At equilibrium,
The rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reaction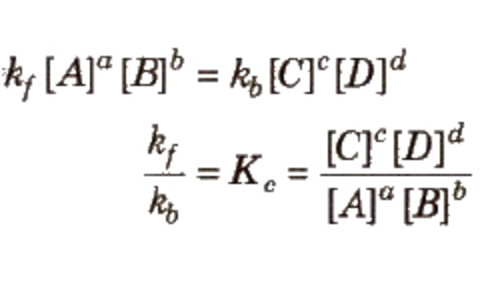
The product of the molar concentration of the products, each raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficients divided by the product of the molar concentration of the reactants, each raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficients is constant at constant temperature and is called Equilibrium constant.
For Gas Phase Reactions
The equilibrium constant can be expressed in terms of the partial pressures of the reactants and the products. If expressed in terms of partial pressure, it is denoted by Kp.
Where PA , PB , PC , PD are the partial pressure of A ,B ,C , D in the reaction mixture.
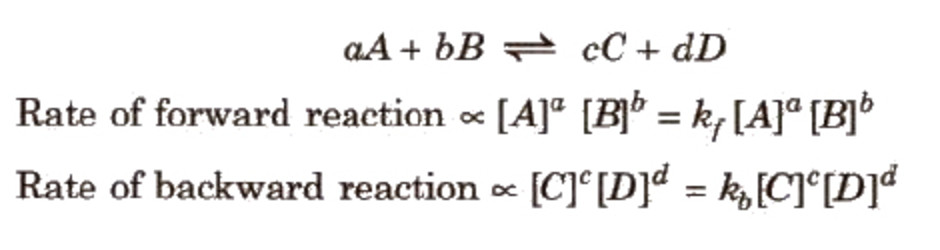
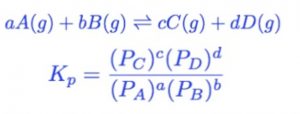
Leave a Reply