Question 1 Define the term ionic bond?
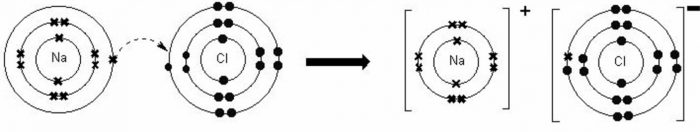
Question 2 Explain the formation of sodium chloride by electron transfer?
Question 3 Give few properties of ionic compounds?
Question 4 Why ionic compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state?
Ionic Bond
Ionic bond is formed by transfer of electrons from one atom to another. In this one atom can donate electrons to achieve the inert gas electron configuration and the other atom needs electrons to achieve the inert gas configuration.
Metals having 1,2,3 electrons in their outer shell donate electrons.
Metals having 4,5,6,7 electrons in their outer shell accept electrons.
Formation of Sodium Chloride
Properties of Ionic Compounds
(1) They are usually crystalline solids because their oppositely charged ions attract one another strongly and form a regular crystal structure.
(2) They have high melting and boiling point.
The ionic compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so lots of heat energy is required to break this force.
(3) They are usually soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents.(kerosene, petrol, benzene, acetone)
(4) They conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted.
Ionic compounds are made up of ions but do not conduct electricity in solid state because ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces and cannot move freely.
When we dissolve ionic compound in water, the structure is broken and ions become free to move and conduct electricity.
very well explained
I like this explanation thanks