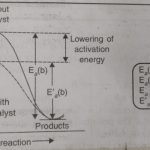
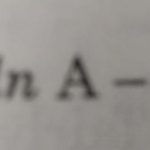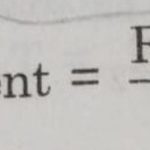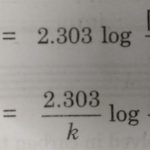The rate of a reaction can be increased by raising the temperature. However, temperature can be raised within certain limits because in certain cases, the reactants become unstable at higher temperatures and decompose. Many reactions are made to proceed at an increased rate by the presence of some other substance. For example : a mixture of H2 and O2 does not react at … [Read more...] about Effect of Catalyst on Reaction Rate
Chemical Kinetics
Arrhenius Equation and Activation Energy
Arrhenius Equation Arrhenius proposed a quantitative relationship between rate constant and temperature as: k= Ae-Ea/RT This equation is called Arrhenius equation in which constant A is known as Arrhenius factor or frequency factor. It is also called pre-exponential factor. It is a constant specific to a particular reaction. This factor is related to number of binary … [Read more...] about Arrhenius Equation and Activation Energy
Collision Theory
Pseudo Chemical Reactions Some reactions are first order each with respect to two different reactants i.e., A+B-------> Products Rate = k[A] [B] If one of the reactants is present in high concentration (solvent) then there is very little change in its concentration. The concentration of that reactant remains practically constant during the reaction. For example, if … [Read more...] about Collision Theory
Half Life Period of a Reaction
Half life period of a reaction is defined as the time during which the concentration of a reactant is reduced to half of its initial concentration. or The time in which half of a reaction is completed. It is generally denoted as t½ The half life period of a first order reaction may be calculated as given below: The first order rate equation for the reaction A … [Read more...] about Half Life Period of a Reaction
Experimental Determination of Order of a Reaction
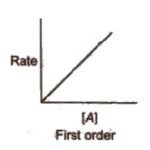
Experimental Determination of Order of a Reaction (1) Graphical method This method is used when there is only one reactant. It involves the following steps: 1) The concentrations of the reactants are measured by some suitable method. 2) A graph is plotted between concentration and time. 3) The instantaneous rates of the reaction at different times are calculated by … [Read more...] about Experimental Determination of Order of a Reaction