Question 1 Define the term photosynthesis?
Question 2 Name the parts of plant?
Question 3 Name the green coloured pigment present in the leaves of plant. Also state its function?
Question 4 Explain the process of photosynthesis?
Question 5 Name the gas used and produced in photosynthesis?
Question 6 What is transpiration. Explain with the help of an activity to show that transpiration take place in plants?
Question 7 What are tap roots. Give example?
Question 8 What are fibrous roots. Give example?
Question 9 Why photosynthesis is essential for plants?
Question 10 What is leaf. What are the functions of leaves. Explain the main parts of leaf with diagram?
Question 11 State the main functions of stem?
Question 12 What is root. What are the main functions of root?
Question 13 Give an activity to show that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
Also Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 7 Getting to know Plants
Contents
- 1 Parts of Plant
- 2 Root
- 3 Types of Root
- 4 Food stored in roots
- 5 Leaf
- 6 Structure of leaf
- 7 Function of chlorophyll
- 8 Process of photosynthesis
- 9 Transpiration
- 10 Activity: Leaves make food by photosynthesis
- 11 Activity: To show that sunlight is necessary for Photosynthesis
- 12 Activity : Transpiration in plants
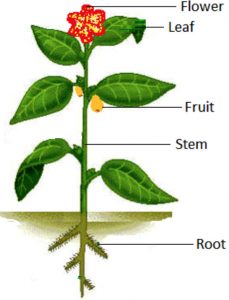
Parts of Plant
The main parts of plants are : Root, Stem and leaves.
Root
That part of the plant which is below the ground (in the soil), is called root.
The main functions of root are:
(1) Roots anchor the plant to the soil. It means that root fix the plant firmly to the soil or ground. This prevents the plant from being pulled out easily or blown away by the wind.
(2) Roots absorb water and mineral from the soil. These are needed for the manufacture of food by plant leaves.
(3) Roots that help in holding the soil together. In this way, roots prevent the soil from being blown away by wind or washed away by water and help in the conversation of soil.
Types of Root
Roots are primarily of two types:-
(1) Tap roots, and
(2) Fibrous roots
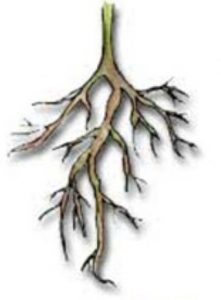
Tap Root
Tap root is a straight tapering root which grows vertically down into soil and gives out branches on all the sides.
Tap root is the main root and and the smaller, side roots are called lateral roots.
Tap root itself is a quite thick but its branches are much thinner.
Some examples are Pea Plant, Neem tree, mango tree, Marigold, Tulsi, Gram, Carrot, Radish, Beet and Turnip.
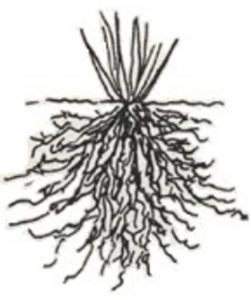
Fibrous Root
The fibrous root consist of many thin, fibre-like roots of a similar size.
The fibrous roots spread out in the soil and give a firm support to the plant.
Some of the plants which have fibrous roots are Sweet potato, Paddy (rice), Grass, Maize, Millet (Bajra), Sugarcane and Bamboo.
Food stored in roots
The Minerals present in soil get dissolved in this water. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and the stem carries them to the leaves. The leaves prepare food. The food prepared in leaves is carried by the stem to all the parts of the plant, which includes roots. Some of the plants store food in their roots. We eat such roots as food. For example radish, carrot, sweet potato, turnip and tapioca. which we eat as food are the roots of the respective plants.
Stem
The part of a plant which rises vertically up from the ground is called stem.
The Stems of the plants are, however, weak and cannot stand erect. The stem of the tree is the strongest part of the tree and is know as trunk. Most of the tree trunks are covered with a tough layer called “bark“.
The main functions of the stem of a plant are as follows :
(1) The stem holds the plant upright (or erect).
(2) The stem of a plant carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plant.
(3) The stem carries the prepared food from leaves to other parts of the plant .
(4) The stem hold the leaves in such a way that the leaves are able to get plenty of sunlight for preparing food by photosynthesis.
Tubes in stem
The stem of a plant has a large number of narrow tubes inside it.
(1) One type of tubes in the stem carry water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts. The leaves of the plant make food by photosynthesis.
(2) Another types of tubes present in the stem carry food from the leaves to all other parts of the plants, including roots.
Leaf
The leaf is a thin, broad, flat and green part of a plant which is attached to the stem or branch.
A plant has large number of leaves. Leaves of different plants have different shapes and sizes, but all of them have same basic structure.
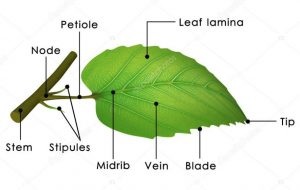
Structure of leaf
(1) A leaf consists mainly of two parts lamina and petiole.
Lamina is commonly as leaf blade and petiole is commonly known as leaf stalk.
The broad green part of the leaf is called lamina.
The thin stalk with which leaf is attached to the stem is called “petiole”.
(2) There is a mid-rib or main vein in the centre of lamina. A large number of veins spread out from the mid-rib to all the parts of the leaf. The mid-rib and veins consist of bundles of tiny tubes some of which carry water into the leaf, and other carry away the food from the leaf.
(3) There are minute pores on the surface of a leaf which are called stomata which
(i) allows the gases to move in and out of the leaf
(ii) also allow excess water vapours to go out of the leaf.
The leaves of plants contain a green coloured pigment called chlorophyll.
Function of chlorophyll
(1) Chlorophyll impart green colour to the leaves.
(2) Chlorophyll can absorb energy from sunlight.
The leaves has three main functions
(1) The leaves make food for the plant by photosynthesis.
(2) The leaves get rid of excess water from the plant through transpiration.
(3) The leaves carry out the process of respiration in plants.
The leaves make food for the plant by the process of photosynthesis.
In photosynthesis the green leaves of plant combine carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight to make food and Oxygen gas.
Process of photosynthesis
(1) Carbon dioxide gas needed for making food is taken by the leaves from air and water is carried into leaves from the soil through the stem.
(2) Sunlight provides the energy for making food.
(3) Chlorophyll present in the green leaves helps in tracking energy from sunlight.
(4) Oxygen gas is produced in the leaves during photosynthesis. This oxygen goes into air.
(5) The simplest food prepared by the leaves by photosynthesis is glucose. Some of the glucose is converted into starch. This starch is stored as food in various parts of the plant.
The process by which green plants use sunlight to make food from carbon dioxide and water is called photosynthesis.
Transpiration
Plants keeps on absorbing water from the soil all the time through its roots due to this a lot of water collects in the body of the plant. Some of the water is used by the plant in making food . The extra water present in the body of plant is given out constantly as water vapours through the tiny pores of the leaves. The evaporation of water from the leaves of plant is called transpiration.
During transpiration the excess water present in the plant is lost into the air as water vapours. Plants release a lot of water vapour into the air through the process of transpiration. This water vapour in air helps in bringing rain.
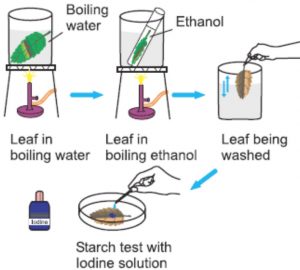
Activity: Leaves make food by photosynthesis
(1) Pluck a green leaf from a potted plant which has been kept in sunlight.
(2) Put the green leaf in a small beaker and cover it completely by adding alcohol.
(3) Place the beaker containing leaf and alcohol in a bigger beaker containing water.
Heat the water in biggest beaker over a burner. The hot water will then heat alcohol in small beaker. The hot alcohol removes the green colour from the leaf.
(4) Keep heating till all the green colour of the leaf is removed. The leaf becomes almost colourless and the alcohol becomes green.
(5) Take out the decolourised leaf from alcohol and wash it thoroughly with water to remove chlorophyll.
(6) Place the decolourised leaf in a petri-dish. Pour dilute iodine solution over the decolourised leaf with the help of a dropper.
(7) The leaf turns blue black showing the presence of starch in it. The starch is the food which has been prepared by the leaf by photosynthesis.
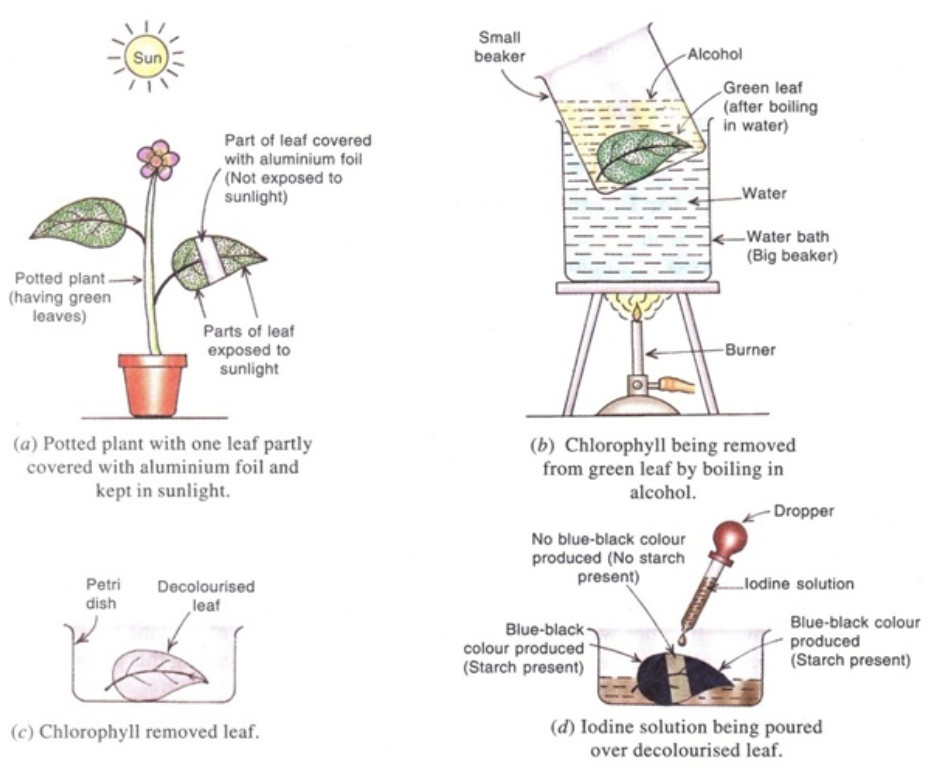
Activity: To show that sunlight is necessary for Photosynthesis
(1) Take a potted plant having green leaves and place it in completely dark place for 2 to 3 days to destarch its leaves.
(2) Take a thin strip of aluminium foil and wrap it in the centre of one leaf on both the sides, while the leaf is still attached to the plant. The aluminium foil should be fixed tightly to the leaf so that sunlight may not enter it from the side. Only the middle part of the leaf is covered with aluminium foil. The remaining part of leaf remains uncovered.
(3) Keep the potted plant in bright sunlight for 3 to 4 days.
(4) Pluck the partially covered leaf from the plant and remove the aluminium foil.
(5) Remove chlorophyll from this leaf by heating in alcohol. The leaf becomes colourless.Wash it with water.
(6) Place the decolourised leaf in a petri-dish. Pour dilute iodine solution over the decolorised leaf with the help of a dropper.
(7) The middle part of leaf which was covered by aluminium foil, does not turn blue black on adding iodine solution, showing that no starch is present in the middle part of the leaf. This means that the middle part of the leaf which does not get sunlight, could not make starch food by photosynthesis.
(8) The uncovered parts of leaf which were exposed to sunlight, turn blue black on adding iodine solution, showing that starch is present in the outer parts of the leaf.This means that the outer parts of leaf which got sunlight, could make starch food by photosynthesis.
Activity : Transpiration in plants
(1) Take a well-watered potted plant having big leaves.
(2) Enclose a leafy stem of the plant in a clean polythene bag and seal the mouth of bag properly.
(3) keep this potted plant in sunlight for 2 to 3 hrs.
(4) We will see a number of water droplets on the inner side of the polythene bag.
(5) The leaves of plant give out water vapour.Since the leaves are enclosed in polythene bag, the water vapours cannot escape into air.
(6) The water vapour given out by the covered leaves keeps on collecting inside the polythene bag.
(7) Some of this water vapour condenses to form tiny drops of water.
(8) This activity shows that the leaves of plant lose water through transpiration.
| Notes for Chapter 7 : Getting to Know Plants |


this is very good
This is a well explained presentation of this topic and will always help students in school topics and for general knowledge
children can always get more knowledge by seeing websites like this and focus when they are board of looking at the books they get from school
Very much interesting and informative
It was very informative
Very well covered in simple ,easy to understand steps
Lovely information helps in making project thanks u so much dear teacher it’s has been great help
Indeed very good efforts and service to students. Thanks a lot.
Such beautiful notes…..No need of downloading apps if you can find such amazing notes on google itself…..Really..your efforts are great.As a parent of 6th std child,no need of books also.
This is superb
It’s very helped me
This was helpful for writing notes and the diagrams are clear.
I could revise 2-3 chapters here and this is very helpful
I recommended this to my classmates and they study here in this site.
Thank you for this knowledge. would request for some Quizzes so that we can test our child’s knowledge