Acids like HCl, H2SO4 ,HNO3 when dissolved in water dissociates almost completely thus producing a large number of H+ ions. These acids are called strong acids.
Acids like CH3COOH , HF, H2CO3, H3PO4 dissociates only to a small extent in the aqueous solution giving small amount of H+ ions and hence are called weak acids.
Bases like NaOH , KOH dissociate almost completely in the aqueous solution producing a large number of OH‾ ions and are called strong bases.
Bases like NH4OH , Ca(OH)2 , Al(OH)3 dissociate only to a small extent in the aqueous solution and are therefore called weak bases.
The dissociation of weak acids or weak bases in water can be represented:
CH3COOH + H2O CH3COO‾ + H3O+
NH3 + H2O NH4+ (aq) + OH‾(aq)
If a weak acid is represented by HA , its dissociation in water can be represented by the equilbrium:
HA + H2O A‾ (aq) + H3O+ (aq)
Applying the law of chemical equilibrium, the expression constant will be:
As water is solvent, its concentration is large and remains almost constant.
HA + (aq) H+ (aq) + A‾ (aq)
Knowing the value of the dissociation constant of the acid, Ka and the concentration of the weak acid HA taken, concentration of H3O+ or H+ in the solution can be calculated as:
HA +aq H+ (aq) + A‾ (aq)
Initial conc of HA is C mol L‾1
Initial conc of H+ is 0 M
Initial conc of A‾ is 0 M
Final conc of HA at equilibrium is (C-x) M
Final conc of H+ at equilibrium is x M
Final conc of A‾ at equilibrium is x M
Ka = x × x / C-x
Ka = x2 / C- x
x is very small as compared to the initial concentration C ,x can be neglected in comparison to C.Hence the equation is simplified to the form:
Ka = x2 / C
x= √Ka × C
The dissociation of a weak base in water can be represented by the equilibrium:
BOH + aq B+ (aq) + OH‾ (aq)
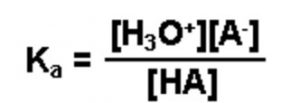
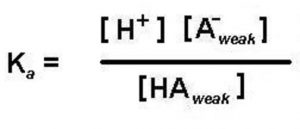
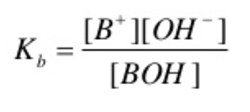
Leave a Reply