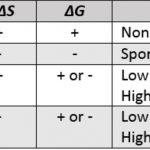
Another thermodynamic quantities that helps in predicting the spontaneity of a process is Gibbs free energy or Gibbs energy of Gibbs function. It is denoted by G and is given by the equation G=H -TS where H is the heat content ,T is the absolute temperature and S is the entropy of the system. G1 = H1 -TS1 for the initial state G2 = H2 -TS2 for the final … [Read more...] about Gibbs Free Energy
Thermodynamics
Entropy
Entropy Entropy is a measure of randomness or disorder of the system. The greater the randomness, higher is the entropy. Solid state has the lowest entropy, the gaseous state has the highest entropy and the liquid state has the entropy in between the two. Entropy is a state function. The change in its value during a process, is called the entropy change. ΔS = S2 … [Read more...] about Entropy
Spontaneous and Non-spontaneous Process
A process which under some conditions may take place by itself or by initiation independent of the rate is called spontaneous process. A process which can take place by itself or has an urge or tendency to take place is called spontaneous process. A spontaneous process is simply a process which is feasible. The rate of the process may vary from extremely slow to … [Read more...] about Spontaneous and Non-spontaneous Process
Bond Enthalpy
Bond energy is the amount of energy released when 1 mole of bonds are formed from the isolated atoms in the gaseous state or the amount of energy required to dissociate one mole of bonds present between the atoms in the gaseous molecules. It is represented by Δ b H or Δbond H. For diatomic molecules like H2, O2, N2, Cl2, HCl, HF etc. the bond energies are equal to their … [Read more...] about Bond Enthalpy
Enthalpy Changes During Phase Transitions
Enthalpy of Fusion Enthalpy of fusion is the enthalpy change accompanying the transformation of one mole of a solid substance into its liquid state at its melting point. it is also called molar enthalpy of fusion. The molar enthalpy of fusion ( Δ fus H ) of ice is +6 KJ mol-1. H2O ( s ) → H2O ( l ) Δfus H = + 6 KJ mol-1 The enthalpy of freezing has same value as … [Read more...] about Enthalpy Changes During Phase Transitions