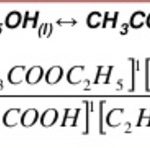Law of Mass Action The rate at which a substance reacts is proportional to its active mass and hence the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the active masses of the reactants. The active mass means molar concentration i.e. number of moles dissolved per litre of the solution. Suppose x g of NaOH are dissolved in V litres of solution. Then we can … [Read more...] about Law of Mass Action
Chemistry
Characteristics of Equilibrium Constant
Characteristics Of Equilibrium Constant (1) The value of the equilibrium constant for a particular reaction is always constant depending only upon the temperature of the reaction and is independent of the concentration of the reactant with which we start or the directions from which the equilibrium is approached. (2) If the reaction is reversed, the value of equilibrium … [Read more...] about Characteristics of Equilibrium Constant
Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constant
The numerical value of the equilibrium constant for a particular reaction is constant as long as the temperature is kept constant. The rate of a chemical reaction increases with increase in temperature. The extent of this increase in rate depends upon the energy of activation of the reaction. Since the energy of activation for the forward and backward reaction are … [Read more...] about Effect of Temperature on Equilibrium Constant
Equilibria in Physical Processes
Equilibrium represents the state of a process in which the properties like temperature, pressure, concentration of the system do not show any change with the passage of time. If the opposing processes involve only physical changes, the equilibrium is called physical equilibrium. If the opposing processes involve chemical changes i.e. the opposing processes are chemical … [Read more...] about Equilibria in Physical Processes
Gibbs Free Energy
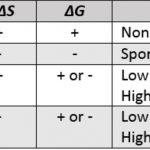
Another thermodynamic quantities that helps in predicting the spontaneity of a process is Gibbs free energy or Gibbs energy of Gibbs function. It is denoted by G and is given by the equation G=H -TS where H is the heat content ,T is the absolute temperature and S is the entropy of the system. G1 = H1 -TS1 for the initial state G2 = H2 -TS2 for the final … [Read more...] about Gibbs Free Energy