Question 1 What is meant by an electric circuit?
Question 2 Draw a circuit consisting of a cell, a torch bulb and connecting wires?
Question 3 What is meant by a complete circuit?
Question 4 What is meant by an open circuit?
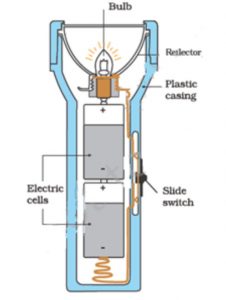
Question 5 Draw a labelled diagram of a torch?
Question 6 Where does a torch gets electricity from?
Question 7 Why do we need a switch in the torch?
Question 8 How does a fused bulb differ from a normal bulb?
Question 9 What happens to the circuit when the bulb in it gets fused?
Question 10 What is the purpose of using an electric switch?
Question 11 Name some electrical gadgets which have switches built into them?
Question 12 What is the function of a switch?
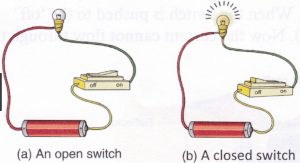
Question 13 What is an open switch?
Question 14 What is a closed switch?
Question 15 What is torch?
Also, Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
Contents
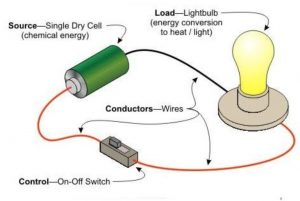
Electric Circuit
An electric circuit is a path along which electricity can flow.
A simple electric circuit consists of a cell, torch bulb and two pieces of wire (called connecting wires).
(1) Connect the torch bulb to the positive and negative terminals of a cell by using two pieces of wire.
(2) One end of the wire is connected to the positive terminal (metal cap) of the cell and the other end of this wire is connected to the metal tip at the base of the torch bulb.
(3) One end of the second wire is connected to the negative terminal (metal disc) of the cell, and the other end of this wire is connected to the metal case of the torch bulb.
(4) On connecting the torch bulb between the two terminals of the cell, the bulb lights up or glows. The bulb lights up because electricity flows through its filament.
(5) Electricity or electric current from one end of the cell flows along the wire through the bulb and then back to the cell along the other wire.
(6) The wires and bulb form a continuous path between the two terminals of the cell for electricity to flow through. This path is called an electric circuit.
The electric circuit provides a complete path for electricity to pass (or current to flow)
between the two terminals of an electric cell. The bulb glows only when electricity (or electric current) passes through the circuit.
Complete Circuit or Closed Circuit
An electric circuit in which there is no gap in the connections between the terminals of the cell, wires and bulb, etc., is called a complete circuit or closed circuit. A bulb lights up when the circuit is complete (or closed).
In a closed circuit, the electric current passes from one terminal of the cell to the
other through connecting wires and bulb. In an electric circuit, the direction of flow of electricity (or electric current) is taken to be from the positive terminal of the cell to the negative terminal of the cell.
The electric circuit in which there is a gap in the connections between the terminals of the cell, wires and the bulb, etc is called an open circuit (or incomplete circuit). Electricity does not flow through an open circuit because there is a gap in its path. A bulb will not light up if there is a gap in the circuit. A bulb will not light up if the circuit is open (or broken).
Fused Bulb
Sometimes an electric bulb does not glow even if it is connected to a cell by wires without any gap in the circuit. This can happen if the bulb has got fused. When the filament (thin wire) of a bulb gets broken, the bulb is said to be fused.
A bulb may fuse due to normal wear and tear of the filament or when too much electricity is passed through it suddenly. A break in the filament of a bulb means a break in the path of electricity between the terminals of the cell.
When we have a fused bulb in a circuit, the circuit gets open (or broken) and electricity cannot pass through it. Since no electricity passes through the broken filament of a fused bulb, a fused bulb does not light up even if it connected properly to a cell.
We should made the electric circuit by using metal wires (such as copper wires) because
copper wires are conductors of electricity. That is, copper wires can conduct (or carry) electricity through them. We make a circuit using cotton threads or jute strings, then the bulb will not glow. This is because the cotton threads or jute strings are non-conductors of electricity (they are insulators). That is cotton threads or jute strings cannot conduct (or carry) electricity through them. Thus, electricity can only flow if there is a complete circuit made of conductors (such as electric wires, bulb, etc.)
A Switch
If we want to ‘turn on’ or ‘turn off’ a bulb (or any other electrical appliance) easily, we should connect a switch in the electric circuit. The switch is a simple device which is used to ‘open’ or close a circuit.
Open Circuit
An open circuit means that there is a break (or gap) in the circuit whereas a closed circuit means that it is a complete circuit (having no gap).
Switch
A switch is a simple device which breaks a circuit or completes a circuit, as desired by us. A switch works by opening and closing a gap in an electric circuit.
When the switch is in the ‘off position’, a gap opens up in the circuit due to which electricity stops flowing in the circuit and hence the electrical appliance stops working.
When the switch is turned on, the gap in the circuit is closed and a complete circuit is made. Due to complete circuit, electricity starts flowing in the circuit and electrical appliance will now start working.The purpose of using a switch is to ‘turn on’ or ‘turn off’ an electrical appliance by closing the circuit or opening the circuit respectively.
Some of the electrical appliances which have inbuilt switches are table fan, room heater, room cooler, mixer and grinder, table lamp, washing machine, hair drier, drilling machine, torch, television, radio set and microwave, oven. It is usually very difficult and inconvenient to keep the two wires (coming from a cell) in touch with the two terminals of a torch bulb just by holding the bulb in hand or by fixing with adhesive tape. So, for the sake of convenience, the torch bulb is fixed in a bulb holder. The two terminals of the bulb are connected to the two terminals of the bulb holder for making connections in the circuit.
Similarly, a cell can also be put in a small cardboard box so as to hold two wires in contact with its two terminals, rather than using rubber bands or adhesive tape for this purpose.
Adding a Switch to the Electric Circuit
An electric circuit consist of a cell, a torch bulb and two wires which makes the bulb light up. If we want to turn the bulb on’ and off easily, we should add a switch in the circuit.
We have a cell having a positive terminal (+) and a negative terminal (-). The positive terminal of the cell is connected to one end of the switch with a wire. Another wire connects the other end of switch to one side of the bulb holder.
The negative terminal of the cell is connected to the other end of the bulb holder directly by means of a wire. Thus, the positive terminal of cell is connected to the bulb holder through a switch but the negative terminal of the cell is connected to bulb holder directly.
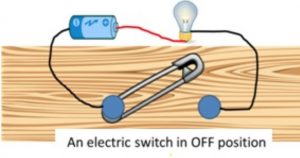
(a) In the circuit, the safety pin is not touching the other drawing pin, so the switch is in the off position. There is a gap between the end of safety pin and the second drawing pin.
The circuit is incomplete (or open) due to which electricity does not flow in the circuit in this case. So the bulb does not light up.
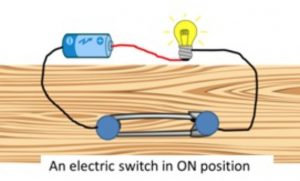
(b) Move the safety pin so that its free end now touches the other drawing pin. We will see that the bulb lights up. Actually, when we make the free end of safety pin touch the other drawing pin, the safety pin covers the whole gap between the two drawing pins.
Since the safety pin is made of metal, it completes the circuit and allows electricity to pass through it. Due to this the bulb lights up.
The switch is now said to be in ‘on’ position. As long as the switch remains in the ‘on position, electricity will keep on flowing in the circuit and the bulb will continue to glow.
(c) Now move the free end of the safety pin away from the second drawing pin. This will again create a gap in the circuit. The electricity will stop flowing in the circuit and hence the bulb will stop glowing.
Thus, we can turn off the lighted bulb by bringing the switch back to the off position.
The switch can be used to ‘turn on’ or ‘turn off’ the bulb again and again as desired by us.
Torch
A torch is a portable electric lamp which uses two (or more) cells to light a small bulb. A torch is used to provide light when going out during a dark night or when electricity supply fails at home. The torch has a bulb that lights up when it is switched on.
A torch contains a simple electric circuit. In a torch, two (or more) cells are connected to a torch bulb through a sliding switch. When the torch is needed to provide light, we close the sliding switch by pushing it forward so that the circuit is completed and the bulb lights up.
When the torch light is not needed, the sliding switch is opened by pushing it backwards so that the circuit breaks and bulb is turned off. A torch gets electricity from the cells kept inside it.
A torch has two or more cells. The cells in a torch have to be joined correctly. The two cells in a torch are joined like this: The positive terminal of one cell is always kept in contact with the negative terminal of the other cell. The positive terminal of first cell is in contact with the base of the bulb and the positive terminal of second cell is in contact with the negative terminal of the first cell.
| Notes for Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits |

Thank you for the write up, Mrs Shilpi Nagpal. Please may I have a pdf copy of Electricity and Circuit. I would like to know more about it and equally teach and assess my students with it.
Thank you for your understanding.
Notes are very helpful . Thankyou
The notes were very helpful and helped in Exams also
THANKYOU SO MUCH
EXCELLENT POINTS!!!
Well done mam
Thank you God bless you
Thank you so much.
The notes are helpful.
thank you so much for this.. my science teacher in 6th grade was so bad and I needed a basic understanding, ill start to understand more but I wanted to send my thanks