Organometallic Compounds
Organometallic compounds are those compounds which contain one or more metal-carbon bonds. All the compounds containing carbon and a metal atom are not organometallic. We use this term for compounds which contain at least one M-C bond.
For example
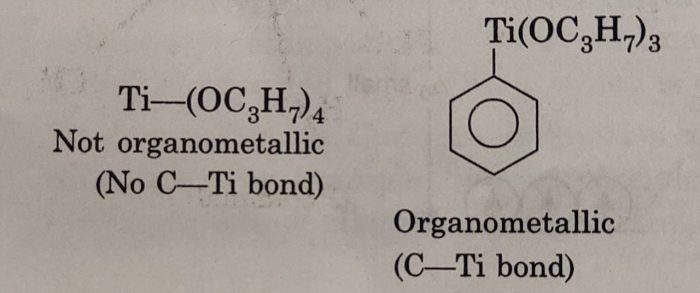
An alkoxide such as (C3H7O4)Ti is not considered to be an organometallic compound because the organic group is bonded to Ti atom by oxygen and there is no Ti-C bond. The compound C6H5Ti(OC3H7)3 is an organometallic compound because it contains a Ti-C bond (C6H5-Ti) in the compound.
EC. Frankland was the first chemist to synthesise an organometallic Compound, dimethylzinc, (CH3)2Zn in 1848. He also prepared other compounds containing metal-carbon bonds such as :
Contents
Classification of Organometallic Compounds on the basis of nature of metal-carbon bond
(1) σ-bonded organometallics
(1) σ-bonded organometallics
(i) Grignard reagents: R-Mg-X where X= halogen, R= alkyl or aryl group.
(ii) Diethyl zinc, (C2H5)2Zn, dimethyl magnesium, dimethyl beryllium, etc.
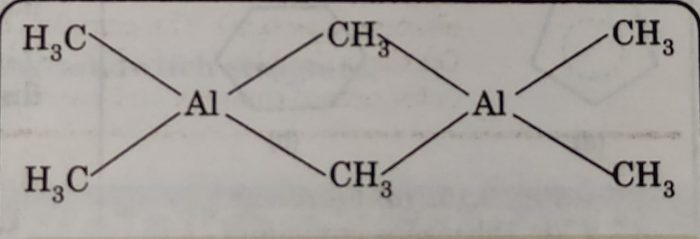
(iii) Trimethyl aluminium (CH3)3Al: It exists as a dimer [Al2(CH3)6] with two methyl groups acting as bridges between two aluminium atoms. In this structure, two methyl groups act as bridges between two Al-atoms. The alkyl bridge is formed by multicentre (2 Al-atoms and one C-atom) bonding.
Tri-aryl aluminium i.e., tri-phenylaluminium (C6H5)3Al also exists as dimer.
(iv) Tetra ethyl tin, Sn(C2H5)4 and tetramethyl tin, Sn(CH3)4 tetramethylsilane , trimethylarsine, etc.
![Structure of [Si(CH3)4] and [As(CH3)3]](https://classnotes.org.in/wp-content/uploads/Structure-of-SiCH34-and-AsCH33-700x303.jpeg)
(v) Lithium alkyl compounds are covalent compounds and generally have tetrameric structures. For example: methyllithium, CH3Li exists in the solid state as tetrameric units (LiCH3)4]
(2) π-bonded organometallics
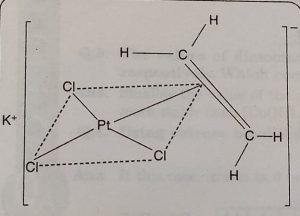
(i) Zeise’s salt K[PtCl3(C2H4)]
In this structure the three Cl-atoms and the middle point of ethylene double bond form a square plane. The platinum atom is present in the centre of the square and C = C double bond of ethylene molecule is perpendicular to plane containing Pt and Cl atoms.
It is written as K[PtCl3(η2-C2H4)]- The number of carbon atoms bound to the metal is indicated by the Greek letter ‘η’ (eta) followed by a number. In this case, Pt is bound to two carbon atoms and therefore, it is written as η2.
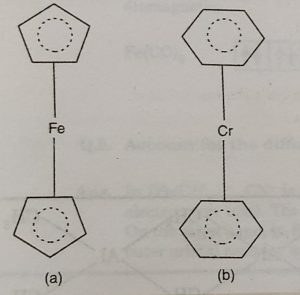
(ii)Ferrocene or bis (cyclopentadienyl) iron, Fe(η2-C2H5)2
The structure of ferrocene is regarded as sandwich structure in which the iron atom is sandwiched between two C2H5 organic rings. The planes of the rings are parallel so that all the carbon atoms are at the same distance from the iron atom.
Ruthenocene, Ru(C5H6) and osmocene Os(C5H5)2 have structures similar to ferrocene.
(iii) Dibenzene chromium, Cr(η6-C6H6)2
Synthesis of Organometallic Compounds
(1) Preparation of Organometallic Compounds Containing σ-Bond only
(i) Grignard reagents are prepared by the slow addition of organic halide to a stirred suspension of magnesium turnings (or metal) in the appropriate solvent in the absence of air and moisture.
The reactivity of alkyl halide is RI >RBr>RCl and alkyl is more reactive than aryl.
(ii) Diethyl zinc is prepared by heating zinc with boiling alkyl halide in an inert atmosphere (CO2 or N2).
(iii) Tetra alkyl organometallics are prepared by treating metal halides with organometallic reagents :
(a) nC4H9Br + 2Li → n-C4H9Li + LiBr
SnCl4 + 4C4H9Li → (C4H9)4Sn + 4LiCl
(b) C2H5Br + Mg → C2H5MgBr
PbCl4 + 4C2H5MgBr → (C2H5)4P+ 4MgBrCl
It can also be prepared by using an alloy
(2) Preparation of π-Complexes
(ii) Ferrocene is prepared by the following reaction:
(iii) Dibenzene chromium is obtained by heating benzene with chromium vapours :
Dear Mrs Shilpi Nagpal
Congratulations and thanks to your this wonderful service.
I refer your website to our First Year BSc Chemistry students.
Thank You