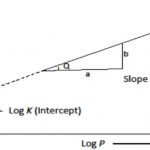
Adsorption Isotherm The adsorption on a given surface generally increases with increase in pressure (for gases) and concentration (for solutions) at a constant temperature. The extent of adsorption of a gas per unit mass of adsorbent depends upon the pressure of the gas. The relation between the amount of substance adsorbed by the adsorbent and the equilibrium gas pressure … [Read more...] about Adsorption Isotherms and Isobars
Class 12
Adsorption of Gases On Solids
Adsorption of Gases on Solids The extent of adsorption of a gas on a solid surface is affected by the following factors: 1) Nature of the gas 2) Nature of adsorbent 3) Specific area of the adsorbent 4) Effect of temperature 5) Effect of pressure 6) Activation of adsorbent. Nature of the gas (or adsorbate) The adsorption depends upon the nature of the gas … [Read more...] about Adsorption of Gases On Solids
Types of Adsorption
Types of Adsorption Depending upon the nature of forces which hold the molecules of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent, the adsorption is classified into two types: 1) Physical adsorption and 2) Chemical adsorption. Physical Adsorption When the particles of the adsorbate are held to the surface of the adsorbent by the physical forces such as van der Waals … [Read more...] about Types of Adsorption
Adsorption
The surface of a solid has a tendency to attract and retain the molecules of the phase with which it comes into contact. These molecules remain only at the surface of the solid and do not penetrate into the bulk. For example: When a small amount of finely divided charcoal is put into vessel containing a gas, it is observed that the pressure of the gas decreases rapidly at … [Read more...] about Adsorption
Effect of Catalyst on Reaction Rate
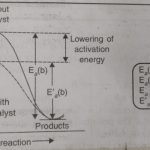
The rate of a reaction can be increased by raising the temperature. However, temperature can be raised within certain limits because in certain cases, the reactants become unstable at higher temperatures and decompose. Many reactions are made to proceed at an increased rate by the presence of some other substance. For example : a mixture of H2 and O2 does not react at … [Read more...] about Effect of Catalyst on Reaction Rate