Question 1 Name the most important source of light on Earth?
Question 2 What are natural sources of light. Give example?
Question 3 What are luminous objects. Give example?
Question 4 What are non-luminous objects. Give example?
Question 5 What are man-made sources of light. Give example?
Question 6 What are transparent materials. Give examples?
Question 7 what are translucent materials. Give example?
Question 8 What are opaque materials. Give examples?
Question 9 On what principle does a pinhole camera object?
Question 10 Why we cannot see a book placed behind a wooden screen?
Question 11 How we are able to see a table lying in a room though it does not give out its own light?
Question 12 Why we cannot see the objects placed in a dark room?
Question 13 Give an activity to show that light travels in a straight line?
Question 14 State 2 differences between a pinhole camera image and shadows?
Question 15 What is a shadow?
Question 16 What is rectilinear propagation of light?
Question 17 How are we able to see the moon?
Question 18 What are the main characteristics of the image in a pinhole camera?
Question 19 What are the three things required to observe a shadow?
Also Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 Light and Shadow
Contents
Light
Light is a form of energy. We cannot see an object in the darkness. We need a source of light to make the object visible. During the day, Sun’s light allow us to see objects. At night artificial light makes us see objects. Light enables us to see objects from which it comes from or from which it is reflected light. We detect light with our eyes.
Sources of light
An object which gives out light is called a source of light.
The various sources of light around us are Sun, stars, bulb, tubelight, kerosene oil lamp, candle, torch, firefly etc.
The most important source of light for us is the Sun. It is about 150 million km away from us, its light makes the daytime bright on the earth. At night we use an electric bulb, tube light, lamp, candle or torch as a source of light.
Natural and Man-made sources of light
Sources of light can be divided into two groups: natural source of light and man made sources of light.
Natural Sources of light : Those sources of light which occur in nature as such are called natural sources of light.
For example: Sun, stars, meteors, firefly are natural sources of light.
Man-made sources of light : Those sources of light which have been made by man are called man-made sources of light.
For example: Electric bulb, tubelight, kerosene oil lamp, candle, torch are non-luminous sources of light.
Luminous and Non-luminous objects
An object which gives out its own light is called luminous object.
For example: Sun, stars, burning candles, electric bulb, glowing tube light, television screen, a piece of red hot iron, flame of gas burner, firefly are all luminous objects.
Since luminous objects give out their own light, they can be seen even in the dark. A luminous object can be seen because the light given out by it enters our eyes.
An object which does not give out its own light is called a non-luminous object.
For example: table, chair, book, flower pot, plants, clothes, bags, pen, pencil, mirror, shoe, moon, earth, planets, etc.
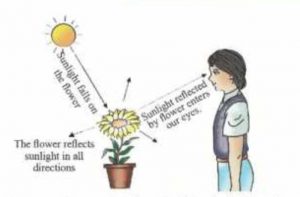
The non-luminous objects can be seen only when the light coming from a luminous object falls on them. This light is reflected by non-luminous objects in all directions. When this reflected light enters our eyes, we can see the non-luminous objects.
For example: Moon is a non-luminous object which does not have its own light. We can see the moon because it reflects sunlight into our eyes. When sunlight falls on the surface of moon, then some of this light sunlight is reflected by the moon towards the earth. And to us it appears as if the light is being given out by the moon itself. But moonlight is the sunlight which is reflected from the surface of moon. The planets can also be seen in the sky because they are reflectors of Sunlight.
A flower is a non-luminous object. It does not give its own light. We can see a flower because it reflect sunlight falling on it into our eyes. The flower reflects some of the sunlight falling on it in all the direction. When the sunlight reflected by flower enters our eyes, we are able to see the flower. During night time, the flower is visible to us because it reflects the light received from an electric bulb.
We can see many things kept in a room during the day on which sunlight does not fall directly. All the objects outside the room scatter the sunlight falling on them in all the direction. Even the air scatters some sunlight. It is this scattered sunlight which enters the room and helps us to see the things lying in the room which are not in direct sunlight.
We can see the table because it reflects the light falling on it in all directions. And when this reflected light coming from the table enters our eyes, we are able to see the table.
Transparent, translucent and opaque materials
Depending on behaviour towards light all the materials can be classified as transparent, translucent or opaque objects.
Transparent materials or objects
Those materials which allow all the light to pass through them are called transparent material.
For example: glass, polythene, air, water, oil.
If we look at a burning candle through a sheet of clear glass, we can see the candle and its flame clearly. This is because glass is a transparent material which allows all the light coming from candle and its flame to pass through it.
The window panes in our homes are usually made of transparent glass.
Our spectacles glasses are also transparent.
The glass tumbler in our kitchen are also transparent objects.
The test tube, flasks and beakers in Science laboratory are transparent.
A car windscreen is transparent.
If we are able to see through an object clearly, it is allowing all the light to pass through it and hence it is a transparent object.
Translucent Material
Those material which allow only some of the light to pass through them are called translucent materials.
For example: ground-glass, butter paper, oil paper, tissue paper, sheet of white cotton, muddy water, clouds etc.
If we look at burning candle through a piece of ground glass or butter paper we can see only a dim light of the candle. We can neither see the candle itself nor the candle flame clearly through the ground glass.
The windows of bathrooms in our homes are made of translucent material called ground glass so that though some outside light may enter the bathroom but nothing is visible clearly from outside.
Clouds are translucent material. Though we cannot see the sun through clouds on the cloudy day but still there is some sunlight all around. This is because being translucent, clouds allow some of the sunlight to pass through them due to which there is a light on earth even on cloudy day.
The translucent objects absorbs or reflect a good part of light falling on them and allow only some of the light to pass through them.
Opaque Objects
Those materials which do not allow any light to pass through them are called opaque materials.
For example: cardboard, book, door, metal sheet, brick wall, stones etc.
If we look at the burning candle through a piece of cardboard held in front of our eyes, we cannot see anything at all. This is because the cardboard does not allow the light of candle flame to pass through it and reach our eyes.
We cannot see anything through a wooden door because the wooden door is an opaque object which does not allow any light to pass through it.
The Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them because they absorb or reflect all the light falling on them.
Light travels in straight line
If we Shine a torch on a dark night we will see that the beam of light produced by a torch travels straight into darkness.
The beams of search light at the airport show that light travels in straight lines.
The beam of light coming from the projections room of a cinema hall and falling on the screen also shows that light travels in a straight line.
The formation of shadow by a source of light also suggest that the light travels in straight line. This is because if light could bend and travel in curved lines, then it would have reached behind the object and hence no shadow could have been formed.
The property of light travelling in straight line is called rectilinear propagation of light.
Activity 1
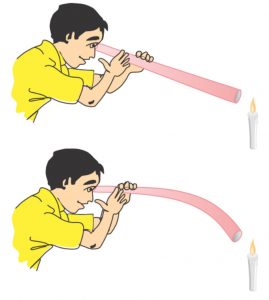
Fix a lighted candle on a table. Take a rubber tube, stretch it straight and look through it at the flame of the candle with one eye. We will find that when the rubber tube is straight, we can see the light of candle flame through it.
Now bend the rubber tube a little and look through it at the candle flame again. We cannot see the light of candle flame through a bent rubber tube. This means that the light of candle flame can travel through the hole of straight rubber tube but not through the bent rubber tube.
Activity 2
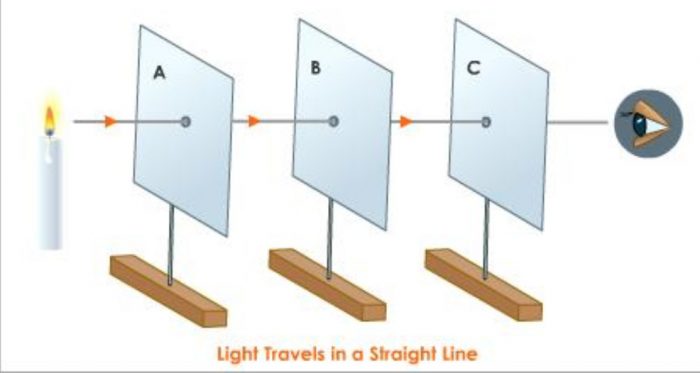
Fix the three cardboards vertically on the table in such a way that their holes are in a straight line.
Place a burning candle behind the farthest cardboard. The candles should have its flame at about the same height as the holes in the cardboards.
Look at the candle flame through the hole in the first cardboard. We can see the candle flame through the holes of the cardboards. Thus when all the cardboard holes are in straight line, light from candle reaches our eyes.
Now push the middle cardboard slightly out of its position so that the three holes do not remain in a straight line. If we look through the hole in the first cardboard, we cannot see the flame of candle now. This means that when all the holes of cardboard are not in a straight line, the light of the candle flame does not reach our eyes.
This shows that light travels in a straight path.
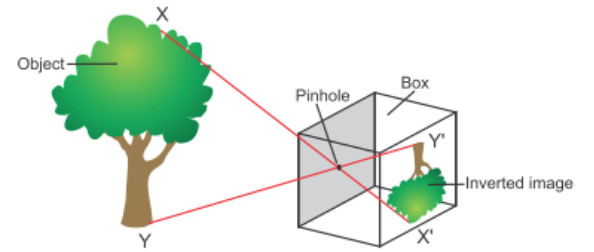
Pinhole camera
The pinhole camera consists of a closed box having a small pinhole in the front and a translucent screen at the back.
The translucent screen at the back side of the pinhole camera box is made of butter paper or tracing paper. The butter paper acts as a screen to receive the image of the object. Since butter paper is translucent, some light can pass through it due to which we can see the image formed on it by keeping our eye behind the pinhole camera.
Uses
It is usually used to view the images of various objects like trees and buildings.
The pinhole camera can also be used to take photograph of an object if a photographic film is placed on the screen.
Principle
The pinhole camera works on the principle that light travels in a straight line.
Light rays coming from an object and going in through the pinhole, travel in straight line to the screen.
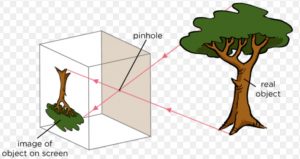
If we look into the pinhole camera by keeping our eye at its back side, we will see an image of the tree on the screen. This is because some of the light coming from the tree passes through the pinhole to form an image on the screen.
A ray of light coming from the point X of the tree passes through the pinhole in a straight line to form an image at point X’ on the screen. Another ray of light coming from the bottom Y of the tree also passes through the pinhole in a straight line to form an image at point Y’ on the screen. In this same way, each point on the tree XY forms its corresponding image on the screen between X’ and Y’. In this way, the image X’Y’ is produced on the screen.
The light coming from tree passes through the pinhole of the pinhole camera in a straight line. The working of pinhole camera illustrates the property that light travels in straight line.
The light rays XX’ and YY’ coming from the top and bottom of the tree crossover at the pinhole . Due to the crossing over of light rays at the pinhole, the top of the tree comes at the bottom in image and the bottom of the tree comes at the top in image.
Inverted Image
The upside down image of an object formed by a pinhole camera is called an inverted image.
An inverted image is formed in a pinhole camera because the light rays coming from the top and bottom of the object cross over at the pinhole.
Main characteristics of the image in a pinhole camera
(1) The image in a pinhole camera is inverted as compared to the object.
(2) The image in a pinhole camera is real because it can be formed on a screen.
(3) The image in a pinhole camera is of the same colour as the object.
(4) The image in a pinhole camera can be smaller than the object or equal to the object or bigger than the objects.
(5) A pinhole camera can also be used to take the photograph of an object if a photographic film is placed on the screen. The pinhole cameras were used for taking photographs.
The pinhole cameras is kept small so that only a very small number of light rays pass through it and a sharp image of the object is formed on the screen.
If the pinhole camera is made bigger, then a large number of light rays from a given point of the object pass through it due to which a blurred image of the object is formed.
Natural pinhole
On a sunny day, when we pass under a tree covered with a very large number of leaves, we often see bright circular patches of light on the ground. These bright circular patches of light are the pinhole images of the sun. This is because the small holes between the cluster of the leaves act as a pinhole and light coming from the sun passes through these natural pinholes to form bright circular images of the sun on the ground below the shady tree. In this case, the sun is the objects, the tiny gaps between leaves are the pin holes and the ground at as the screen.
Shadows
When an object is placed in front of a source of light, it produces a shade or dark area behind it. Shadows are formed when light is stopped by an object.
An opaque objects stops the light completely, so an opaque object casts a dark shadow behind it.
A translucent objects stops the light partially, so a translucent object casts a weak shadow.
A transparent object does not stop any light from passing through it so a transparent object does not cause any shadow behind it.
A shadow is formed when an opaque object comes in the path of light and stops it. An object forms shadow on the opposite side to the source of light. The shadows of objects are usually similar in outline to the object and hence we can identify the object from their shadows.
The shadow of a ceiling fan hung in the centre of room will fall on the side opposite to the lighted electric bulb. A lighted candle fixed in a room will also cast our shadow and that of the ceiling fan on the opposite side.
The sunlight also forms shadows of the objects which are on the ground or near the ground. If we stand in the sun, our body cast a shadow on the ground. And when we walk in the sun, our shadows always walk with us.
Our shadow is very long in the morning when the sun just rises. The length of our shadow goes on decreasing till noon. Our shadow is shortest at noon. The length of our Shadow starts increasing in the afternoon. And our shadow becomes very long in the evening, just before sunset.
The shadow of an object can be seen only on a screen. The surface such as the walls of a room, a building and even ground act as screen for the shadows which we see in our everyday life.
We require 3 things to observe a shadow
(1) A source of light
(2) An opaque object
(3) A screen on which the shadow can be seen.
Shadows are formed because light rays travels in a straight line, and they cannot bend round the corners of the objects. The shape of the shadow is also the same as the shape of the object because light travels in a straight line path.
When a bird is on the ground, we can see its shadow which is formed by sunlight. The bird obstructs the sunlight to form shadow on the nearby ground. When the same bird is flying high up in the air, even then the bird obstructs the sunlight falling on it but its shadow is not seen on the ground because the ground is very, very far below the bird.
When an aeroplane is parked on the ground, we can see it shadow which is formed by sunlight. The aeroplane obstructs the sunlight to form a shadow on the nearby ground.
When the same aeroplane is flying high up in the air, even then the aeroplane obstructs the sunlight falling on it but its shadow is not seen on the ground because the ground is very, very far below the aeroplane.
Sometimes the shadow of opaque objects are not seen clearly. Our shadow and that of a ceiling fan formed by an electric bulb or a lighted candle can be seen clearly but the shadow formed by a fluorescent tube light cannot be seen clearly.
An electric bulb and candle forms of shadows because they are comparatively small sources of light.
A fluorescent tube light does not form sharp shadows because it is quite large source of light. Since a fluorescent tube light is very long, therefore, some of the light from it always reaches behind the opaque objects leading to the formation of a very faint shadows. The shadows formed by fluorescent tube light are so faint that it is usually very difficult to see them.
No Shadow can be formed when there is no source of light as on a dark moonless night or in a dark room.
Characteristics of shadow of an Object
(1) The shadow of an object is erect i.e. same side up as the object.
(2) The shadow of an object is real.
(3) Irrespective of the colour of the object the shadow is always black.
(4) The shadow can be smaller than object, equal or bigger than object.
Difference between pinhole image and Shadow:
(1) The pinhole image of an object is inverted whereas the shadow of an object is erect.
(2) The pinhole image of an object is of the same colour as the object but the shadow of an object is always black.
The formation of image in a pinhole camera and the formation of shadow by object placed in the path of light provide the evidence that light travels in a straight line.
| Notes for Chapter 11 Light, Shadows and Reflections |
Super activity’s plz upload in pdf format….
Nice job dear. Nicely explained every concept. Keep it up.
Yes please upload in pdf format
Amazing article, I gain lots of knowledge from this post.
Thank you for sharing this article
Excellent notes Ma’am!
Thankyou for the well prepared notes.
Well explained. Thank u do much.Kindly explain reflection too.
Now i’m extremely fascinated as well as your writing abilities while well as with the structure for your website.. Anyway keep up to date the nice top quality publishing, it is actually unusual to take a look a great website like this one at present.
Hi. Thanks for the lovely lesson on ‘light’
Very well explained ma’am. Really notes are too good.
A lovely and well explained lesson thanks for this keep it up