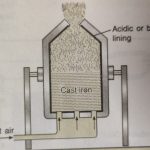
Extraction of Crude Metal from Concentrated Ore The process of working of the concentrated ore to extract metal depends upon the nature of the ore as well as the nature of the impurities present in the ore. The concentrated ore must be converted into a form which is suitable for reduction. Generally, the sulphide ores are converted to oxides before reduction because oxides … [Read more...] about Extraction of Crude Metal from Concentrated Ore
Chemistry
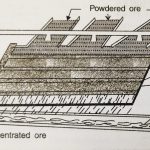
Crushing, Grinding and Concentration of the Ore
Extraction of Elements Most of the elements do not occur in the free state in nature but these occur in the combined states. In the combined states, metals are usually found in the oxidised form (e.g., Fe2O3, MnO2, SnO2 etc.), while non-metals occur in the reduced form such as halide ions (Cl¯, Br¯, I¯). The metals can be obtained from their oxidised forms by reduction … [Read more...] about Crushing, Grinding and Concentration of the Ore
Modes of Occurrence of Elements and Metals
Modes of Occurrence of Elements The elements generally occur in the free state (called native state) or in the combined state. This is mainly because of different chemical reactivities of elements. 1) Native State The elements which have very low reactivity and are not attacked by oxygen or air, moisture, carbon dioxide or other non-metals occur in the free state, called … [Read more...] about Modes of Occurrence of Elements and Metals
Emulsions, Gels and Application of Colloids
Emulsions Emulsions are the colloidal solutions in which both the dispersed phase and the dispersion medium are liquids. Emulsions are liquid-liquid colloidal systems i.e. the dispersion of finely divided droplets in another liquid. Any two immiscible liquids form an emulsion. For example: milk is a naturally occurring emulsion in which the particles (or globules) of … [Read more...] about Emulsions, Gels and Application of Colloids
Coagulation and Protection of Colloidal Solution
Coagulation of Colloidal Solutions 1) A small amount of an electrolyte is necessary for the stability of the colloidal sol. The ions of the electrolytes are adsorbed on the sol. particles and impart them some charge; positive or negative. 2) The charged colloidal particles repel one another and are prevented from coming close together to unite into bigger particles . 3) … [Read more...] about Coagulation and Protection of Colloidal Solution