Question 1 What is the main cause of wind movements on the surface of the earth?
Question 2 The uneven heating of earth can take place under two situations? What are these two situations?
Question 3 Explain how winds are produced by uneven heating on the earth between the equator and the poles not blow in the exact south-north direction?
Question 4 Explain how uneven heating of land and ocean water in summer generates winds?
Question 5 Explain why when we blow air in the space between two inflated balloons and hanging about 10 cm apart on a stick, the two balloons come closer?
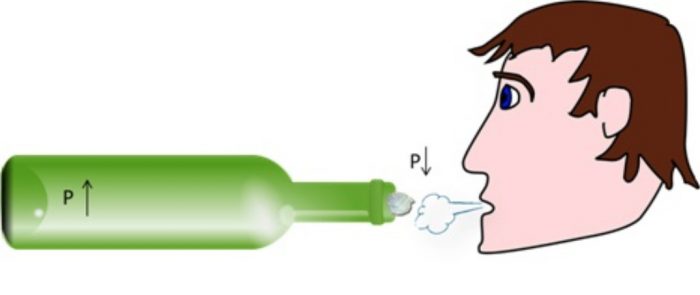
Question 6 A small paper ball is kept in the neck of a glass bottle held horizontally? Explain why, it is difficult to force the paper ball by blowing air into the bottle?
Question 7 What would happen if high speed winds blows over a house having weak tin roof?
Question 8 What are monsoon winds?
Question 9 Name an instrument to measure wind speed?
Question 10 Name an instrument to find wind direction?
Question 11 Why monsoon winds are very important for our country?
Contents
Wind
Wind is the movement of air which depends on the difference in air pressures (or atmospheric pressures) in the two regions.
Air moves (or flows) from the regions of high air pressure to regions of low air pressure in the atmosphere. The greater the difference in air pressure, the faster the air moves.
Uneven heating on the earth in different regions is the main cause of wind movements.
The equator of earth is at the minimum distance from the sun , so the region around the equator of earth (called equatorial region) gets the maximum heat from the sun and hence it is very hot.
As a region gets more and more away from the equator (towards the poles), the amount of sun’s heat received by the region goes on decreasing gradually leading to less hot climates (or cooler climates).
The poles of the earth (north pole and south pole) are at the maximum distance from the sun and hence get the minimum heat from the sun. So, the polar regions of the earth are very cold.
The uneven heating on the earth (which produces winds) can take place under two situations:
(1) Uneven heating between the equator and poles of the earth, and
(2) Uneven heating of land and water of oceans.
Wind is Produced by the Uneven Heating Between Equator and Poles of Earth
The regions close to the equator of earth get the maximum heat from the sun, so the air in equatorial regions gets heated and becomes warm . The warm air rises in the equatorial regions of earth creating an area of low air pressure. The cooler air from the regions of up to 30 degrees latitude belt on both the sides of the equator (being at higher pressure), rushes towards the equator to take the place of warm, rising air. This makes the wind to blow from the north and south directions towards the equator. The air at latitudes of about 60 degrees on both sides of the equator is warmer than at the poles.So, the warmer air at about 60 degrees latitudes rises up creating regions of low air pressure and cold air from the polar regions (being at higher pressure) rushes in to take its place. This makes the winds blow from the poles of the earth towards the warmer regions up to about 60 degrees latitudes. These winds also blow from the north and south directions towards the warmer latitude regions.
The winds produced by the uneven heating of the earth between the equator and the poles do not blow in the exact north-south direction because a change in the direction of winds is caused by the rotation of the earth on its axis.
Wind is produced by the Uneven Heating of Land and Water in Oceans
In summer, land near the equator of earth heats up faster than the water in oceans, so most of the time, the temperature of land is higher than that of water in oceans. The air over the land gets heated and rises creating a low pressure area. The cooler air from over the oceans(being at higher pressure), rushes towards the land. This causes the wind to blow from the oceans towards the land. The winds blowing from the oceans towards the land in summer are called monsoon winds.The process in which the winds coming from the oceans carry a lot of water vapour and bring rains is a part of the ‘water cycle’ in nature.
In India, the land gets heated much more in summer than the water in the Indian ocean. This uneven heating of land’ and ‘water in Indian ocean’ during summer, generates monsoon winds from the Indian ocean. The monsoon winds coming from the south-west direction in summer carry a lot of water vapour from the Indian ocean and bring heavy rains.
During summer, wind blows from the oceans towards land. In winter, the direction of wind flow gets reversed. During winter, wind blows from the land towards the ocean.
During winter, land cools down faster than the water in oceans. So, the temperature of water in oceans is higher than that of land. The warm air over the oceans rises up creating a region of low pressure and cooler air from the land rushes towards the ocean. This causes wind to blow from land towards the oceans. The winds coming from colder land regions (or colder winds) carry only a little of water vapour and hence bring only a small amount of rain in winter season.
High speed winds
Fast moving air creates a region of low pressure. Fast blowing wind creates a region of low pressure. High speed wind are accompanied by reduced air pressure.
Activity
Take two balloons of equal size. Fill a little water into both the balloons (to make them slightly heavier) .Inflate both the balloons by filling air into them with mouth (or pump) and tie their mouths properly with strong threads. Hang the two inflated balloons about 10 cm apart on a stick with the help of threads tied to their mouths.
If we blow air (or wind) in the space between the two balloons from our mouth, we will see that the two balloons come closer. When we blow air (for wind) between the balloons, then the fast moving air (or fast moving wind) creates a region of low air pressure in the space between the two balloons. The air pressure on the outside of the balloons being higher, pushes the two balloons towards each other and makes them come closer. The fast moving air (or fast moving wind) creates a region of low air pressure (or reduced air pressure).
Activity
Take a piece of paper and crumple it to make a small paper ball.Hold an empty glass bottle on its side and place the small paper ball in the neck of the bottle just inside its mouth.Now blow air into the bottle from our mouth. When we blow air into the bottle, the paper ball kept in the neck of the bottle remains unaffected, the paper ball does not go inside the bottle. When we blow air into the mouth of the bottle, then the air in the neck of bottle has high speed. This fast moving air reduces the air pressure in the neck of the bottle. The air pressure inside the bottle being higher, constantly pushes the paper ball out and does not allow it to go inside the bottle. It shows that increased wind speed is accompanied by a reduced air pressure.
If high speed winds blow over the roofs of houses, they will reduce the air pressure above the roofs. And if the roofs of houses are weak, then higher air pressure from below will lift up the roofs which can then be blown away by the fast winds.
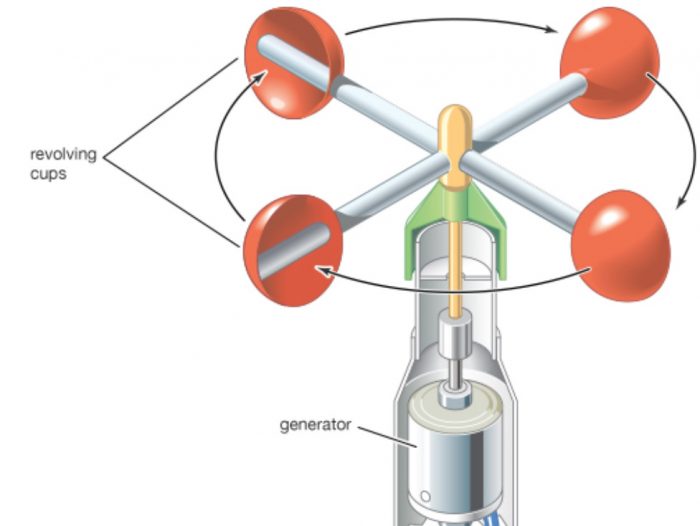
The wind speed is measured by an instrument called anemometer.
The most common type of anemometer consists of 3 or 4 cups mounted on a rod which can rotate freely.The cups catch the wind and rotate. The greater the speed of wind, the faster the cups rotate. At the base of the anemometer is a scale. The speed of wind (in kilometres per hour) is read from this scale. The anemometer is installed on a tall most where the wind blows freely around it.
The direction of wind at a place is found by using an instrument called wind vane. The arrow of wind yane moves until it points to the direction from which the wind is blowing. If the arrow points to the south, it shows that the wind is blowing from the south direction.
High speed winds can be destructive
Wind plays an important role in the formation of thunderstorms, cyclones and tornadoes which can cause disasters.
Storm
A period of violent weather with strong winds, and usually rain (or snow), is called a storm. A storm affects the surface of earth and all the objects on it.
Lightning
A natural flow of high voltage electricity within a cloud (or between a cloud and earth) which appears as a bright flash of light in the sky, is called lightning. For a cloud to become electrically charged and produce lightning, its temperature must be close to the freezing point of water.
Thunder
The loud sound which is heard a little after a lightning flash is seen in the sky is called thunder. The high voltage electric spark of lightning heats the air in the atmosphere to a very high temperature. This extreme heating causes the air to expand at an explosive rate producing a loud sound called thunder.

Thank you so much ma’am
A lot of thanks to you
Lots of thank you mam. It became very useful for me because I was absent while teaching this lesson mam. Thanks a lot man