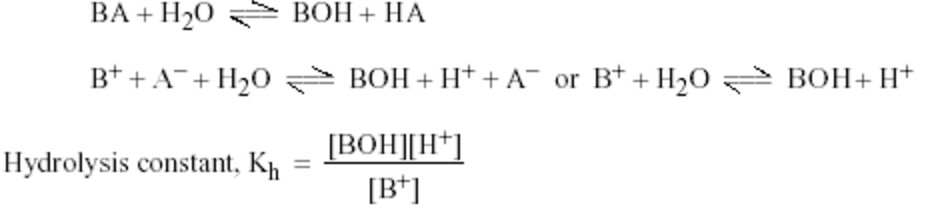
Thanks for the notes
Thanks for these notes
thank you so much Mrs Shilpi. I really appreciate this. it is so important
Great site. Very useful. Thanks a lot.
Fantastic
I was searching this one for so long thank you❤
That is very good effort