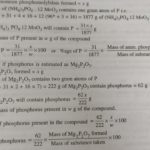Quantitative analysis means to determine the percentage of each element. Estimation of Carbon and Hydrogen Principle. A known mass of the organic compound is heated strongly with excess of dry copper oxide in a current of dry air or oxygen (free from carbon dioxide). Under these conditions, carbon present in the organic compound is oxidized to carbon dioxide and hydrogen is … [Read more...] about Quantitative Analysis
Organic Chemistry - Some Basic Principles and Techniques
Qualitative Analysis
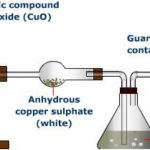
Qualitative Analysis Qualitative analysis means to detect the various elements present in it. The elements which commonly occur in organic compounds are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Detection of Carbon and Hydrogen Principle: The presence of carbon and hydrogen, in an organic compound, is detected by heating the given compound with dry Copper(II) oxide or … [Read more...] about Qualitative Analysis
Purification of Organic Compounds
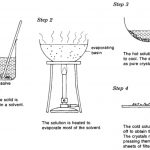
Here are some of the important methods which are commonly employed for the purification of organic compounds: Filtration The process of filtration is used to separate insoluble solid component of a mixture from the soluble components in a given solvent. It is used to separate a mixture of naphthalene and urea using water as solvent. Urea dissolves in water while … [Read more...] about Purification of Organic Compounds
Types of Organic Reactions
All the organic reactions can be classified into the following eight types: Substitution reactions Addition reactions Elimination reaction Rearrangement reactions Condensation reaction Isomerisation reaction Pericyclic reactions Polymerization reactions Substitution Reaction A substitution reaction is that which involves the direct replacement of … [Read more...] about Types of Organic Reactions
Free Radicals
Free Radical A free radical may be defined as an atom or a group having an odd or unpaired electron. These are generally produced by the homolytic cleavage of a covalent bond. Classification of Free Radicals Free radicals are also classified as primary (1°) , secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) according as the carbon carrying the unpaired electron is primary, secondary … [Read more...] about Free Radicals