Class 8 Science Chapter 8 |
Cell Structure and Functions NCERT Solutions
1. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled body. (T/F)
(b) Muscle cells are branched. (T/F)
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. (T/F)
(d) Amoeba has irregular shape. (T/F)
Answer:
(a) Unicellular organisms have one-celled body. (T)
(b) Muscle cells are branched. (F)
(c) The basic living unit of an organism is an organ. (F)
(d) Amoeba has irregular shape. (T)
2. Make a sketch of the human nerve cell. What function do nerve cells perform?
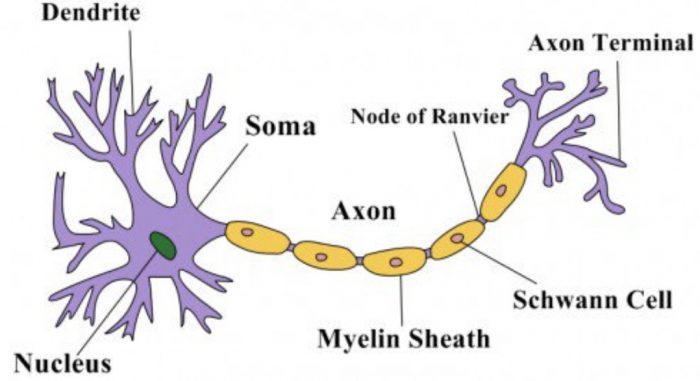
The function of nerve cell is to transmit message to the brain and also to take away messages from brain to the receptors organs. They help to control and coordinate the working of different parts of the body.
3. Write short notes on the following.
(a) Cytoplasm
It is a transparent jelly like material which fills the cell between nucleus and cell membrane. It has many tiny structures in it. The various structures present in the cytoplasm of a cell are called organelles. Cytoplasm of all cells contain other organelles such as mitochondria, golgi bodies, nucleus and ribosomes. The cytoplasm and nucleus taken together make up protoplasm. Most of the metabolic activities occur inside cytoplasm.
4. Which part of the cell contains organelles?
Cytoplasm, gelatinous fluid inside a cell contains various organelles like mitochondria, Golgi bodies, ribosomes etc.
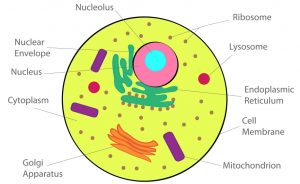
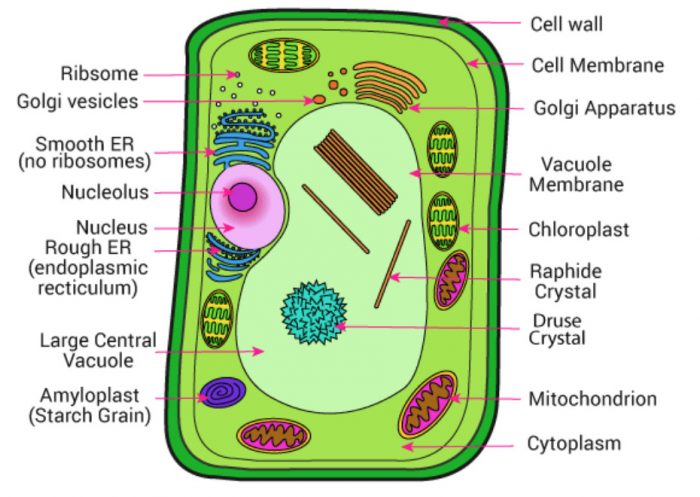
5. Make sketches of animal and plant cells. State three differences between them.
Animal cell
Plant cell
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| (1) Cell wall is present. | Cell wall is absent. |
| (2)Vacuole are small in size | Vacuole are large in size |
| (3) Plastids are present | Plastids are absent |
6. State the difference between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
| Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
| (1) The cells having nuclear material without nuclear membrane are termed as prokaryotic cells | The cells having a well-organized nucleus with a nuclear membrane are termed as eukaryotic cells |
| (2) They are unicellular | They are multicellular |
| (3) The nuclear material is in direct contact with the cytoplasm. | The nuclear membrane in eukaryotic cell is not in direct contact with cytoplasm, |
| (4) For ex: Bacteria, blue green algae | For Ex: Amoeba, cheek cell, onion peel cell , plants, animals, protozoa, fungi |
7. Where are chromosomes found in a cell? State their function.
Nucleus contains thread like structures called chromosomes. They contain genes. The function of chromosomes is to transfer the characteristics from the parents to the offspring through the genes.
8. ‘Cells are the basic structural units of living organisms’. Explain.
Cells are the basic units of life. All the living things are made up of cells. They are the building blocks of plants and animals. A cell is the smallest unit of life which has a definite structure and performs a specific function. Cells exist in various shapes and sizes and perform a wide range of activities. Their shapes and sizes are related to the function it performs.
9. Explain why chloroplasts are found only in plant cells?
They are green coloured organelles present in the cytoplasm of plant cells. The green colour of chloroplast is due to the presence of a green pigment called chlorophyll in them. Chlorophyll can absorb sunlight energy. In chloroplast, carbon dioxide and water combine in the presence of sunlight energy to produce food such as glucose. They are found only in those plant cells which carry out photosynthesis.
10. Complete the crossword with the help of clues given below.
Across
1. This is necessary for
photosynthesis.
3. Term for component present
in the cytoplasm.
6. The living substance in the
cell.
8. Units of inheritance present
on the chromosomes.
Down
1. Green plastids.
2. Formed by collection of
tissues.
4. It separates the contents of
the cell from the surrounding
medium.
5. Empty structure in the cytoplasm.
7. A group of cells
Answer:
Across:
Chlorophyll
Organelle
Protoplasm
Genes
Down:
Chloroplasts
Organ
Membrane
Vaculoe
Tissue

I like this
I like this it is very nice for me