Contents
Adsorption Isotherm
The adsorption on a given surface generally increases with increase in pressure (for gases) and concentration (for solutions) at a constant temperature.
The extent of adsorption of a gas per unit mass of adsorbent depends upon the pressure of the gas. The relation between the amount of substance adsorbed by the adsorbent and the equilibrium gas pressure (or concentration for solutions) at constant temperature is called an adsorption isotherm.
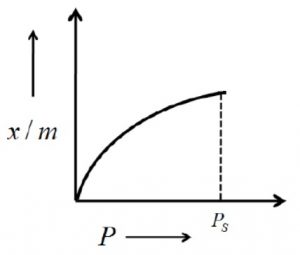
The extent of adsorption is usually expressed as x/m where x is the mass of adsorbate and m is the mass of the adsorbent.
The extent of adsorption (x/m) increases with pressure and becomes maximum corresponding to pressure ps called equilibrium pressure. Since adsorption is a reversible process, the desorption also takes place simultaneously. At this pressure (ps) the amount of gas adsorbed becomes equal to the amount of gas desorbed so that the extent of adsorption becomes constant even though the pressure is increased. This state is also called saturation state and ps is called saturation pressure.
Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm
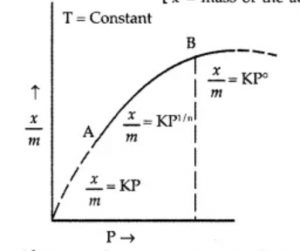
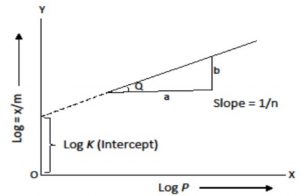
where n can take any whole number value which depends upon the nature of adsorbate and adsorbent. The above relationship is also called Freundlich’s adsorption isotherm.
Calculation of K and n of adsorption isotherm
Adsorption Isobars
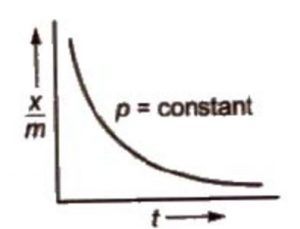
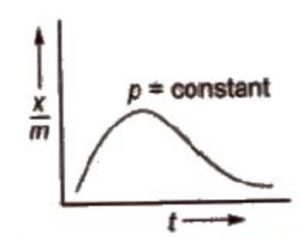
In case of chemisorption, the adsorption initially increases with rise in temperature and then decreases. Like all chemical reactions, some activation energy is required for chemisorption.
a) At low temperature, x/m is small.
b) As temperature is increased the molecules of the adsorbate gain energy and become equal to activation energy so that proper bonds are formed with the adsorbent molecules.
c) Therefore, initially amount of gas adsorbed increases with rise in temperature. Further
increase of temperature will increase the energy of molecules which have already been adsorbed.
d) This would increase the rate of desorption and, therefore, decrease the extent of adsorption.
The adsorption isobar graphs can be used to distinguish between physical and chemical adsorptions. In physical adsorption, there is a regular decrease as temperature increases. However, in chemisorption, there is initial increase and then it decreases.
Adsorption from solution
Solid adsorbents adsorb certain solutes from solution in preference to other solutes and solvents.
For example : animal charcoal decolourises impure sugar solution by adsorbing colouring dye in preference to sugar molecules.
Leave a Reply