Question 1 What are the main organs of human respiratory system?
Question 2 State the harmful effects of smoking?
Question 3 What is yawning? what are the various situations under which yawning occurs?
Question 4 Why do we sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust particles ?
Question 5 Why do mountaineers carry oxygen gas cylinders with them?
Question 6 What is the function of haemoglobin in blood?
Contents
Human Respiratory System
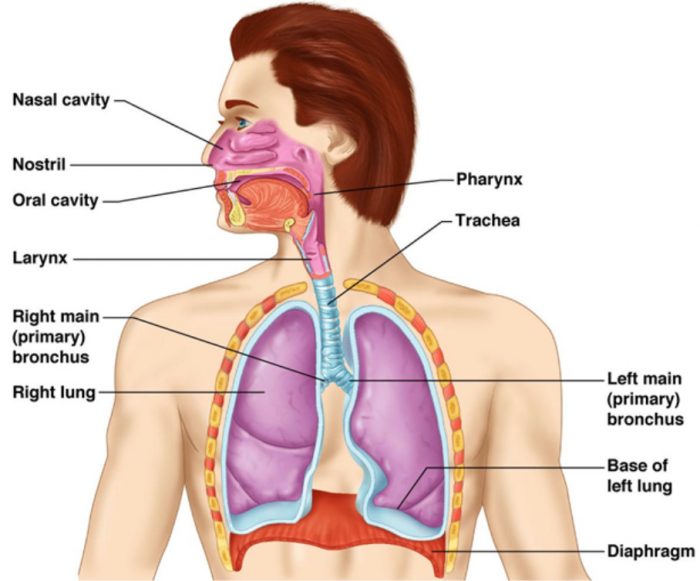
The main organs of human respiratory system are: Nose, Nasal passages (Passages in the nose), Trachea, Bronchi, Lungs and Diaphragm.
(1) Our nose has two holes which are called nostrils.
(2) There is a passage in the nose behind the nostrils. This is called nasal passage (or nasal cavity)
(3) The nasal passage joins the nostrils to the trachea.
(4) The trachea is a tube which is also called windpipe.
(5) The upper end of trachea has a voice box called larynx. The trachea (or windpipe) branches into two smaller tubes called bronchi at its lower end.
(6) The two bronchi are connected to the two lungs-one to the left lung and other to the right lung.
(7) Each bronchus divides in the lungs to form a large number of still smaller tubes called bronchioles.
(8) The smallest bronchioles have tiny air-sacs at their ends. The pouch-like air-sacs at the ends of the smallest bronchioles are called alveoli. The walls of alveoli are very thin and they are surrounded by very thin blood capillaries. The exchange of gases between the air and blood takes place takes place across the walls of the alveoli.
(9) The diaphragm is a curved sheet of muscle below the lungs.
(10) The breathing organs of human beings are lungs. Our lungs lie in the chest cavity, which is bound by the rib cage and diaphragm. The muscles of rib cage and diaphragm help in breathing in and breathing out.
(a) When we breathe in and out, our chest goes up and down. When we breathe in air, our chest cavity expands. This expansion movement of the chest cavity helps in sucking in air (containing oxygen in it).
(b) When we breathe out air, then the chest cavity contracts. This contraction movement of the chest helps in squeezing out carbon dioxide from the walls of the lungs and expelling it from the body.
Working of respiratory system in human beings
We breathe in air through the nose. The air enters the nostrils, passes through the nasal passage, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and finally reaches the lungs. In the lungs, air passes through a large number of small tubes called bronchioles and then reaches the tiny air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are surrounded by very thin blood vessels called capillaries which cary blood in them. The oxygen of air diffuses out from the alveoli into the blood in the capillaries. The blood carries oxygen to all the parts of the body. This oxygen is carried by a red pigment called haemoglobin present in the red blood cells
As blood passes through the tissues of the body, the oxygen present in it diffuses into the cells. This oxygen combines with the digested food (glucose) present in cells to release energy. The materials like fatty acids and glycerol (produced by the digestion of fats) are also oxidised during respiration to produce energy. The waste products of respiration, carbon dioxide and water, enter into blood. Blood carries the carbon dioxide and water to the alveoli in the lungs. From the lungs, carbon dioxide and water vapour are removed with the air we breathe out.
Sneezing
The sudden expulsion of air from the nose due to the irritation of nasal passage, is called sneezing.
The air around us sometimes contains various types of small, unwanted particles such as dust, smoke, pollens, etc. Now, there are some very fine hair inside our nose in the nasal passage (or nasal cavity). When we inhale air, the unwanted particles present in air usually get trapped in the hair present in our nasal passage. The particles of dust, smoke and pollens present in inhaled air get past the hair in the nasal passage and irritate the lining of nasal passage, as a result of which we sneeze. Sneezing expels all the unwanted particles from the inhaled air so that a dust free, clean air enters into our lungs.
Yawning
The action of opening one’s mouth wide while taking a long and deep breath of air (without any control over it) is called yawning.
A person yawns when he is tired, bored, stressed, over-worked, feeling sleepy or drows.
Yawning is caused by insufficient oxygen in the body. When we are tired, bored, stressed, over-worked, feel sleepy or drowsy, we do not breathe as deeply as we normally do and hence our breathing rate slows down. Due to slower breathing rate, less oxygen (of air) goes into our body which is insufficient for respiration (production of energy). Yawning helps in bringing more oxygen into our blood because during yawning our mouth opens wide and we take a long and deep breath of air.
Smoking
Smoking tobacco in the form of beedi , cigarette or cigar damages our lungs gradually and causes ill health. Smoking sends tobacco smoke inside the body. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke damage the lungs in many ways.
Some of the harmful effects of smoking are as follows:
(1) Smoking destroys the lung tissue gradually due to which breathing becomes very difficult.
(2) Smoking causes lung cancer.
(3) Smoking causes heart diseases.
(4) Smoking also damages the health of non smokers who inhale the air containing tobacco smoke.
Thanks your notes are full of knowledge.veey helpful
Its very knowledgeable and useful too. Thanks!!!
Thank you this is very helpful for me . You are brilliant thanks once again
These notes are really helpful thank you
Your notes are excellent