In an organic reaction, the organic compound called the substrate reacts with a suitable attacking species called the reagent to form products. The formation of products may occur either directly from the reactants through a transition state or through the formation of one or more intermediates. Sometimes by products are also formed from intermediates. Organic … [Read more...] about Electrophiles and Nucleophiles
Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
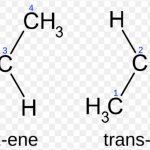
Stereoisomerism
Isomers which have same structural formula but have different relative arrangement or atoms or groups in space are called stereoisomers and the phenomenon is called stereoisomerism. cis-trans isomerism is an example of stereoisomerism. Due to π-bonding between the two carbon atoms, the rotation around carbon-carbon double bond is prohibited and hence the geometry of … [Read more...] about Stereoisomerism
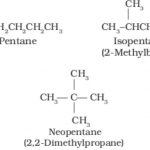
Structural Isomerism
Isomerism Two or more compounds having the same molecular formula but different chemical and physical properties are called isomers and the phenomenon is known as isomerism. It is of 2 types: 1) Structural isomerism 2) Stereoisomerism 1) Structural Isomerism : Compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures i.e. different arrangement of … [Read more...] about Structural Isomerism
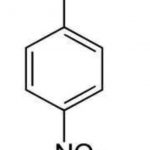
Nomenclature For Di and Polyfunctional Aromatic compounds
1) When an aromatic compound contains two or more functional group, it is named as a derivative of the compound with the principal functional group at position 1. 4-Nitrobenzoic acid 2-Aminophenol 3-Acetylbenzonitrile 4-Iodo-2-methylphenol 3-Bromo-4-hydroxybenzoic acid 2) If all the functional groups present in the benzene ring are such … [Read more...] about Nomenclature For Di and Polyfunctional Aromatic compounds
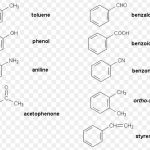
Nomenclature of Simple Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic Compounds Aromatic compounds contain one or more isolated or fused benzene rings. An aromatic compound consist of two parts : (1) Nucleus: The most ideal aromatic compound is benzene. It is represented by a regular hexagon of six carbon atoms with three alternate single and double bonds. This is called the nucleus. The ring may be represented by any of the … [Read more...] about Nomenclature of Simple Aromatic Compounds