1) Physical Properties (a) Heterogeneous Character The colloidal solutions are heterogeneous in nature consisting of two phases (1) dispersed phase and (2) dispersion medium. Because of the small particle size, the colloidal solutions generally appear to be homogeneous to the naked eye but their heterogeneity can be confirmed by seeing under electron microscope. (b) … [Read more...] about Properties of Colloidal Solution
Class 12
Methods of Preparation and Purification of Colloidal Solutions
Preparation of Lyophilic Colloids The lyophilic colloids have strong affinity between particles of dispersed phase and dispersion medium. Therefore, these colloidal solutions are readily formed by simply mixing the dispersed phase and dispersion medium under ordinary conditions. For example: The substances like gelatin, gum, starch, egg albumin etc. pass readily into water … [Read more...] about Methods of Preparation and Purification of Colloidal Solutions
Classification of Colloids
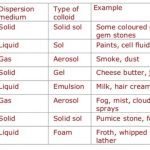
Classification of Colloids The colloids are classified on the basis of the following criteria : 1) Physical state of dispersed phase and dispersion medium. 2) Natural of interactions between dispersed phase and dispersion medium. 3) Type of particles of the dispersed phase. Classification based on the Physical state of the Dispersed phase and Dispersion … [Read more...] about Classification of Colloids
Colloidal State
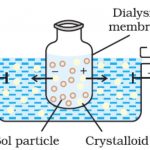
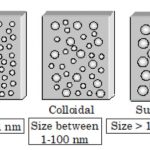
Colloidal State Certain solutes such as starch, glue, gelatin etc. could not pass through the parchment membrane while the ordinary solutes such as sodium chloride, urea , sugar etc. can easily do so. Thus, colloid is not a substance but it is a state of a substance which depends upon the molecular size. Three Types of Solutions On the basis of particle size of the … [Read more...] about Colloidal State
Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reaction and Zeolites
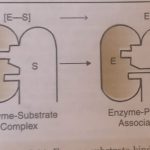
Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reactions The various steps involved in the enzyme catalysed reaction are given below: Step 1. Binding of the enzyme (E) to substrate (S) to form enzyme-substrate complex. E + S ⇔ ES (fast, reversible) ES is called the enzyme-substrate complex. Step 2. Dissociation of enzyme-substrate complex to form the products. ES -------> EP … [Read more...] about Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reaction and Zeolites